1. Overview
RawNet: Advanced end-to-end deep neural network using raw waveforms for text-independent speaker verification (RawNet 1) 出自会议:INTERSPEECH 2019.
(论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.08104.pdf
代码:https://github.com/Jungjee/RawNet.)
Improved RawNet with Feature Map Scaling for Text-independent Speaker Verification using Raw Waveforms (RawNet 2) 出自会议:INTERSPEECH 2020.
(论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2004.00526v2.pdf
代码:vailable at https://github. com/Jungjee/RawNet.)
Pushing the limits of raw waveform speaker recognition (RawNet 3) 出自会议:INTERSPEECH 2022.
( 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.08488.pdf
代码:https://github.com/Jungjee/ RawNet and https://github.com/clovaai/voxceleb_ trainer.)
论文单位:韩国Naver Corporation,Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
2. RawNet 1
Direct modeling of raw waveforms using deep neural networks. Less processed features as input allows data-driven approaches with DNNs to yield better discriminative representations compared to using knowledgebased acoustic features.
Advantages:
1. Minimization of pre-processing removes the need for exploration of various hyper-parameters such as the type of acoustic feature to use, window size, shift length, and feature dimension.
2. With recent trends of DNN replacing more sub-processes in various tasks, a raw waveform DNN is well positioned to benefit from future advances in deep learning.
Spectrogram-based CNN can only see fixed frequency regions depending on the internal
pooling rule.
2.1 Front-end: RawNet
RawNet adopts a convolutional neural network-gated recurrent unit (CNN-GRU) architecture.

1. input features are first processed using the residual blocks to extract frame-level embeddings.
2. A GRU is then employed to aggregate the frame-level features into a single utterance-level embedding.
3. Utterance-level embedding is then fed into one fully-connected layer. The output of the fully-connected layer is used as the speaker embedding and is connected to the output layer, where the number of nodes is identical to the number of speakers in the training set.
2.2 Objective functions
The main objectives is to minimize intra-class covariance and maximize inter-class covariance of
utterance-level features.
To consider both inter-class and intra-class covariance, we utilize center loss and speaker basis loss in addition to categorical cross-entropy loss for DNN training.
Center loss function was proposed as

where xi refers to embedding of the ith utterance, cyi refers to the center of class yi, and N refers to the size of a mini-batch.
Speaker basis loss aims to further maximize interclass covariance.

where wi is the basis vector of speaker i and M is the number of speakers within the training set
This loss function considers a weight vector between the last hidden layer and a node of the softmax output layer as a basis vector for the corresponding speaker.
The final objective function:

where LCE refers to categorical cross-entropy loss and refers to the weight of LC.
2.3 DNN-based back-end classification
In speaker verification, cosine similarity and PLDA are widely used for back-end classification to determine whether two speaker embeddings belong to the same speaker.
RawNet1 propose an approach using the concatenation of the speaker embedding, test utterance, and their element-wise multiplication.(Element-wise binary operation of speaker embeddings to represent relationships) NOT CLEAR

