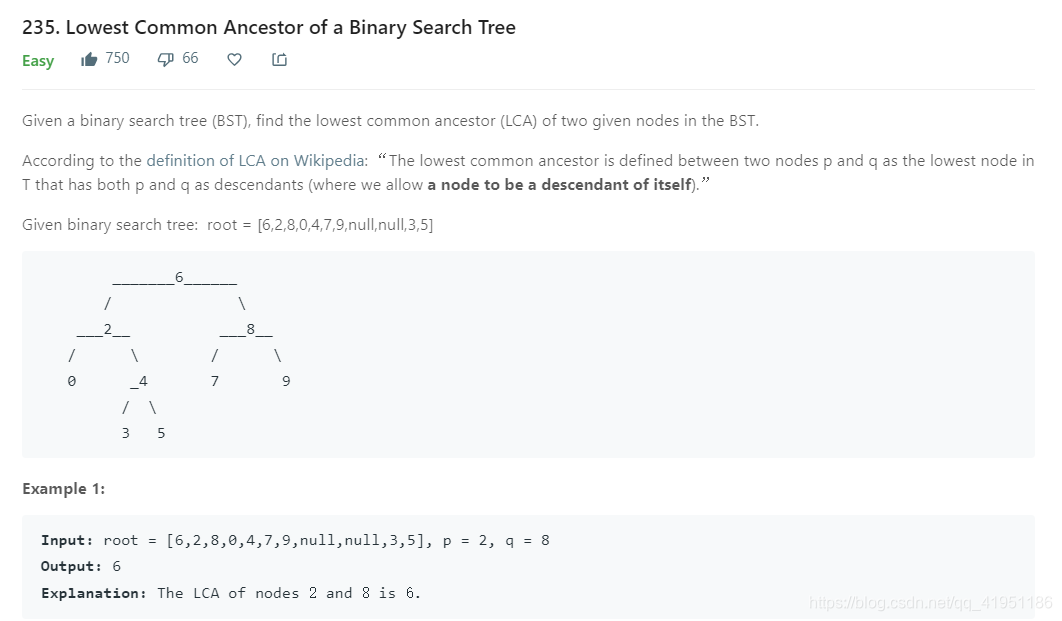
我开始想到的方法是从root开始find,先找到p,保存路径,然后沿路径(往回)节点开始,依次find节点q,找到的话,该节点就是最低的公共祖先。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> path=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode res=new TreeNode(-1);//find p,保存路径节点
while(p.val!=root.val){
if(p.val<root.val){
path.add(root);
root=root.left;
}
else{
path.add(root);
root=root.right;
}
}
path.add(p);
for(int i=path.size()-1;i>=0;i--){//从路径往回查找q,找到的话结束,返回结果
TreeNode cur=path.get(i);
while(cur!=null){
if(q.val==cur.val){
res=path.get(i);
break;
}
else if(q.val<cur.val)
cur=cur.left;
else
cur=cur.right;
}
if(res.val!=-1)
break;
}
return res;
}
}
此外,考虑最低公共祖先cp的特点:p和q在cp的左右子树上(一边一个),cp的祖先cp‘都是p和q的公共祖先,但此时p和q都在cp’的一棵子树上。以此可以找到算法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while( (root.val - p.val) * (root.val - q.val) > 0) {
root = p.val < root.val ? root.left : root.right;
}
return root;
}
}
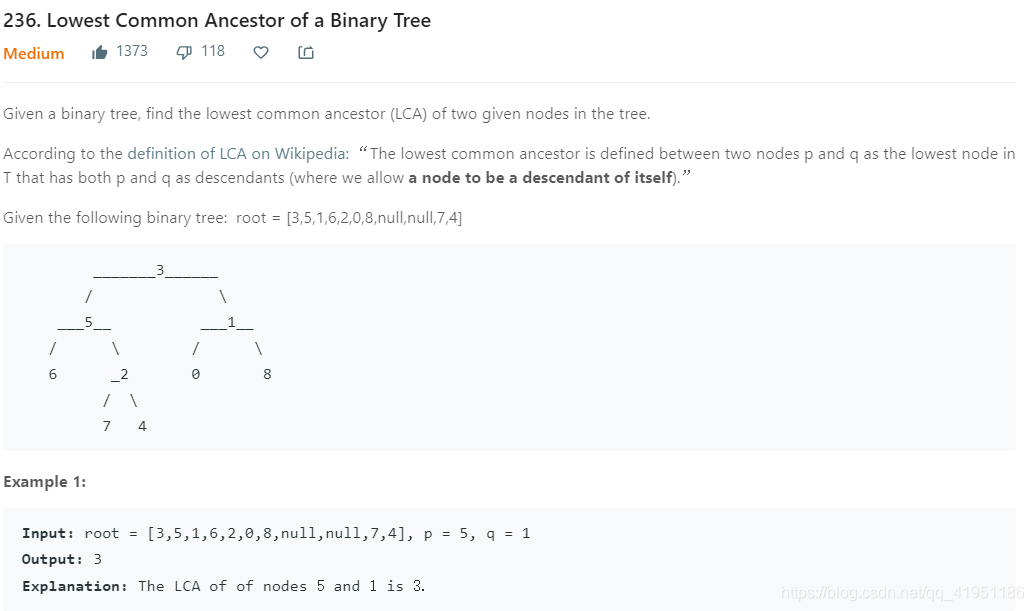
理解:
当遍历到一个root点的时候,
1.判断root是不是null如果root为null,那么就无所谓祖先节点,直接返回null就好了
2.如果root的左子树存在p,右子树存在q,那么root肯定就是最近祖先
3.如果pq都在root的左子树,那么就需要递归root的左子树,右子树同理
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || p == root || q == root){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null) {
return right;
}
else if (right == null) {
return left;
}
else {
return root;
}
}
}
























 418
418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








