VBA代码了解——弹框、提取内容
编写代码,插入模块,开始编写代码:
编写代码,弹出弹框
'Sub 表示一个程序,理解为一段代码的集合
Sub 编写第一个VBA代码()
'MsgBox 弹出一个弹框,显示以下信息
MsgBox "这是我的第一个的 VBA 代码"
End Sub
开始运行代码;
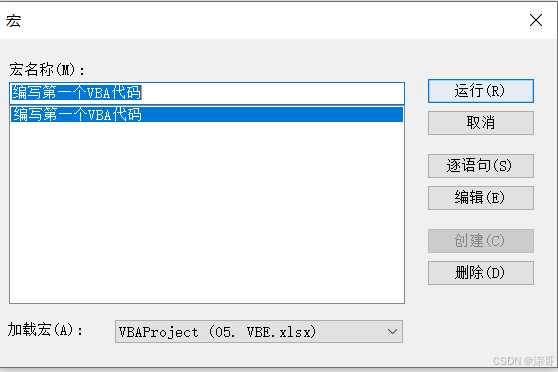
代码结果:
注:
1、vbe环境会自己补充代码,例如格式,大小写关键字,但不是万能的;
2、tab 的格式,对于多行代码,需要注意格式的问题;阅读代码方便;
编写代码,提取内容
'Sub 表示一个程序,理解为一段代码的集合
Sub 编写第一个VBA代码()
'MsgBox 弹出一个弹框,显示以下信息
MsgBox "这是我的第一个的 VBA 代码"
'提取单元格的内容
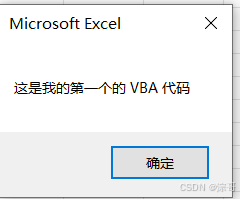
MsgBox "A1单元格的内容是:" & Range("B2").Value
End Sub
代码结果:
变量的编写
变量的含义
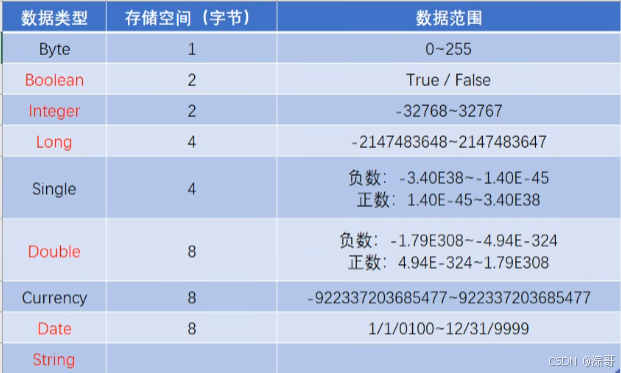
注:
字节:计算机中存储空间的大小;
变量三要素:
- 数据类型
- 变量名
- 变量值
案例
案例1:
Sub 变量()
' 声明定义一个变量,用Dim 给变量起名字,Score, 数据类型为整型
Dim Score As Integer
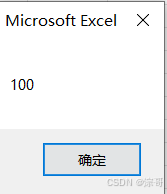
Score = 100
MsgBox Score
End Sub
运行结果:
案例2:
代码:
Sub 变量()
' 声明定义一个变量,用Dim 给变量起名字,Score, 数据类型为整型
Dim Score As Integer
Score = 100
MsgBox Score
Score = 200
MsgBox Score
' 超出范围,显示溢出
Score = 50000
MsgBox Score
End Sub
运行结果:
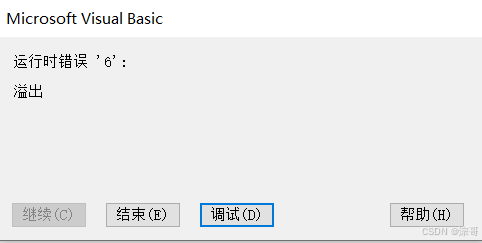
注:溢出时,数据大小过小,往大调即可;
案例3:
代码:
Sub 变量()
' 小数类型的数据
Dim Price As Double
Price = 100.34
MsgBox Price
' 日期类型的数据
Dim To_day As Data
To_day = #10/4/2024#
MsgBox To_day
End Sub
运行结果:


注:
日期显示以电脑格式为准;
编写需要加#符号;
案例4:
代码:
Sub 变量()
' 字符类型的数据
Dim str As String
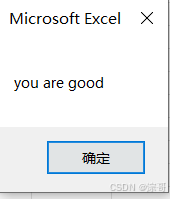
str = "you are good"
MsgBox str
' 布尔类型的数据
Dim bool As Boolean
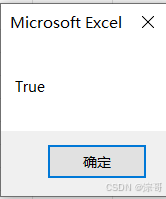
bool = True
MsgBox bool
End Sub
运行结果:
案例5:(多变量声明)
代码:
Sub 变量()
' 声明定义一个变量,用Dim 给变量起名字,Score, 数据类型为整型
Dim Score As Integer, Price As Double
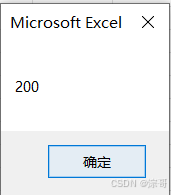
Score = 200
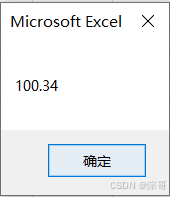
Price = 100.34
MsgBox Score
MsgBox Price
End Sub
运行结果:
注:
- 通常,数据类型应当固定;
- variant :可变数据类型;无法确定数据类型,浪费内存空间;
强制变量声明
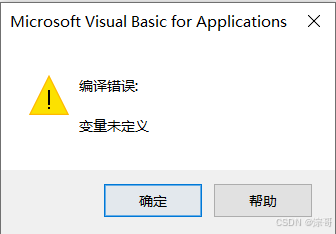
代码未添加 Option Explicit 时,不会报错,即Sco没有定义;
代码添加之后,就会报错,对我们写代码有益;
案例:
Option Explicit
Sub OptionTest()
Dim Score As Integer
Score = 10
MsgBox Score
MsgBox Sco
End Sub
运行结果:
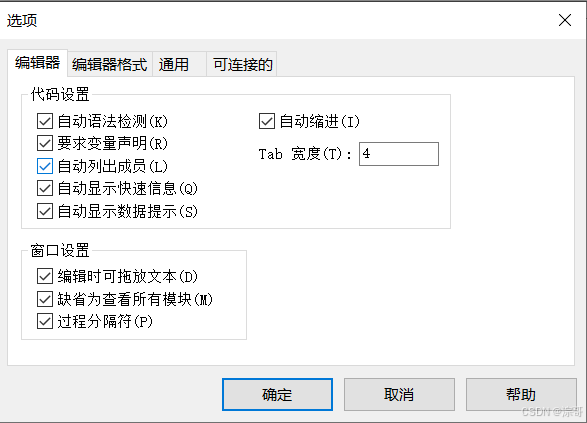
在工具框——选项勾选 要求变量声明 ;将自动添加 Option Explicit 代码;代码习惯;
