1.根据树的前序遍历和中序遍历创建一棵二叉树
思路:
1)在前序中找到根的值。preorder[0].
2)在中序中找到根的值所在的下标,下标即为左子树的结点个数。
3)切出左子树的前序和中序。preorder,跳过1,截取的长度是根的下标;inorder,不跳过,长度为根的下标。递归调用,创建左子树。将根结点和左子树关联起来。
4)切出树的前序和中序。preorder跳过1和下标。长度为:整棵树的长度-左子树的长度。inorder,跳过下标和1,长度是整棵树的长度-左子树的长度。递归调用,创建右子树。将右子树和根关联起来。
5)返回根结点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int find(int[] array,int v){
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i]==v){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder.length==0){
return null;
}
//1.根据前序,找到根的值,并且创建根结点
int rootValue=preorder[0];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootValue);
//2.在中序中找到根的值
int leftSize=find(inorder,rootValue);
//3.切出左子树的前序和中序
int[] leftPreorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1,1+leftSize);
int[] leftInorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,leftSize);
//4.关联根、左子树
root.left=buildTree(leftPreorder,leftInorder);
//5.切出右子树的前序和中序
int[] rightPreorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1+leftSize,preorder.length);
int[] rightInorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,1+leftSize,inorder.length);
//6.关联右子树和根
root.right=buildTree(rightPreorder,rightInorder);
return root;
}
}
2.根据树的中序遍历和后序遍历创建一棵二叉树
思路:
1)取根结点的值,并创建根结点。
2)查找根结点在中序遍历中的下标。
3)划分左子树的中序遍历和后序遍历。
4)创建左子树并关联根结点和左子树。
5)划分右子树的中序遍历和后序遍历。
6)创建右子树并关联根结点和右子树。
7)返回根结点。
class Solution {
private int find(int[] inorder,int v){
for(int i=0;i<inorder.length;i++){
if(inorder[i]==v){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(inorder.length==0){
return null;
}
//1.先取根结点的值,并创建根结点。
int rootValue=postorder[postorder.length-1];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(rootValue);
//2.查找根结点在中序遍历中的下标
int leftindex=find(inorder,rootValue);
//3.划分左子树的中序遍历和后序遍历
int[] leftinorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,leftindex);
int[] leftpostorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,0,leftindex);
//4.关联根和左子树
root.left=buildTree(leftinorder,leftpostorder);
//5.划分右子树的中序遍历和后序遍历
int[] rightinorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,leftindex+1,inorder.length);
int[] rightpostorder=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,leftindex,postorder.length-1);
//6.关联根和右子树
root.right=buildTree(rightinorder,rightpostorder);
return root;
}
}
3.根据二叉树创建字符串
需要采用前序遍历的方式,将一棵二叉树转换为一个由括号和整数组成的字符串。空结点采用"()"表示,而且需要省略一切不影响字符串与原始二叉树之间的一对一映射关系的字符串。最后返回的结果要删除掉第一个字符和最后一个字符。使用String类的delete(fromIndex,toIndex)删除,不包括toIndex处的字符。
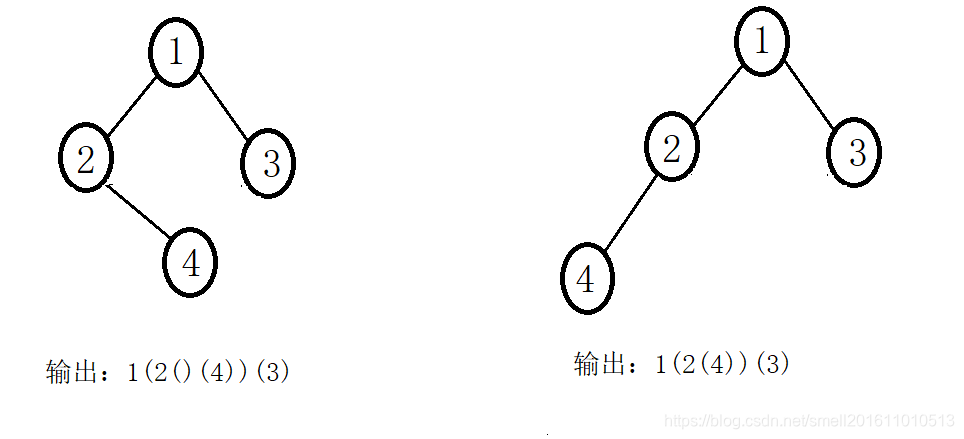
由此可见,每次遍历在输出根结点前,会先输出"(",然后输出根的值,递归遍历左右子树,最后再输出")"。特殊情况:当左子树为空,右子树不为空时,中间要先拼接"()",然后再遍历左右子树,最后再拼接")"。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private void preorder2str(TreeNode t,StringBuilder sb){
if(t==null){
return;
}
sb.append("(");
sb.append(t.val);
if(t.left==null&&t.right!=null){
sb.append("()");
}else{
preorder2str(t.left,sb);
}
preorder2str(t.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode t) {
if(t==null){
return "";