2.4 Experiment and results
Dataset:VoxCeleb1 dataset
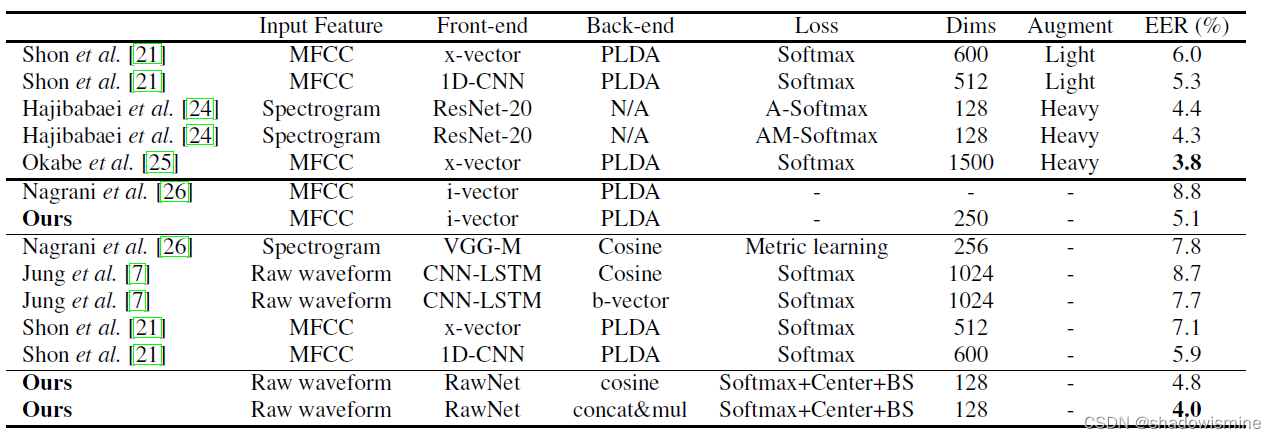
3. RawNet 2
RawNet 1 VS RawNet 2
1. Replacing RawNets first convolutional layer with a sinc-convolution layer.
2. Replacing the gated recurrent unit (GRU) layer of RawNet with the self-attentive pooling and
self-multi-head-attentive pooling mechanisms. (No, the GRU better aggregates
frame-level representations into an utterance-level representation.)
3. propose to scale the filter axis of feature maps using a sigmoid-based mechanism (FMS).
4. simplified the loss functions from using categorical cross-entropy (CCE), center, and speaker basis loss to using only CCE loss.
5. modified the training dataset from VoxCeleb1 to VoxCeleb2
6. applied a test time augmentation (TTA) method in the evaluation phase (20 %
overlap)


3.1 sinc-convolution layer
It is a type of a bandpass filter, where cut-off frequencies are set as parameters that are
optimized with other DNN parameters.
SincNet架构(2018)
标准CNN中,第一个卷积层将执行输入波形与FIR滤波器之间的时域卷积。卷积定义如下:

其中,x[n]代表语音信号,h[n]代表长度为L的滤波器,y[n]代表滤波后的输出。
标准CNN中,每个滤波器的L个权重都需要从数据中学习得来。相反地,SincNet只需要输入信号与仅有少量可学参数θ的预设函数g进行卷积,如下等式:

受数字信号处理中标准滤波方式的启发,一种合理的选择是使用由矩形带通滤波器组成的滤波器组来定义g。频域中,带通滤波器可表示成两个低通滤波器的差:

其中,f1和f2分别是学习得到的低截止频率和高截止频率,rect表示频域中的矩形窗。
经过IFT转换到时域后,g表示为:
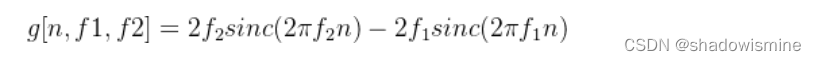
其中,sinc函数定义为:sinc(x)=sin(x)/x
截止频率可以在[0, fs/2]范围内随机初始化,fs代表输入信号的采样率。除此之外,也可采用梅尔尺度滤波器组的截止频率来进行初始化,其优点是在包含说话人身份关键信息的频率较低的部分设置更多滤波器。
为确f1>=0且f2>=f1,上述公式中的f1和f2实际上由以下等式替换:
需要指出的是,实际上并没有强制f2满足奈奎斯特采样定理,因为作者观察到这个限制在训练时自然满足。此外,各个滤波器在这个阶段并没有学习到增益。增益将在后续网络层学习。
理想的带通滤波器(具有完全平坦的通带和无穷衰减的阻带),要求滤波器权重的个数L是无限的。对g进行截断将只能得到通带具有波纹且阻带为有限衰减的近似理想滤波器。缓解这个问题的一种方法是加窗。加窗是通过将截断的g与窗函数w相乘实现的,旨在对g末尾突变的不连续点进行平滑,文章中采用的是Hamming窗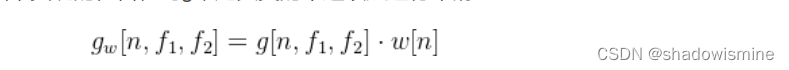
汉明窗对频率的选择性很高。然而,结果显示使用其他窗函数时,没有显著差异。
SincNet中涉及的所有操作都是完全可微的,且滤波器截止频率可以和其他CNN参数那样使用SGD或其他梯度优化方法进行联合优化。
SincNet架构:第一层为sinc卷积,紧接着是标准CNN流水线操作(池化、归一化、激活、dropout),然后将多个标准卷积或者全连接层堆叠在一起,最后使用softmax分类器进行说话人分类。

