Performance and Scalability: How To Fit a Bigger Model and Train It Faster (huggingface.co)
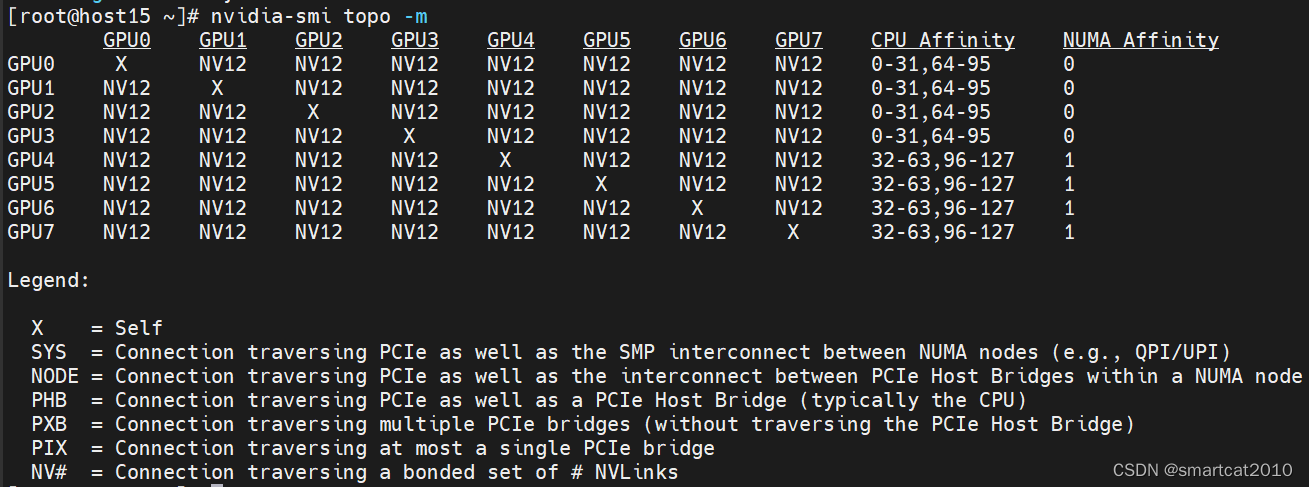
12个NVLink互联,任意2个GPU之间的带宽=单个NVLink的带宽*12
不用Zero等频繁通信的方式,只是普通DDP训练大模型的话,因为每个batch只通信一次,有没有NVLink对训练速度差比大约只有20%
3种计算:
Transformers architecture includes 3 main groups of operations grouped below by compute-intensity.
Tensor Contractions
Linear layers and components of Multi-Head Attention all do batched matrix-matrix multiplications. These operations are the most compute-intensive part of training a transformer.
Statistical Normalizations
Softmax and layer normalization are less compute-intensive than tensor contractions, and involve one or more reduction operations, the result of which is then applied via a map.
Element-wise Operators
These are the remaining operators: biases, dropout, activations, and residual connections. These are the least compute-intensive operations.
显存Memory占用都在哪儿:
Model Weights
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for fp32 training
- 6 bytes * number of parameters for mixed precision training
Optimizer States
- 8 bytes * number of parameters for normal AdamW (maintains 2 states)
- 2 bytes * number of parameters for 8-bit AdamW optimizers like bitsandbytes
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for optimizers like SGD (maintains only 1 state)
Gradients
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for either fp32 or mixed precision training
Forward Activations
- size depends on many factors, the key ones being sequence length, hidden size and batch size.
There are the input and output that are being passed and returned by the forward and the backward functions and the forward activations saved for gradient computation.
Temporary Memory
Additionally there are all kinds of temporary variables which get released once the calculation is done, but in the moment these could require additional memory and could push to OOM. Therefore when coding it’s crucial to think strategically about such temporary variables and sometimes to explicitly free those as soon as they are no longer needed.
Functionality-specific memory
Then your software could have special memory needs. For example, when generating text using beam search, the software needs to maintain multiple copies of inputs and outputs.
FP16 mixed precision training过程:
If we look at what’s happening with FP16 training (mixed precision) we have:
- the model has two copies in memory: one in half-precision for the forward/backward computations and one in full precision - no memory saved here
- the forward activations saved for gradient computation are in half-precision - memory is saved here
- the gradients are computed in half-precision but converted to full-precision for the update, no saving there
- the optimizer states are in full precision as all the updates are done in full-precision
The gain for FP16 training is that in each of those cases, the training with the flag
--fp16is twice as fast, which does require every tensor to have every dimension be a multiple of 8 (examples pad the tensors to a sequence length that is a multiple of 8).Summary: FP16 with apex or AMP will only give you some memory savings with a reasonably high batch size.
