注:作者为初学者,有些知识不太熟悉,可能描述有误,望见谅。
BCE
二元交叉熵(Binary Cross-Entropy, BCE)是深度学习中用于二分类任务的损失函数,衡量模型预测概率与真实标签之间的差异。适用于输出为概率值(如Sigmoid激活后的结果)的场景,例如图像分类中的正/负样本判断。
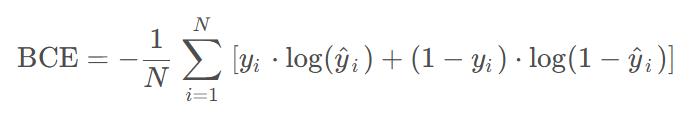
PyTorch提供了BCELoss和BCEWithLogitsLoss两种实现方式。
代码示例:
(1)BCELoss要求输入已经经过sigmoid激活函数(输出在0到1之间):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 假设预测值和真实标签的shape均为 [batch_size]
bce_loss = nn.BCELoss()
output = torch.sigmoid(model(input)) # 需手动sigmoid
loss = bce_loss(output, target)
(2)BCEWithLogitsLoss结合了sigmoid和BCE,数值稳定性更好(推荐使用这种):
bce_logits_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
output = model(input) # 无需手动sigmoid
loss = bce_logits_loss(output, target)
注:与网络中的激活函数不冲突,BCEWithLogitsLoss 只关心最后一层有没有额外加 sigmoid。
适用场景:
(1)语义分割
二分类:血管、视网膜、皮肤病变、道路、缺陷检测等几乎默认先上 BCE(+Dice)。
多分类:先做成 One-vs-Rest 再用 BCE(等价于多标签交叉熵),例如同时分割“肿瘤+水肿+坏死”。
(2)边缘检测 / 轮廓预测
HED、RCF、DexiNed 等系列网络输出边缘概率图,损失就是逐像素 BCE(有时给正边缘像素加高权重)。
(3)生成式模型
GAN 里的判别器、VAE 的重建项(像素灰度归一化到 0–1 后)常用 BCE,最早 DCGAN 就这么干。
Dice
Dice系数(Dice Coefficient)是一种用于衡量集合相似度的指标,广泛应用于图像分割、医学影像分析等领域。其定义为两个集合交集大小的两倍除以两个集合大小的和。Dice系数的取值范围在0到1之间,数值越大表示相似度越高。
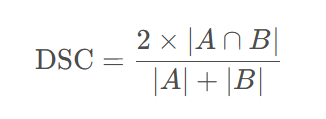
Dice系数在图像分割任务中常被用作评估模型性能的指标,尤其是在医学影像分割中。它可以衡量预测分割结果与真实标签之间的重叠程度,帮助评估模型的准确性。
代码示例:
模拟了一个二值分割任务的预测结果和标签,展示了如何计算Dice系数和Dice损失。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def dice_coefficient(pred, target, smooth=1e-6):
"""
计算Dice系数
:param pred: 预测的分割结果(经过sigmoid或softmax)
:param target: 真实的分割标签(0或1)
:param smooth: 平滑系数,避免除以零
:return: Dice系数
"""
intersection = (pred * target).sum()
union = pred.sum() + target.sum()
dice = (2. * intersection + smooth) / (union + smooth)
return dice
class DiceLoss(nn.Module):
"""
Dice损失函数
"""
def __init__(self, smooth=1e-6):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.smooth = smooth
def forward(self, pred, target):
dice = dice_coefficient(pred, target, self.smooth)
return 1 - dice # 返回Dice损失
# 示例用法
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 模拟预测结果和真实标签
pred = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(1, 1, 256, 256)) # 假设预测结果经过sigmoid
target = torch.randint(0, 2, (1, 1, 256, 256)).float() # 二值标签
# 计算Dice系数和Dice损失
dice_score = dice_coefficient(pred, target)
dice_loss = DiceLoss()(pred, target)
print(f"Dice Coefficient: {dice_score.item():.4f}")
print(f"Dice Loss: {dice_loss.item():.4f}")
代码解释:
dice_coefficient函数接收预测结果和真实标签,计算两者的交集和并集,最终返回Dice系数。平滑系数smooth用于避免分母为零的情况。
DiceLoss类继承自nn.Module,将Dice系数转换为损失值(1 - Dice系数),便于模型优化。
可能的疑问点:把 Dice 系数变成 1 − Dice 只是为了“把越大越好的指标变成越小越好的损失”,与梯度下降法的方向保持一致。
PyTorch 默认的 optimizer.step() 是沿负梯度方向更新参数,也就是“让损失变小”。Dice 系数最大为 1(完美重叠),最小为 0(毫无重叠),越大越好。因此取 1 − Dice 后,完美时损失=0,最差时损失≈1,越小越好,正好符合优化器的“下山”方向。
BCE与Dice结合使用
医学影像分割任务中常使用二元交叉熵(BCE)与Dice Loss结合的方式,主要由于两者互补的特性。
BCE Loss逐像素计算分类误差,对类别不平衡敏感,能保证像素级分类精度;Dice Loss直接优化分割区域的重叠度,对目标区域大小变化鲁棒,但可能忽视像素级细节。结合两者可平衡局部和全局优化目标。
代码示例(pytorch):
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class BCEDiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight_bce=0.5, weight_dice=0.5, smooth=1e-5):
super(BCEDiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.weight_bce = weight_bce
self.weight_dice = weight_dice
self.smooth = smooth
def forward(self, pred, target):
# BCE Loss计算
bce_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, target)
# Dice Loss计算
pred = torch.sigmoid(pred)
intersection = (pred * target).sum()
union = pred.sum() + target.sum()
dice_loss = 1 - (2. * intersection + self.smooth) / (union + self.smooth)
# 加权结合
total_loss = self.weight_bce * bce_loss + self.weight_dice * dice_loss
return total_loss
代码参数解释:
(1)初始化:
weight_bce:控制 BCE 损失的权重,默认 0.5。
weight_dice:控制 Dice 损失的权重,默认 0.5。
smooth:平滑系数,用于防止 Dice 系数计算时分母为零,默认 1e-5。
(2)forward:
pred:模型输出的预测值(未经 sigmoid 激活)。
target:真实标签(一般为 0 或 1)。






















 1237
1237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