提出的SincNet具有以下特性:
- 收敛速度快
- 参数少
- 计算效率高
- 具有可解释性
SincNet优于其他模型,DNN上性能更好,但DNN必须为每个新的说话人进行微调,灵活性不如d-vector。

具体可以参考论文Mirco Ravanelli, Yoshua Bengio, “Speaker Recognition from raw waveform with SincNet”(2018)

3.2 filter-wise feature map scaling (FMS)
The FMS uses a scale vector whose dimension is identical to the number of filters with values between 0 and 1 derived using sigmoid activation.

We also propose various methods to utilize the FMS to scale given feature maps, i.e., multiplication, addition, and applying both.
let c = [c1; c2; ... ; cF ] be a feature map of a residual block, where T is the sequence length in
time, and F is the number of filters.
1. derive a scale vector to conduct FMS by first performing global average pooling on the
time axis,
2. feed-forwarding through a fully-connected layer followed by sigmoid activation.
3. utilize different operations (addition, multiplication, etc) to scale given feature maps.


3.3 Experiment and results


Among application of various related methods, System #6 (SE) demonstrated the best result.
4. RawNet 3
Even the latest architecture demonstrates equal error rate (EER) of 1.29% , whereas the widely
adopted ECAPA-TDNN architecture and its variants have consistently reported EERs under 1%.
Therefore propose a new model architecture combining several recent advances in deep learning together with RawNet2 to overcome this challenge.


Contributions:
1. We propose a new raw waveform speaker recognition architecture, namely RawNet3, that demonstrates EER under 1% in the VoxCeleb1 evaluation protocol;
2. We explore raw waveform speaker verification model with a self-supervised learning framework for the first time and outperform contrastive-based existing works;
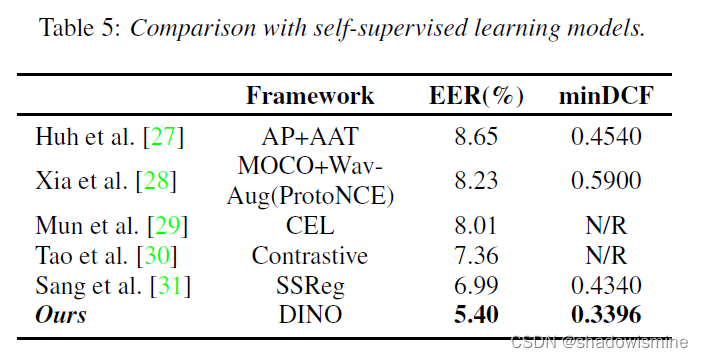
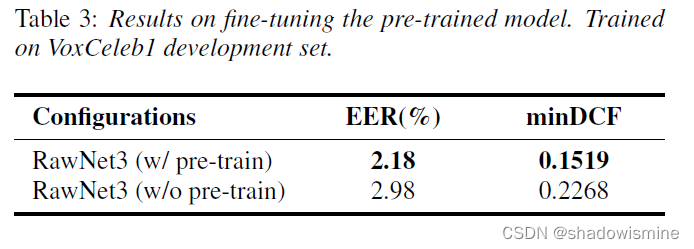
3. We demonstrate the effectiveness of self-supervised pretraining under semi-supervised learning scenario.
4.1 Framework
ECAPA-TDNN vs RawNet 3


