整体分析
问题:通过给定的前面的特征信息,来预测阳性数量(tested_positive)。是一个典型的回归问题,在HW1中我们主要是初探全连接神经网络,看看不同的神经网络在模型测试集中的性能表现。在深度学习中,我们主要关注的是模型的泛化误差,当然训练误差也是我们应该关注的,如果说训练误差非常大,在测试集上的表现一般也很差,这个问题可以参考李宏毅老师前面讲述的深度学习的性能表现问题分析,评估不同情况下的问题原因。
Kaggle提交地址:HW01
1.分析训练集和测试集数据(了解模型的特征和标签)
tr_path = 'covid.train.csv' # path to training data
tt_path = 'covid.test.csv' # path to testing data
import pandas as pd
data_view = pd.read_csv(tr_path)
print(data_view.info()) # (2700,95) 除开Id列共93列特征信息,一列标签值
输出:
# <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
# RangeIndex: 2700 entries, 0 to 2699
# Data columns (total 95 columns)
分析(2700,95),其中除开id列和label标签列,共有93个特征信息列。
共有 2700个实体
同理打印测试集的信息为(893,94),测试集中去除了标签列
2.将训练集划分为训练集和验证集(9:1)实现Dataset和DataLoader,进行数据集的读取和加载
class COVID19Dataset(Dataset): # 继承了pytorch中Dataset类,实现__getitem__方法和__len__方法
''' Dataset for loading and preprocessing the COVID19 dataset '''
def __init__(self,
path,
mode='train',
target_only=False): # init的方法读取数据集,并且将数据集中按照训练模式进行划分
self.mode = mode
# Read data into numpy arrays
with open(path, 'r') as fp:
data = list(csv.reader(fp))
data = np.array(data[1:])[:, 1:].astype(float) #去掉首行的特征名字和id列,获取所有样本的特征和标签信息
if not target_only:
feats = list(range(93))
else:
# TODO: Using 40 states & 2 tested_positive features (indices = 57 & 75)
pass
if mode == 'test': # 测试模式
# Testing data
# data: 893 x 93 (40 states + day 1 (18) + day 2 (18) + day 3 (17))
data = data[:, feats] # 取出所有的特征信息
self.data = torch.FloatTensor(data) # 转换成Tensor格式
else:
# Training data (train/dev sets)
# data: 2700 x 94 (40 states + day 1 (18) + day 2 (18) + day 3 (18))
target = data[:, -1] # 训练模式下取出标签和特征数据
data = data[:, feats]
# Splitting training data into train & dev sets
if mode == 'train':
indices = [i for i in range(len(data)) if i % 10 != 0] # 9/10的特征数据
elif mode == 'dev':
indices = [i for i in range(len(data)) if i % 10 == 0] # 1/10的特征数据
# Convert data into PyTorch tensors
self.data = torch.FloatTensor(data[indices]) # 训练特征数据
self.target = torch.FloatTensor(target[indices]) # 训练目标数据
# Normalize features (you may remove this part to see what will happen) # 对40列后的特征信息进行正则化
self.data[:, 40:] = \
(self.data[:, 40:] - self.data[:, 40:].mean(dim=0, keepdim=True)) \
/ self.data[:, 40:].std(dim=0, keepdim=True)
self.dim = self.data.shape[1] #特征信息的维度
print('Finished reading the {} set of COVID19 Dataset ({} samples found, each dim = {})'
.format(mode, len(self.data), self.dim))
def __getitem__(self, index): # 返回数据集特征和标签
# Returns one sample at a time
if self.mode in ['train', 'dev']:
# For training
return self.data[index], self.target[index]
else:
# For testing (no target)
return self.data[index]
def __len__(self): # 返回数据集长度
# Returns the size of the dataset
return len(self.data)
DataLoader实现
def prep_dataloader(path, mode, batch_size, n_jobs=0, target_only=False): # 将train.csv 中 文件 按照9:1划分为训练集和测试集
''' Generates a dataset, then is put into a dataloader. '''
dataset = COVID19Dataset(path, mode=mode, target_only=target_only) # Construct dataset
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset, batch_size, # dataset,batch_size
shuffle=(mode == 'train'), drop_last=False, # 是否丢弃尾部数据
num_workers=n_jobs, pin_memory=True) # 多线程 #Construct dataloader
return dataloader
3.model实现
通过继承nn.Module类,实现前向传播的forward方法。
class NeuralNet(nn.Module):# 神经网络
''' A simple fully-connected deep neural network '''
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(NeuralNet, self).__init__()
# Define your neural network here
# TODO: How to modify this model to achieve better performance?
# self.net = nn.Sequential(
# nn.Linear(input_dim, 64),
# nn.BatchNorm1d(64),
# nn.Dropout(p=0.2),
# nn.Linear(64, 32),
# nn.ReLU(),
# nn.Linear(32,16),
# nn.ReLU(),
# nn.Linear(16,1)
# )
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128,64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32,16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16,8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8,4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4,1)
)
# Mean squared error loss
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # 定义的均方损失函数,返回损失的均值
def forward(self, x):
''' Given input of size (batch_size x input_dim), compute output of the network '''
return self.net(x).squeeze(1)
def cal_loss(self, pred, target):
''' Calculate loss ''' # Calculate loss
# TODO: you may implement L2 regularization here
return self.criterion(pred, target)
4.训练过程及代码实现
def train(tr_set, dv_set, model, config, device):
''' DNN training '''
n_epochs = config['n_epochs'] # Maximum number of epochs
# Setup optimizer 设置优化器
optimizer = getattr(torch.optim, config['optimizer'])(
model.parameters(), **config['optim_hparas'])
min_mse = 1000.
loss_record = {'train': [], 'dev': []} # for recording training loss
early_stop_cnt = 0
epoch = 0
while epoch < n_epochs:
model.train() # set model to training mode
for x, y in tr_set: # iterate through the dataloader
optimizer.zero_grad() # set gradient to zero
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # move data to device (cpu/cuda)
pred = model(x) # forward pass (compute output)
mse_loss = model.cal_loss(pred, y) # compute loss
mse_loss.backward() # compute gradient (backpropagation)
optimizer.step() # update model with optimizer
loss_record['train'].append(mse_loss.detach().cpu().item())
# After each epoch, test your model on the validation (development) set.
dev_mse = dev(dv_set, model, device)
if dev_mse < min_mse:
# Save model if your model improved
min_mse = dev_mse
print('Saving model (epoch = {:4d}, loss = {:.4f})'
.format(epoch + 1, min_mse))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), config['save_path']) # Save model to specified path
early_stop_cnt = 0
else:
early_stop_cnt += 1
epoch += 1
loss_record['dev'].append(dev_mse)
if early_stop_cnt > config['early_stop']:
# Stop training if your model stops improving for "config['early_stop']" epochs.
break
print('Finished training after {} epochs'.format(epoch))
return min_mse, loss_record
Load data and model
tr_set = prep_dataloader(tr_path, 'train', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
dv_set = prep_dataloader(tr_path, 'dev', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
tt_set = prep_dataloader(tt_path, 'test', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
5.Train model and test model