Additionally, under mixed precision when possible, it’s important that the batch size is a multiple of 8 to efficiently use tensor cores.
Note that in some situations the speed up can be as big as 5x when using mixed precision. e.g. we have observed that while using Megatron-Deepspeed.
推理阶段,可以完全使用fp16或bf16(或INT8、INT4)(因为不需要optimizer梯度更新权重了),加速&节约显存;
Thanks to the fp32-like dynamic range with bf16 mixed precision loss scaling is no longer needed.
also be aware that if you pre-trained a model in bf16, it’s likely to have overflow issues if someone tries to finetune it in fp16 down the road. So once started on the bf16-mode path it’s best to remain on it and not switch to fp16.
TF32: 1+8+10=19bits;NVIDIA在高端GPU上支持,适配TensorCores;对用户来说是透明的,像使用FP32那样使用,NVIDIA芯片在合适的时候会自动转化为TF32;号称throughput相比FP32提升3倍
Batch size: 8或者64的整数倍,可以更有效的利用GPU和TensorCore,加速;batch-size越大,通信占比越小,速度越快;
DP VS. DDP
DistributedDataParallel(DDP) is typically faster thanDataParallel(DP), but it is not always the case:
- while DP is python threads-based, DDP is multiprocess-based - and as such it has no python threads limitations, such as GIL
- on the other hand a slow inter-connectivity between the GPU cards could lead to an actual slower outcome with DDP
DDP是一上来每个进程各自读各自的,只有在加和梯度时AllReduce一把,更新weights也是各算各的;
DP是有个master线程,它一个人读数据,分发给slave线程;最后一层输出汇总发送到master,由master来计算loss,再把loss广播给所有slave;梯度都发送到master,master更新完weights后,把weights发送个所有线程;(master更忙;其他salve更闲)
The only communication DDP performs per batch is sending gradients, whereas DP does 5 different data exchanges per batch.
DP copies data within the process via python threads, whereas DDP copies data via torch.distributed.
DP is ~10% slower than DDP w/ NVlink, but ~15% faster than DDP w/o NVlink
DataLoader
DataLoader(pin_memory=True, ...)which ensures that the data gets preloaded into the pinned memory on CPU and typically leads to much faster transfers from CPU to GPU memory.DataLoader(num_workers=4, ...)- spawn several workers to pre-load data faster -
Mixture of Experts (MoE)
4~5倍训练加速;推理也可加速;
显存占用增大很多!
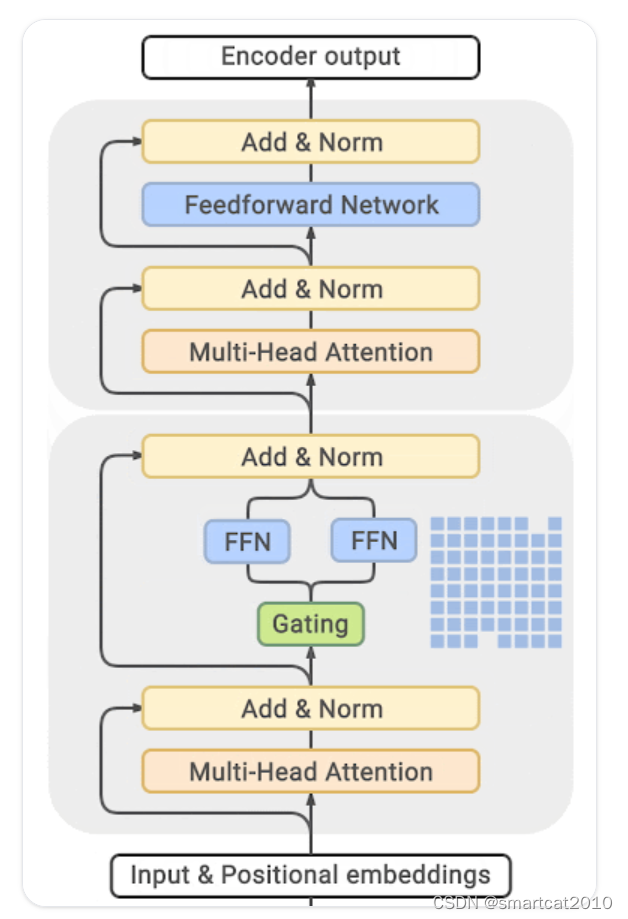
把FFN层,替换成多个,开头用Gating控制路由到哪个;




















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