SE-Res2Block vs AFMS-Res2MP-block

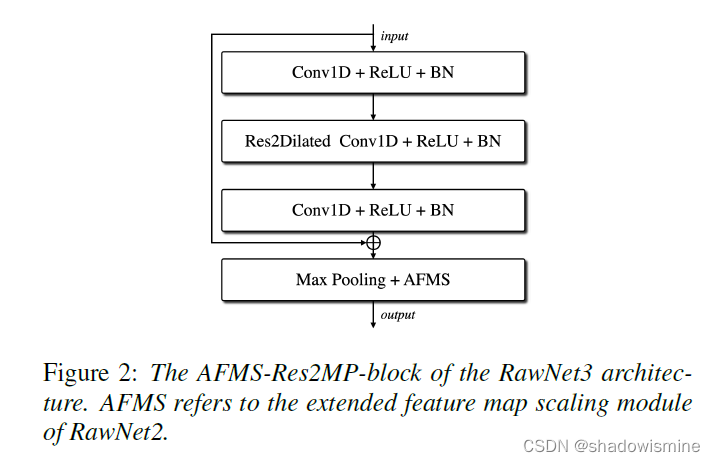
RawNet 2 vs RawNet 3
1. the parameterised analytic filterbank layer is utilised instead of sinc-convolution layer.
2. log and mean normalisation is applied to the analytic filterbank output.
3. the number of backbone blocks and their connections have been adapted, following the
ECAPA-TDNN alike topology.
4. the channel and context dependent statistic pooling replaces a uni-directional gated recurrent
unit layer.

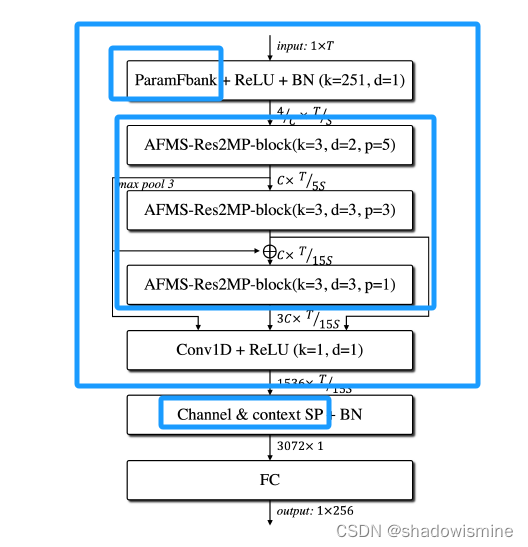
4.2 Supervised Learning
Objective function:
AAM-softmax objective function

4.3 Self-Supervised Learning (DINO - Not Clear)
The DINO framework is one of the most competitive frameworks for self-supervised learning.
DINO involves a teacher and a student network with an identical architecture but different parameters.
The DINO loss is then defined as:
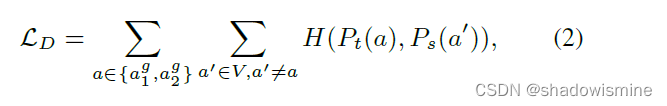
4.4 Experiment
Dataset:VoxCeleb1 and 2 datasets
Supervised Learning as below:

Self-supervised Learning as below:

Semi-supervised Learning (pre-train the model using the DINO self-supervised learning framework, then fine-tune the model using supervised learning with ground truth label-based classification) as below:





 本文概述了RawNet系列在语音识别领域的三次迭代:从原始波形直接建模的RawNet1,到引入Sinc-Conv和FMS优化的RawNet2,再到集成最新深度学习技术的RawNet3。这些工作展示了利用未处理波形进行文本无关的说话人验证的先进方法。
本文概述了RawNet系列在语音识别领域的三次迭代:从原始波形直接建模的RawNet1,到引入Sinc-Conv和FMS优化的RawNet2,再到集成最新深度学习技术的RawNet3。这些工作展示了利用未处理波形进行文本无关的说话人验证的先进方法。

















 7878
7878

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