}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
preorder2str(t,sb);
sb.delete(0,1);//将第一个字符删除
sb.delete(sb.length()-1,sb.length());//将最后一个字符删除
return sb.toString();
}
}
4.二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一棵二叉树,找到该树中两个指定节点p和q的最近公共祖先。
思路:两个结点的情况有三种:
1)p或者q本身一个就是根结点,结果:root
2)p或q不在一棵子树上,结果是root。
3)p和q在一棵子树上,递归这棵子树,继续找。
class Solution {
private boolean find(TreeNode root,TreeNode t){
if(root==null){
return false;
}
if(root==t){
return true;
}
if(find(root.left,t)){
return true;
}
return find(root.right,t);
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==root||q==root){
return root;
}
//判断p和q是否在左子树中
boolean pInLeft=find(root.left,p);
boolean qInLeft=find(root.left,q);
if(pInLeft&&qInLeft){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);//在左子树中查找。
}
//p和q在右子树中
if(!pInLeft&&!qInLeft){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);//在右子树中查找。
}
return root;
}
}
5.二叉树的层序遍历
利用队列实现,过程类似于传销。如果根结点不为空,先向队列中添加根结点(启动),然后开始发展下线:删除队列中的头结点同时记录,打印出头结点的值,(发展下线:)判断头结点的左孩子结点不为空,则向队列中添加左孩子;判断右孩子不为空,则也向队列中添加右孩子。直到队列为空为止。
//层序遍历
private static void levelOrderTravel(Node root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node front=queue.pollFirst();
System.out.print(front.val+" ");
if(front.left!=null){
queue.addLast(front.left);
}
if(front.right!=null){
queue.addLast(front.right);
}
}
}
变形:给定一棵二叉树,返回其按层次遍历的结点值。(即逐层地,从左到右访问所有结点)。
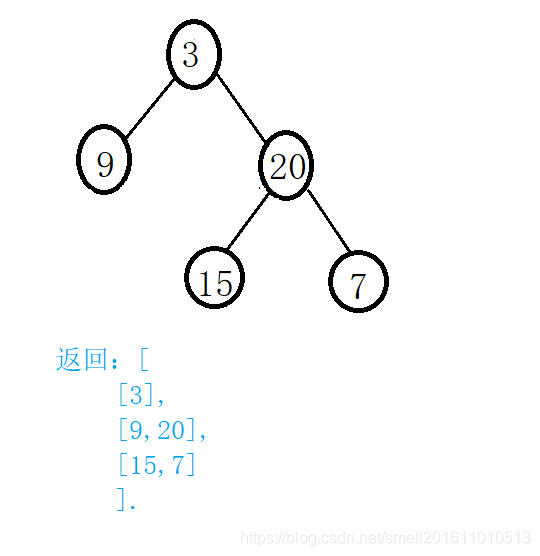
思路类似,代码为:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new ArrayList<>();//初始化最外层的链表
//特殊情况
if(root==null){
return list;
}
//内部类,用来存储树结点和层数
class NodeLevel{
TreeNode node;
int level;
public NodeLevel(TreeNode node,int level){
this.node=node;
this.level=level;
}
}
//初始化内层的链表
LinkedList<NodeLevel> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(new NodeLevel(root,0));
//发展下线
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
NodeLevel front=queue.pollFirst();
TreeNode node=front.node;
int level=front.level;
if(list.size()==level){
//队列中一个都没有
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
list.get(level).add(node.val);//给level层的链表(内部链表)添加结点值
//如果左子树不为空
if(front.node.left!=null){
queue.addLast(new NodeLevel(node.left,level+1));
}
//如果右子树不为空
if(front.node.right!=null){
queue.addLast(new NodeLevel(node.right,level+1));
}
}
return list;
}
}
6.判断二叉树是否是一棵完全二叉树
思路:用带有空结点的层序遍历遍历这棵树,如果遇到空之后的所有都是空,则是完全二叉树;如果遇到空之后又遇到非空,则不是完全二叉树。
//判断完全二叉树
private static boolean isEntireTree(Node root){
if(root==null){
return true;//空树是完全二叉树
}
LinkedList<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(root);
while(true){
//无论是否是空结点,都添加到队列中
Node front=queue.pollFirst();
if(front==null){
//遇到空了,下一步判断队列中剩余的结点是否全是空。
break;
}
queue.addLast(front.left);
queue.addLast(front.right);
}
//判断队列所有的结点是否为空
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node front=queue.pollFirst();
if(root!=null){
return false;//在空结点后又遇到非空结点,说明不是完全二叉树。
}
}
return true;
}
























 304
304

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