变量声明周期
案例一代码:
Option Explicit
Sub Module1()
'声明周期在此子程序当中
Dim Price As Double
Price = 4.5
MsgBox Price
End Sub
Sub Module2()
'不可用变量
MsgBox Price
End Sub
要想使用变量,放入外面即可;
案例二代码:
Option Explicit
Dim Price As Double
Sub Module1()
'声明周期在此子程序当中
Price = 4.5
MsgBox Price
End Sub
Sub Module2()
'不可用变量
MsgBox Price
End Sub
运行 module1 与module2结果:
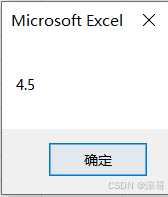
注:变量只能在此模块中使用;
案例三代码:
模块1代码:
Option Explicit
'Dim Price As Double
Public Price As Double
Sub Module1()
'声明周期在此子程序当中
Price = 4.5
MsgBox Price
End Sub
Sub Module2()
'不可用变量
Price = 5.4
MsgBox Price
End Sub
注意关键字 Dim 变成 Public;
模块2代码:
Option Explicit
Sub Module3()
'不可用变量
Price = 15.4
MsgBox Price
End Sub
运行结果:
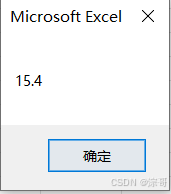
Static 修饰符
未加static 修饰符:
Option Explicit
Sub Static修饰符()
Dim Count As Integer
Count = Count + 1
MsgBox "你已经运行了:" & Count & "次"
End Sub
每一次的运行结果:
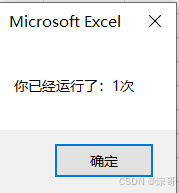
加static 修饰符:
Option Explicit
Sub Static修饰符()
Static Count As Integer
Count = Count + 1
MsgBox "你已经运行了:" & Count & "次"
End Sub
注:注意关键字 Static 的位置;
运行结果:
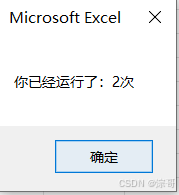
释放内存
方法1:
方法2:
关闭工作簿;
常量的使用
Option Explicit
Sub 常量的使用()
'声明常量的时候赋值,
'声明常量用 const
Const PI As Double = 3.14159
MsgBox PI
'常量不允许赋值
' PI = 3.15
MsgBox PI
End Sub
注:为了更加直观;
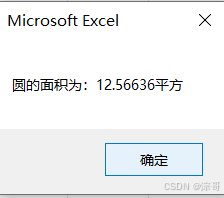
案例1:
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub 常量的使用()
'声明常量的时候赋值,
'声明常量用 const
Const PI As Double = 3.14159
MsgBox PI
'计算半径为2的圆的面积
Dim Area As Double
Area = PI * 2 * 2
MsgBox "圆的面积为:" & Area & "平方"
End Sub
运行结果:
数字运算符
运算符:数学运算符 + - / * ^ mod(取余)
Option Explicit
'数学运算符 + - / * ^ mod
Sub 数学运算符()
Dim num1 As Integer, num2 As Integer
num1 = 4
num2 = 2
Dim Result1 As Integer
Result1 = num1 + num2 '加
Dim Result2 As Integer
Result2 = num1 * num2 '乘
Dim Result3 As Integer
Result3 = num1 / num2 '除
Dim Result4 As Integer
Result4 = num1 ^ num2 '次方
Dim Result5 As Integer
num2 = 3
Result5 = num1 Mod num2 '取余
MsgBox Result1
