1、并查集的原理
在一些应用问题中,需要将n个不同的元素划分成一些不相交的集合。开始时,每个元素自成一个单元素集合,然后按照一定的规律将同一组元素的集合合并,在此过程中要反复用到查询某一个元素归属于哪个集合的运算。适用于描述这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集。
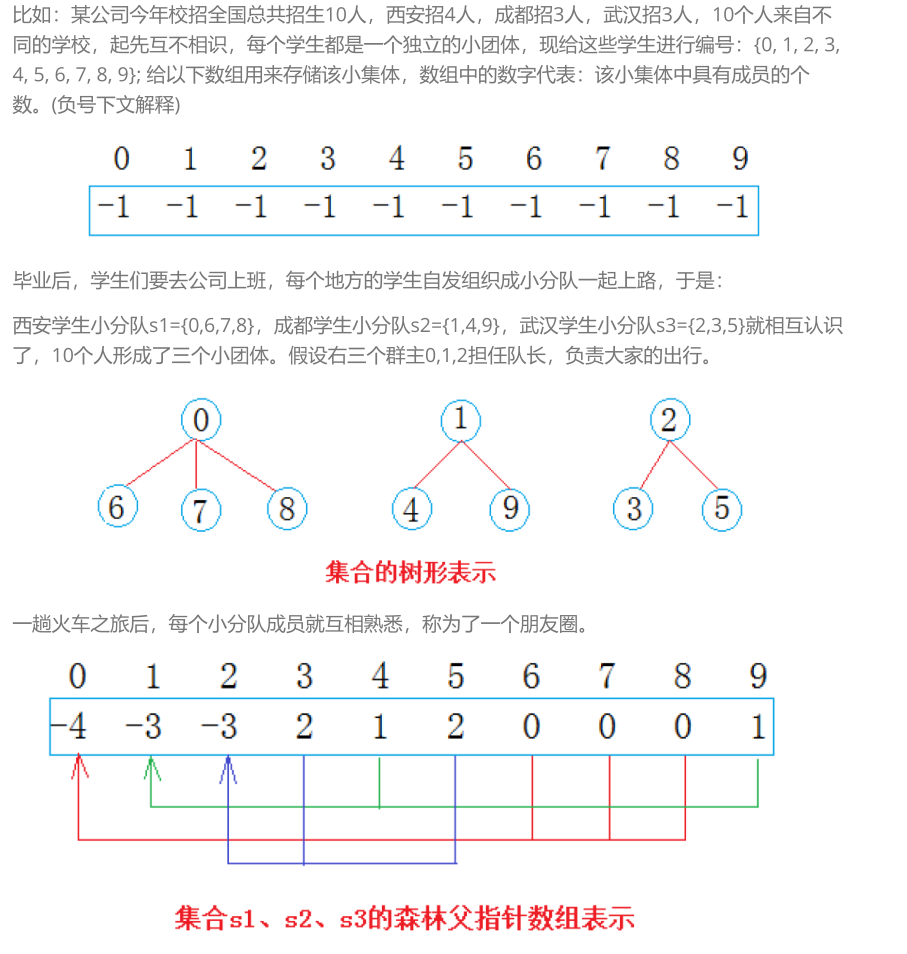
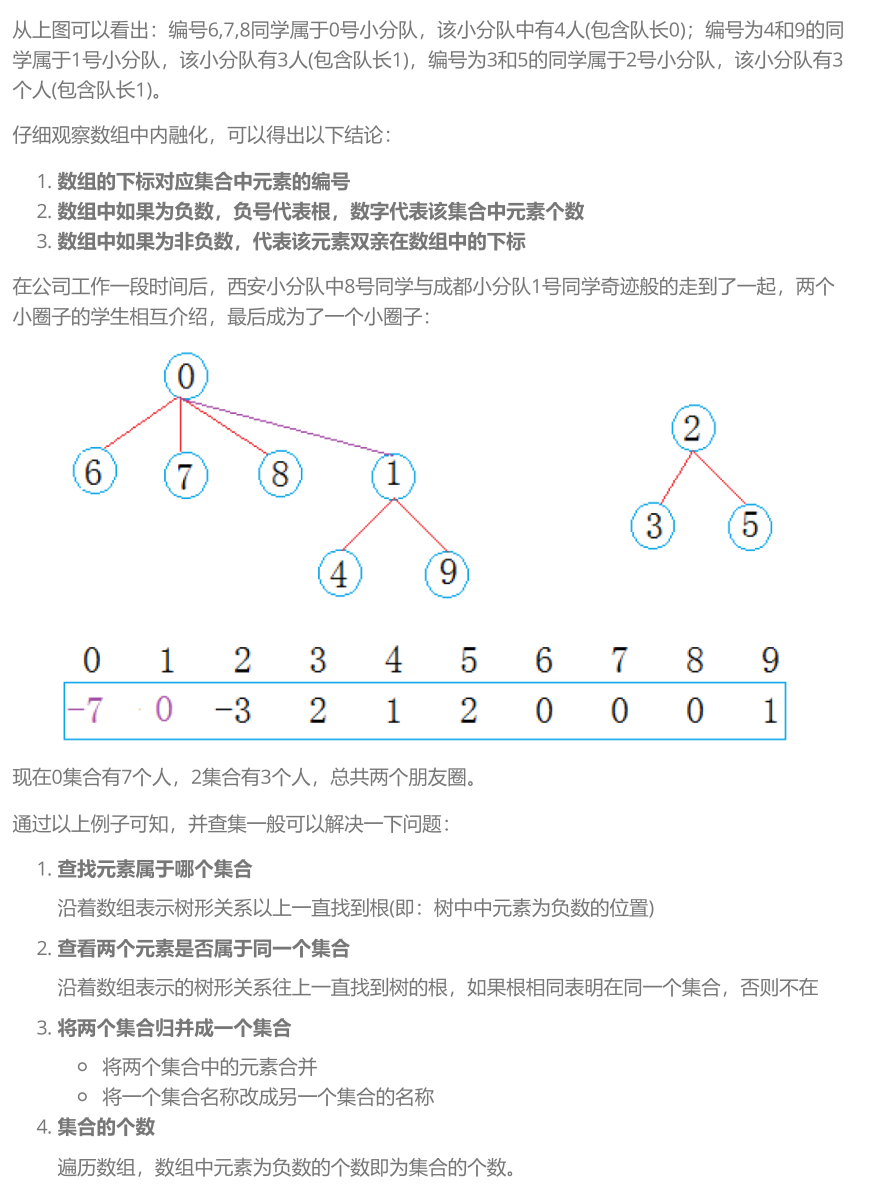
2、并查集的实现
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <map>
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(size_t n)
:_ufs(n, -1)
{ }
void Union(int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(x2);
// 如果本身在一个集合就没必要合并了
if (root1 == root2)
return;
_ufs[root1] += _ufs[root2];
_ufs[root2] = root1;
}
int FindRoot(int x)
{
int parent = x;
while (_ufs[parent] >= 0)
{
parent = _ufs[parent];
}
return parent;
}
bool InSet(int x1, int x2)
{
return FindRoot(x1) == FindRoot(x2);
}
size_t SetSize()
{
size_t size = 0;
for (size_t i = 0;i < _ufs.size();++i)
{
if (_ufs[i] < 0)
{
++size;
}
}
return size;
}
private:
vector<int> _ufs;
};
如果题目中并没有用编号来表示数据,那么在实现并查集时可以用map建立映射关系。
template<class T>
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
UnionFindSet(const T* a, size_t n)
{
for (size_t i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
_a.push_back(a[i]);
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
}
}
private:
vector<T> _a; // 编号找人
map<T, int> _indexMap; // 人找编号
};
3、并查集的应用

class Solution {
public:
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations)
{
vector<int> ufs(26, -1);
auto findRoot = [&ufs](int x)
{
while(ufs[x] >= 0)
{
x = ufs[x];
}
return x;
};
// 第一遍,先把相等的值加到一个集合中
for(auto& str : equations)
{
if(str[1] == '=')
{
int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');
int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if(root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
// 第二遍,判断不相等的在不在同一个集合,在就相悖了
for(auto& str : equations)
{
if(str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = findRoot(str[0] - 'a');
int root2 = findRoot(str[3] - 'a');
if(root1 == root2)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
 C++并查集详解与应用
C++并查集详解与应用





















 1314
1314

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








