A. New Building for SIS
You are looking at the floor plan of the Summer Informatics School's new building. You were tasked with SIS logistics, so you really care about travel time between different locations: it is important to know how long it would take to get from the lecture room to the canteen, or from the gym to the server room.
The building consists of n towers, h floors each, where the towers are labeled from 1 to n, the floors are labeled from 1 to h. There is a passage between any two adjacent towers (two towers i and i + 1 for all i: 1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) on every floor x, where a ≤ x ≤ b. It takes exactly one minute to walk between any two adjacent floors of a tower, as well as between any two adjacent towers, provided that there is a passage on that floor. It is not permitted to leave the building.
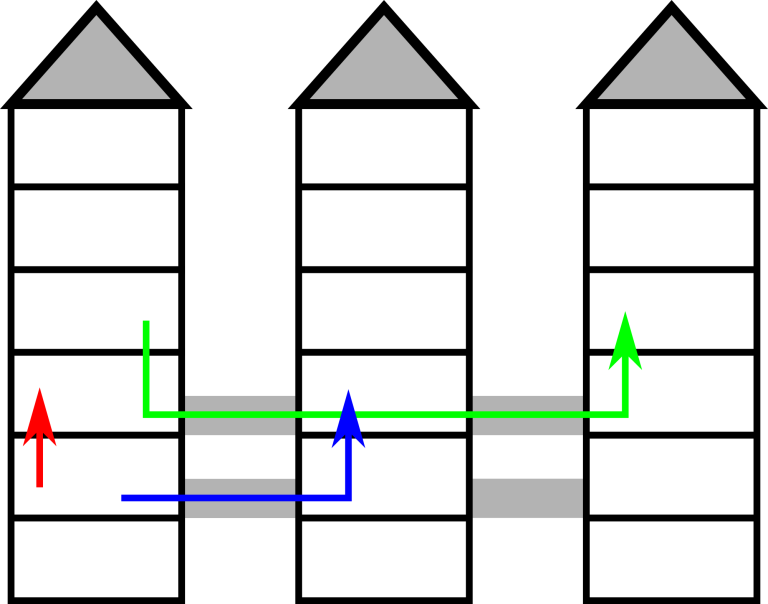
The picture illustrates the first example.
You have given k pairs of locations (ta, fa), (tb, fb): floor fa of tower ta and floor fb of tower tb. For each pair you need to determine the minimum walking time between these locations.
Input
The first line of the input contains following integers:
- n: the number of towers in the building (1 ≤ n ≤ 108),
- h: the number of floors in each tower (1 ≤ h ≤ 108),
- a and b: the lowest and highest floor where it's possible to move between adjacent towers (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ h),
- k: total number of queries (1 ≤ k ≤ 104).
Next k lines contain description of the queries. Each description consists of four integers ta, fa, tb, fb (1 ≤ ta, tb ≤ n, 1 ≤ fa, fb ≤ h). This corresponds to a query to find the minimum travel time between fa-th floor of the ta-th tower and fb-th floor of the tb-th tower.
Output
For each query print a single integer: the minimum walking time between the locations in minutes.
Example
input
3 6 2 3 3 1 2 1 3 1 4 3 4 1 2 2 3
output
1 4 2
解题:简单模拟
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,h,a,b,k,t1,f1,t2,f2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&h,&a,&b,&k);
while (k--){
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&t1,&f1,&t2,&f2);
if (t1==t2){
printf("%d\n",abs(f1-f2));
}
else {
int ans=abs(t2-t1);
if (f1<f2)
swap(f1,f2);
if (f1<a)
ans+=a-f1+a-f2;
else if (f2>b)
ans+=f2-b+f1-b;
else
ans+=f1-f2;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
B. Badge
In Summer Informatics School, if a student doesn't behave well, teachers make a hole in his badge. And today one of the teachers caught a group of nn students doing yet another trick.
Let's assume that all these students are numbered from 11 to nn. The teacher came to student aa and put a hole in his badge. The student, however, claimed that the main culprit is some other student papa.
After that, the teacher came to student papa and made a hole in his badge as well. The student in reply said that the main culprit was student ppappa.
This process went on for a while, but, since the number of students was finite, eventually the teacher came to the student, who already had a hole in his badge.
After that, the teacher put a second hole in the student's badge and decided that he is done with this process, and went to the sauna.
You don't know the first student who was caught by the teacher. However, you know all the numbers pipi. Your task is to find out for every student aa, who would be the student with two holes in the badge if the first caught student was aa.
Input
The first line of the input contains the only integer nn (1≤n≤10001≤n≤1000) — the number of the naughty students.
The second line contains nn integers p1p1, ..., pnpn (1≤pi≤n1≤pi≤n), where pipi indicates the student who was reported to the teacher by student ii.
Output
For every student aa from 11 to nn print which student would receive two holes in the badge, if aa was the first student caught by the teacher.
Examples
input
3 2 3 2
output
2 2 3
input
3 1 2 3
output
1 2 3
Note
The picture corresponds to the first example test case.
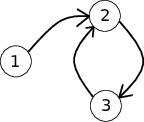
When a=1a=1, the teacher comes to students 11, 22, 33, 22, in this order, and the student 22 is the one who receives a second hole in his badge.
When a=2a=2, the teacher comes to students 22, 33, 22, and the student 22 gets a second hole in his badge. When a=3a=3, the teacher will visit students 33, 22, 33 with student 33 getting a second hole in his badge.
For the second example test case it's clear that no matter with whom the teacher starts, that student would be the one who gets the second hole in his badge.
题解:看清题意,简单模拟
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1005;
int num[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int main()
{
int n,point;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
int x=i;
while (1){
if (vis[x]){
point=x;
break;
}
vis[x]=true;
x=num[x];
}
printf("%d ",point);
}
return 0;
}








 本文介绍两个编程题目:一是关于Summer Informatics School新建大楼内不同地点间的最短行走时间计算;二是针对学生徽章上的洞,确定最先被老师发现两次违规的学生编号。
本文介绍两个编程题目:一是关于Summer Informatics School新建大楼内不同地点间的最短行走时间计算;二是针对学生徽章上的洞,确定最先被老师发现两次违规的学生编号。
















 429
429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