MsgBox Result2
MsgBox Result3
MsgBox Result4
MsgBox Result5
Dim Result6 As Double
num1 = 10
num2 = 20
Result6 = num1 ^ num2 '16 10 的20次方
MsgBox Result6
End Sub
比较运算符
比较运算符: > < = >= <= = <> 不等于
Option Explicit
'比较运算符 > < = >= <= = <> 不等于
Sub 比较运算符()
Dim num1 As Integer, num2 As Integer
num1 = 4
num2 = 2
Dim Result1 As Boolean
Result1 = num1 > num2
Dim Result2 As Boolean
Result2 = num1 >= num2
Dim Result3 As Boolean
Result3 = num1 = num2
Dim Result4 As Boolean
Result4 = num1 < num2
Dim Result5 As Boolean
num2 = 3
Result5 = num1 <= num2
Dim Result6 As Boolean
num2 = 3
Result6 = num1 <> num2 '不等于
'条件成立 true
'条件不成立 false
MsgBox Result1
MsgBox Result2
MsgBox Result3
MsgBox Result4
MsgBox Result5
End Sub
逻辑运算符
逻辑运算符 And Or Not(取反)
Option Explicit
'逻辑运算符 And Or Not(取反)
Sub 逻辑运算符()
Dim num1 As Integer, num2 As Integer, num3 As Integer
num1 = 2
num2 = 10
num3 = 20
Dim Result1 As Boolean
'全部都成立,才会成立
Result1 = (num1 > num2) And (num2 > num3)
Dim Result2 As Boolean
'成立一个,就会成立
Result2 = (num1 > num2) Or (num2 < num3)
Dim Result3 As Boolean
' 取反 之前是false,现在就是true
Result3 = Not (num1 = num2)
'条件成立 true
'条件不成立 false
MsgBox "Result1 :" & Result1
MsgBox "Result2 :" & Result2
MsgBox "Result3 :" & Result3
End Sub
表达式:
常量,变量,运算符的组合;
VBA命名规范
命名规范:
- 数字,字母,下划线;
- 数字,下划线不能开头,字母结合数字,下划线进行命名;
- 见名知意;
- 特殊关键字不可以命名,如Dim,Static,Integer等;
- 不能使用空格,特殊符号命名;
IF选择结构
案例1:
If 条件 Then
执行语句
Else
执行语句
EndIf
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub 选择结构()
Dim Score As Integer
Score = 57
'Then 需要做的工作
'End If 结束
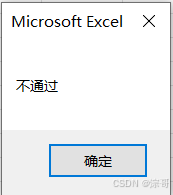
If Score >= 60 Then
MsgBox "通过"
Else
MsgBox "不通过"
End If
End Sub
运行结果:
案例2:
If 条件 Then
执行语句
ElseIf 条件 Then
执行语句
Else
执行语句
EndIf
代码:
Sub 选择结构test2()
Dim Score As Integer
Score = 87
'Then 需要做的工作
'End If 结束
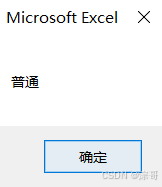
If Score >= 90 Then
MsgBox "优秀"
ElseIf Score >= 80 Then
MsgBox "普通"
Else
MsgBox "不及格"
End If
End Sub
运行结果:
Select 选择结构
案例1:
Select Case 变量
Case Is 条件
执行工作
......