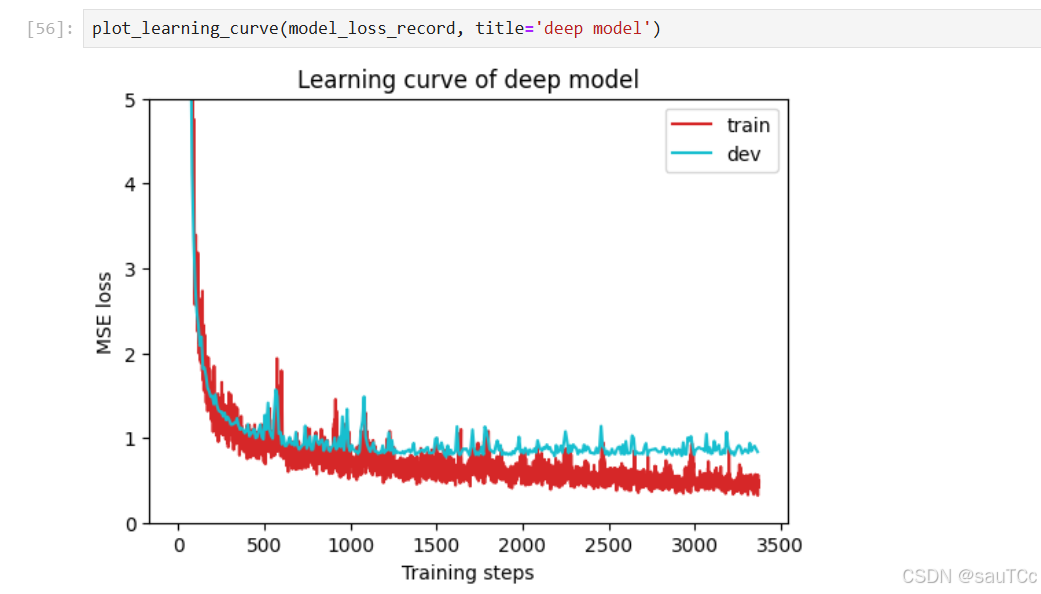
6.在dev验证集上的可视化拟合效果

7.提交Kaggle


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








