迷宫介绍
在生活中我们玩过很多种走迷宫的小游戏,游戏给了一个迷宫,这个迷宫中只有一个入口,我们要从这个入口一直走下去,直到找到出口,这里出口可能是一个,也可能是多个。在这里我简单介绍三种实现起来由易到难的迷宫。
前提说明
我们这里的坐标是x轴正半轴向下伸展,y轴正半轴向右伸展
简单迷宫
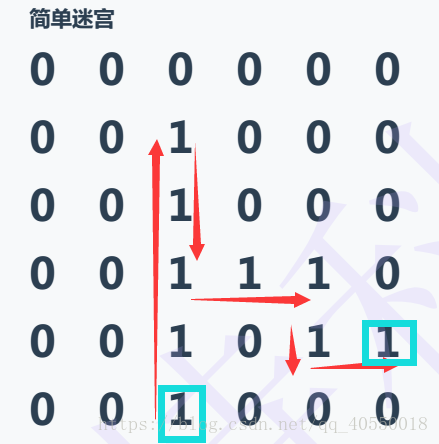
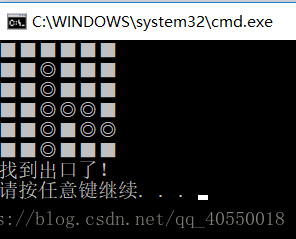
这是一种简单迷宫,有一个入口和一个出口,我们从入口开始按照左上右下的顺序进行尝试走迷宫,如果都走不了,就开始进行回溯,前提是我们走过的路需要提前标记,这样回溯的时候就比较方便了。代码如下:
maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#define ROWS 6
#define COLS 6
#define MAX 100
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
}Position;
typedef Position datatype;
typedef struct Stack{
datatype data[MAX];
int top;
}Stack;
void GoMaze();
maze.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"maze.h"
int maze[ROWS][COLS] = {
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,1,1,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 }
};//迷宫
void StackInit(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack *stack,datatype data)
{
stack->data[stack->top] = data;
stack->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top--;
}
datatype StackTop(Stack *stack)
{
return stack->data[stack->top - 1];
}
int IsExit(Position pos)
{
if (pos.y == COLS - 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int CanPass(Position pos)
{
if (pos.x < 0 || pos.x >= ROWS)
{
return 0;
}
if (pos.y < 0 || pos.y >= COLS)
{
return 0;
}
if (maze[pos.x][pos.y] == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
void PrintMaze()
{
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLS; j++)
{
if (maze[i][j] == 1)
{
printf(" ");//路用空格表示
}
else if (maze[i][j] == 0)
{
printf("■");//墙
}
else
{
printf("◎");//走过的路进行标记方便回溯
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void GoMaze()
{
Stack stack;
StackInit(&stack);
Position entry = { 5,2 };
Position pos = entry;
Position nextpos = pos;
while (1)
{
//标记走过的位置
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 2;
system("cls");//打印前清屏
PrintMaze();
Sleep(300);//有间隔效果看起来会好一点
StackPush(&stack, pos);
//当前是否走到出口
if (IsExit(pos))
{
printf("找到出口了!\n");
return;
}
//没有走到出口,按照左上右下的顺序进行尝试
nextpos.y -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.y += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
//如果都走不了,出栈
StackPop(&stack);
pos = StackTop(&stack);
StackPop(&stack);
}
}
void test()
{
GoMaze();
}
多通路迷宫(不带环)
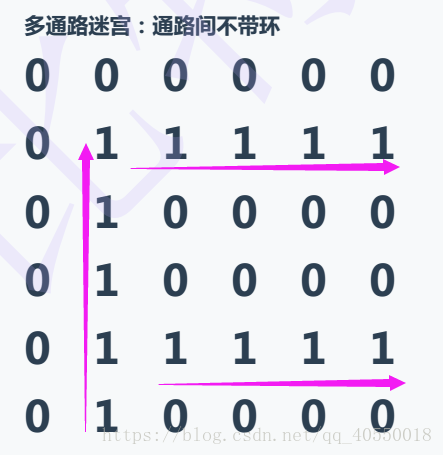
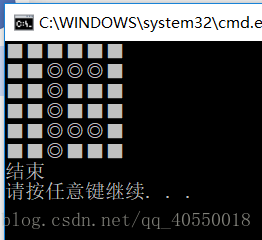
这是第二种迷宫,有一个入口,但是有两个出口。如果还是用第一种简单迷宫的方法,很显然当它找到第一个出口的时候就会停下来,那么我们如果想要把所有的路走找到,当找到第一个出口的时候我们把出口改成墙继续找第二个出口,知道栈里面一个元素都没有的时候就结束。代码如下:
maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#define ROWS 6
#define COLS 6
#define MAX 100
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
}Position;
typedef Position datatype;
typedef struct Stack{
datatype data[MAX];
int top;
}Stack;
void GoMaze();
maze.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"maze.h"
int maze[ROWS][COLS] = {
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,1,1,1 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,1,1,1,1 },
{ 0,0,1,0,0,0 }
};
void StackInit(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack *stack,datatype data)
{
stack->data[stack->top] = data;
stack->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top--;
}
datatype StackTop(Stack *stack)
{
return stack->data[stack->top - 1];
}
int StackEmpty(Stack *stack)
{
if (stack->top == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int IsExit(Position pos)
{
if (pos.y == COLS - 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int CanPass(Position pos)
{
if (pos.x < 0 || pos.x >= ROWS)
{
return 0;
}
if (pos.y < 0 || pos.y >= COLS)
{
return 0;
}
if (maze[pos.x][pos.y] == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
void PrintMaze()
{