Case Is 条件
执行工作
Case Else
执行工作
代码:
Option Explicit
'SelectCase选择结构
Sub 选择结构test1()
Dim Score As Integer
Score = 87
'Case Is 特定情况
'Case Else 除其他值之外的情况
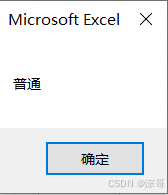
Select Case Score
Case Is >= 90
MsgBox "优秀"
Case Is >= 80
MsgBox "普通"
Case Else
MsgBox "不及格"
End Select
End Sub
运行结果:
注:此选择结构用的不多;
ForNext选择结构
案例1:
For 初始值 To 结束值
执行语句
Next num //每次num自增1 num = num + 1
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub 循环结构()
Dim num As Integer
For num = 1 To 10
MsgBox "循环结构:" & num & "次数"
'next Num 每次num自增1 num = num + 1
Next num
End Sub
案例2:
求1-10的和;
代码:
'求和
Sub 循环结构test2()
Dim num As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
For num = 1 To 10
sum = num + sum
Next num
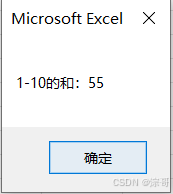
MsgBox "1-10的和:" & sum
End Sub
运行结果:
嵌套For循环结构
循环单独看就可以了;
代码:
'乘法表
Sub 循环结构test3()
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
For i = 1 To 10
For j = 1 To 10
If i <= j Then
sum = i * j
MsgBox i & "*" & j & "=" & sum
End If
Next j
Next i
MsgBox "乘法表:" & sum
End Sub
Step的运用场景
案例1:
step控制自增的大小
代码:
Option Explicit
'Step的应用
Sub 循环结构test2()
Dim num As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
'step 的作用 num = num +2
For num = 1 To 100 Step 2
sum = num + sum
Next num
MsgBox "1-100的奇数和:" & sum
End Sub
运行结果:

如何中断For循环结构
案例:
打断for循环
Exit For
代码:
Sub Breaktest3()
Dim num As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
For num = 1 To 100 Step 2
If num > 50 Then
' 退出for循环
Exit For
End If
sum = num + sum
Next num
MsgBox "1-50的奇数和:" & sum
End Sub
运行结果:
DoWhile 循环结构
满足条件,执行语句
Do While 限制条件
执行语句
Loop
代码:
Option Explicit
'求和
Sub DoWhiletest1()
Dim num As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
num = 0
Do While num <= 10
sum = num + sum
num = num + 1
Loop
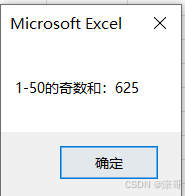
MsgBox "Do While 1-10的和:" & sum
End Sub
运行结果:
DoUntil循环结构
案例:
满足条件,不再执行
Do Until 限制条件
执行语句
Loop
代码:
Option Explicit
'求和
Sub DoUntilltest1()
Dim num As Integer, sum As Integer
sum = 0
num = 0
'满足条件,不再执行
Do Until num > 10
sum = num + sum
num = num + 1
Loop
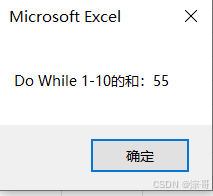
MsgBox "Do until 1-10的和:" & sum
End Sub
运行结果:
编写无参数子过程
- 子过程 、子程序 、 子函数
- 可以将功能分开描述,单击子程序就可以运行;
- Exit Sub 中断子程序;
