目录
Map的一些常用方法
1.V put(K key,V value) 设置 key 对应的value
2.V get(Object key) 返回key对应的value
代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("hello",2);
map.put("world",3);
System.out.println(map.get("hello"));
}
3. V remove(Object key) 删除 key 对应的映射关系
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("hello",2);
map.put("world",3);
System.out.println(map.get("hello"));
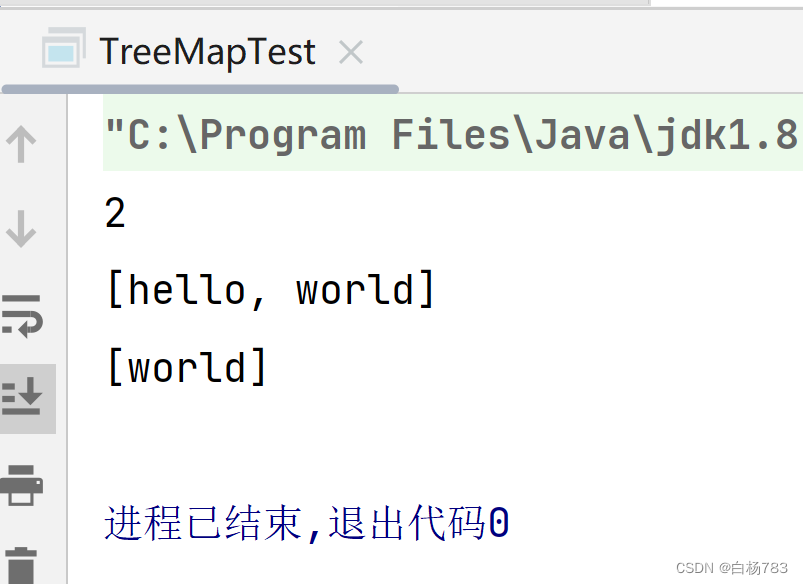
Set<String> set1 = map.keySet();
System.out.println(set1);
map.remove("hello");
Set<String> set2 = map.keySet();
System.out.println(set2);
}
5.Collection<V> values() 返回所有 value 的可重复集合
代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("hello",2);
map.put("world",3);
Collection<Integer> collection = map.values();
System.out.println(collection);
}
注意:我们用返回值类型为Collection来接受map中的values,用返回值类型为Set来接受key,这是因为在map中,key是唯一的,不能有俩个相同的key.所以此时我们用Set来接受key.而在map中,value是可以相同的,所以我们用Collection来接受.
6.Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() 返回所有的 key-value 映射关系
代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("hello",2);
map.put("world",3);
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println(set);
}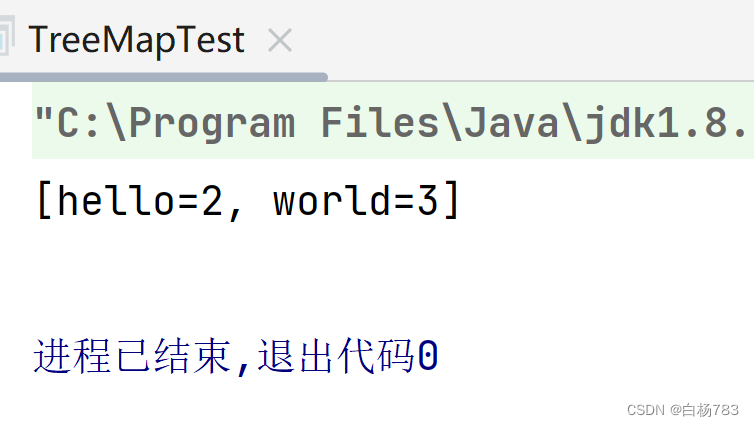
注意这个方法可以用来遍历map中的元素
划重点啦!
1.Map是一个接口,它不能实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
2.Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可重复的
3.Map中的Key是可以全部分离出来的,存储到Set中来进行访问(因为key不能重复)
4.Map中的value是可以全部分离出来,存储到Collection的任何一个子集中(value可能有重复)
5.Map.Entry<K, V> 是Map内部实现的用来存放<key, value>键值对映射关系的内部类,该内部类中主要提供了 <key, value>的获取,value的设置以及Key的比较方式。
6.Map中的键值对不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将key删除掉,然后再重新插入
7.TreeMap的底层是由红黑树来实现的,红黑树可以简单看为我们之前实现的二叉搜索树的优化.因此在TreeMap中,传入的Key必须要是可比较的
8.HashMap底层是由哈希桶实现的,传入的key不需要可比较,但是自定义类型需要重写equals和hashCode方法
Set的一些常用方法
1.boolean add(E e) 添加元素,但重复元素不会被添加成功
代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
System.out.println(set);
}
2.boolean contains(Object o) 判断 o 是否在集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
System.out.println(set.contains("hello"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
System.out.println(set.contains("hello"));
set.remove("hello");
System.out.println(set.contains("hello"));
}
4.void clear() 清空集合
代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("hello");
set.add("world");
set.clear();
System.out.println(set);
}
划重点啦!
1.Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类
2.Set中只储存了key,并且要求key一定是唯一
3.Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中
4.我们一般用Set对集合中的元素进行去重
5.Set中不能插入Null的key
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