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLS; j++)
{
if (maze[i][j] == 1)
{
printf(" ");
}
else if (maze[i][j] == 0)
{
printf("■");
}
else
{
printf("◎");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void GoMaze()
{
Stack stack;
StackInit(&stack);
Position entry = { 5,2 };
Position pos = entry;
Position nextpos = pos;
while (1)
{
//标记走过的位置
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 2;
system("cls");//打印前清屏
PrintMaze();
Sleep(300);//有间隔效果看起来会好一点
StackPush(&stack, pos);
//当前是否走到出口
if (IsExit(pos))
{
printf("找到出口了!\n");
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 0;
goto BACK;
}
//没有走到出口,按照左上右下的顺序进行尝试
nextpos.y -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.y += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
pos = nextpos;
continue;
}
BACK:
//如果都走不了,回溯
StackPop(&stack);
if (StackEmpty(&stack))
{
printf("结束\n");
return;
}
pos = StackTop(&stack);
StackPop(&stack);
}
}
void test()
{
GoMaze();
}
多通路迷宫(带环)
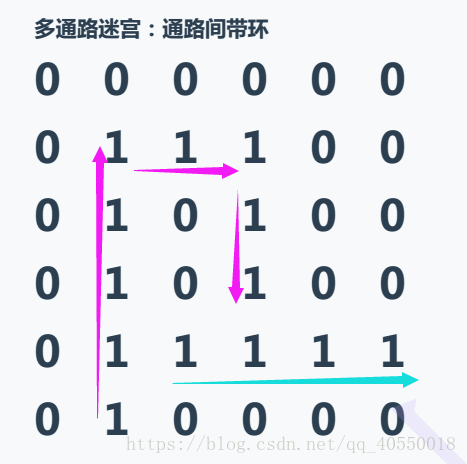
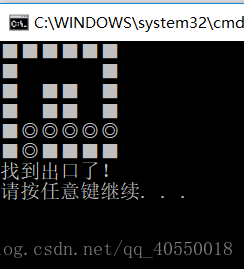
这是第三种迷宫,仍然是多通路,不同的是,这次带了环,和该如何是好呢?这时候我们可以递归的思想,利用递归的思想在回溯的时候可以不用判断之前走过的路了。代码如下:
maze.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#define ROWS 6
#define COLS 6
#define MAX 100
typedef struct {
int x;
int y;
}Position;
typedef Position datatype;
typedef struct Stack{
datatype data[MAX];
int top;
}Stack;
void GoMazeR();
maze.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"maze.h"
int maze[ROWS][COLS] = {
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,1,1,1,0 },
{ 0,1,0,0,1,0 },
{ 0,1,0,0,1,0 },
{ 0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 0,1,0,0,0,0 }
};
void StackInit(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack *stack,datatype data)
{
stack->data[stack->top] = data;
stack->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack *stack)
{
stack->top--;
}
datatype StackTop(Stack *stack)
{
return stack->data[stack->top - 1];
}
int StackEmpty(Stack *stack)
{
if (stack->top == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int IsExit(Position pos)
{
if (pos.y == COLS - 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
int CanPass(Position pos)
{
if (pos.x < 0 || pos.x >= ROWS)
{
return 0;
}
if (pos.y < 0 || pos.y >= COLS)
{
return 0;
}
if (maze[pos.x][pos.y] == 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
}
void PrintMaze()
{
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < COLS; j++)
{
if (maze[i][j] == 1)
{
printf(" ");
}
else if (maze[i][j] == 0)
{
printf("■");
}
else
{
printf("◎");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void GoMazeR(Position pos)
{
Position nextpos = pos;
//标记走过的位置
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 2;
system("cls");//打印前清屏
PrintMaze();
Sleep(300);//有间隔效果看起来会好一点
//当前是否走到出口
if (IsExit(pos))
{
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 1;
printf("找到出口了!\n");
return;
}
//没有走到出口,按照左上右下的顺序进行尝试
nextpos.y -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
GoMazeR(nextpos);
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x -= 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
GoMazeR(nextpos);
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.y += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
GoMazeR(nextpos);
}
nextpos = pos;
nextpos.x += 1;
if (CanPass(nextpos))
{
GoMazeR(nextpos);
}
//回溯之前把走过的路清空
maze[pos.x][pos.y] = 1;
}
void test()
{
Position entry = { 5,1 };
GoMazeR(entry);
}





 本文详细介绍三种迷宫寻路算法:单出口迷宫、多出口迷宫(不带环)及多出口迷宫(带环)。通过递归和栈结构实现路径寻找,展示如何在复杂迷宫中找到所有可能的出口。
本文详细介绍三种迷宫寻路算法:单出口迷宫、多出口迷宫(不带环)及多出口迷宫(带环)。通过递归和栈结构实现路径寻找,展示如何在复杂迷宫中找到所有可能的出口。
















 3217
3217

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