编写有参数子过程
案例1:
带参数的子过程;
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub 有参数(ToNum As Integer)
Dim num As Integer, sum As Long
sum = 0
For num = 1 To ToNum
sum = num + sum
Next num
MsgBox "有参数 1-" & ToNum & "的和:" & sum
End Sub
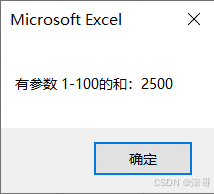
Sub 调参数函数()
有参数 (100)
End Sub
运行结果:

案例2:
多个参数的应用
代码:
Sub 有参数test(ToNum As Integer, steptest As Integer)
Dim num As Integer, sum As Long
sum = 0
For num = 1 To ToNum Step steptest
sum = num + sum
Next num
MsgBox "有参数 1-" & ToNum & "的和:" & sum
End Sub
Sub 调参数函数test()
有参数test 100, 2
End Sub
运行结果:
编写自定义函数
案例:
Function 表示函数过程;
Function有返回值,,子过程没有返回值;
Function 函数名
函数名 = 功能
End Function
代码:
Option Explicit
'Function 表示函数过程,而不是子过程
Function Cubesum(x As Double, y As Double)
Cubesum = x * x * x + y * y * y
End Function
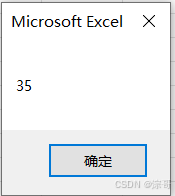
Sub Test()
MsgBox Cubesum(2, 3)
End Sub
运行结果:
一维数组
案例1:
存储数组,访问数据
注:
- LBound 数组最小的角标
- UBound 数组最大的角标
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub Arraytest()
'数组下标 为 1,2,3
Dim Arraytest(1 To 3) As Integer
'为一维数组存储,下标为 1,2,3
Arraytest(1) = 0
Arraytest(2) = 100
Arraytest(3) = 200
' test1
'访问数据
MsgBox Arraytest(2)
' test2
'遍历
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 3
MsgBox Arraytest(i)
Next i
' test3
'LBound 最小的角标
'UBound 最大的角标
For i = LBound(Arraytest) To UBound(Arraytest)
MsgBox Arraytest(i)
Next i
End Sub
运行结果:
Option Base 的作用
案例:
option base 的作用,控制角标;
不做限制,默认为0
代码:
Option Base 1 '下标为1
Option Explicit
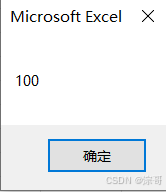
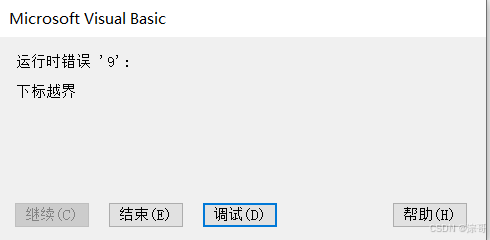
Sub ArrayTest2()
Dim ArrayTest(3) As Integer
'相当于 Dim ArrayTest(0,3) As Integer
'默认最小角标为 0
ArrayTest(0) = 0
ArrayTest(1) = 50
ArrayTest(2) = 100
ArrayTest(3) = 200
Dim i As Integer
For i = LBound(ArrayTest) To UBound(ArrayTest)
MsgBox ArrayTest(i)
Next i
End Sub
运行结果:
下标越界
二维数组
案例:
遍历二维数组
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub Arraytest()
'定义二维数组
Dim Arraytest(0 To 2, 0 To 2) As Integer
'二维数组赋值
Arraytest(0, 0) = 1
Arraytest(0, 1) = 2
Arraytest(0, 2) = 3
Arraytest(1, 0) = 11
Arraytest(1, 1) = 22
Arraytest(1, 2) = 33
Arraytest(2, 0) = 111
Arraytest(2, 1) = 222
Arraytest(2, 2) = 333
'遍历二维数组数组
Dim index As Integer, index1 As Integer
For index = 0 To 2
For index1 = 0 To 2
MsgBox Arraytest(index, index1)
Next index1
Next index
End Sub
运行结果:
代码2:
Sub Arraytest1()
'定义二维数组
Dim Arraytest(0 To 3, 1 To 4) As Integer
'二维数组赋值
Arraytest(0, 1) = 12
Arraytest(0, 2) = 13
Arraytest(0, 3) = 14
Arraytest(0, 4) = 15
Arraytest(1, 1) = 22
Arraytest(1, 2) = 33
Arraytest(1, 3) = 44
Arraytest(1, 4) = 55
Arraytest(2, 1) = 222
Arraytest(2, 2) = 333
Arraytest(2, 3) = 444
Arraytest(2, 4) = 555
Arraytest(3, 1) = 122
Arraytest(3, 2) = 133
Arraytest(3, 3) = 144
Arraytest(3, 4) = 155
'遍历二维数组数组
Dim index As Integer, index1 As Integer
'LBound(Arraytest, 0) 行的最小角标
'UBound(Arraytest, 0) 行的最大角标
For index = LBound(Arraytest, 1) To UBound(Arraytest, 1)
'LBound(Arraytest, 2) 列的最小角标
'UBound(Arraytest, 2) 列的最大角标
For index1 = LBound(Arraytest, 2) To UBound(Arraytest, 2)
MsgBox Arraytest(index, index1)
Next index1
Next index
End Sub
动态数组
案例:
定义一维动态数组
Dim MyDynArray() As Integer
ReDim 表示明确的动态数组的最小角标和最大角标
ReDim MyDynArray(1 To 3)
动态数组赋值
ReDim MyDynArray(1 To 4) '会抹除之前的数据
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub MyDynArray()
'定义一维动态数组
Dim MyDynArray() As Integer
'ReDim 表示明确的动态数组的最小角标和最大角标
ReDim MyDynArray(1 To 3)
'动态数组赋值
MyDynArray(1) = 11
MyDynArray(2) = 201
MyDynArray(3) = 301
'遍历
Dim i As Integer
For i = LBound(MyDynArray) To UBound(MyDynArray)
MsgBox MyDynArray(i)
Next i
'ReDim MyDynArray(1 To 4) '会抹除之前的数据
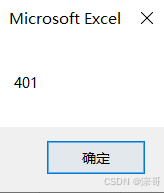
ReDim Preserve MyDynArray(1 To 4) '保存之前的数据
MyDynArray(4) = 401
For i = LBound(MyDynArray) To UBound(MyDynArray)
MsgBox MyDynArray(i)
Next i
End Sub
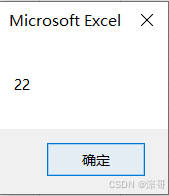
运行结果:
面向对象
设置Range() 的值,设置单元格的属性
Option Explicit
Sub 面向对象()
'设置单元格 A1 的 值
' Range ("A1") 表示单元格 A1 单元格
Range("A1").Value = 100
MsgBox Range("A1").Value
End Sub
Value 取值
Select 选择
Clear 清除
对象层级框架
案例1:
- 活动的工作表
- 指定的工作表
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub 对象层级()
'对象层次访问
'指定的工作簿
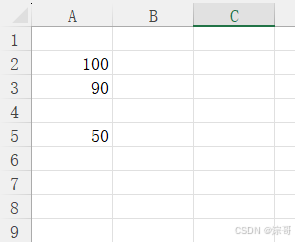
Application.Workbooks("对象.xlsm").Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A2").Value = 100
'简略写法
'指定的工作表
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A5").Value = 50
'目前活动的工作表
Range("A3").Value = 90
End Sub
运行结果:
案例2:
工作表的集合
代码:
Sub 对象层级test()
'目前活动的工作表
Range("A11").Value = 1100
'方法
Range("A11").Select
Range("A11").Clear
'集合也是对象,也有属性和方法
'属性
MsgBox Worksheets("Sheet1").Name
'方法
Worksheets.Add
End Sub
运行结果:
单元格应用
案例1:
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub CellRefTest()
'引用某个单元格
Range("A4").Value = 100
'引用多个单元格
Range("A4,C4,E4").Value = 111
'引用单元格区域
Range("A5:C7").Value = 222
'引用不连续的单元格
Range("A9:C11,E12:G14").Value = 567
'引用单元格区域名称
'Range("test").Value = 1
'引用行和列
Range("22:22").Value = 0 '行
Range("j:j").Value = 0 '列
'引用多行
Range("22:22,44:44").Value = 1 '行
'引用多列
Range("G:G,O:O").Value = 1 '行
'引用相连行 列
Range("36:46").Value = 2 '行
Range("X:Z").Value = 2 '行
End Sub
Cells 和offset 属性
案例1:
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub Cellstest()
'引用工作表中的某个单元格
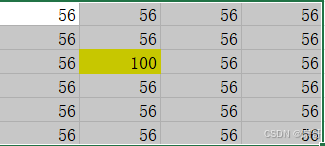
Worksheets("Sheet3").Cells(5, 9) = 45
'引用单元格区域
Range(Cells(8, 2), Cells(13, 5)) = 56
'引用单元格区域中的某个单元格
Range("B8:E13").Cells(3, 2) = 100
End Sub
运行结果:
引用单元格区域中的某个单元格
案例2:
offset
代码:
Sub Offsettest()
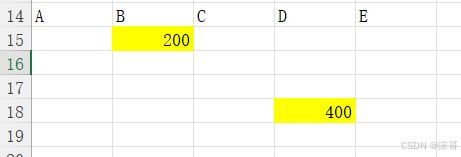
'Offset 属性——偏移量——相对单元格
Range("B15").Offset(3, 2).Value = 400
Range("D18").Offset(-3, -2).Value = 200
End Sub
运行结果:
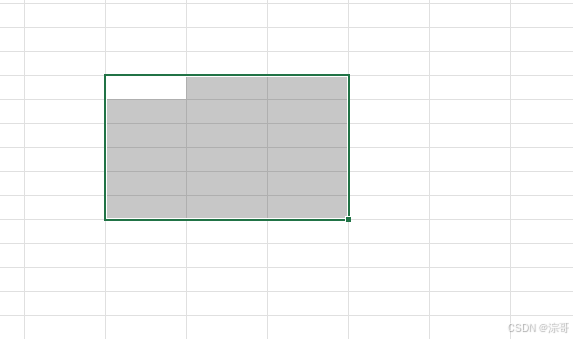
Select 和 Active 方法
案例1:
Select
代码:
Option Explicit
Sub CellRefTest()
Range("B9").Select
Range("C9:E14").Select
End Sub
运行结果
案例2:
Activate offset 区别
代码:
'
'Selection 引用选择单元格、单元格区域
'
'ActiveCell 引用活动单元格
'
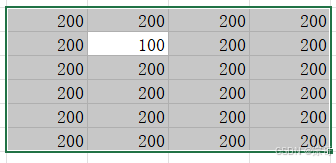
Sub CellRefTest1()
'Activate 方法 活动单元格
Range("B9").Activate
Range("C9:E14").Activate
'Activate offset 区别
Range("G9:J14").Select
Range("H10").Activate
'引用选择单元格、单元格区域
Selection.Value = 200
'引用活动单元格
ActiveCell.Value = 100
End Sub
运行结果:
Range 对象的End属性
案例1:
Ctrl + shift +→ 向右全部区域
Ctrl + shift +↑ 向上全部区域
Ctrl + shift +↓ 向下全部区域
Ctrl + shift +← 向左全部区域
Ctrl +→ 最右单元格
Ctrl +↑ 最上单元格
Ctrl +↓ 最下单元格
Ctrl +← 最左单元格
代码:
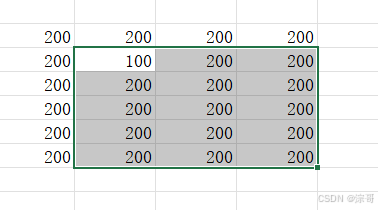
Option Explicit
Sub CellRefTest()
Range("H11").End(xlToLeft).Select
Range("H11").End(xlDown).Select
'模拟 Ctrl + 方向键的作用
Range("H11").End(xlDown).End(xlToRight).Select
'模拟一片区域 Ctrl + 方向键的作用
Range("H10", Range("H10").End(xlDown).End(xlToRight)).Select
End Sub
运行结果:





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








