文章目录
11 进程和线程
11.1 多进程
linux创建子进程:
import os
print('Process (%s) start...' % os.getpid())
# Only works on Unix/Linux/Mac:
pid = os.fork()
if pid == 0:
print('I am child process (%s) and my parent is %s.' % (os.getpid(), os.getppid()))
else:
print('I (%s) just created a child process (%s).' % (os.getpid(), pid))
运行:
Process (876) start...
I (876) just created a child process (877).
I am child process (877) and my parent is 876.
11.1.1 multiprocessing
启动一个子进程并等待其结束:
from multiprocessing import Process
import os
# 子进程要执行的代码
def run_proc(name):
print('Run child process %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
if __name__=='__main__':
print('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p = Process(target=run_proc, args=('test',))
print('Child process will start.')
p.start()
p.join()
print('Child process end.')
结果:
Parent process 928.
Process will start.
Run child process test (929)…
Process end.
11.1.2 Pool
进程池的方式批量创建子进程:
from multiprocessing import Pool
import os, time, random
def long_time_task(name):
print('Run task %s (%s)...' % (name, os.getpid()))
start = time.time()
time.sleep(random.random() * 3)
end = time.time()
print('Task %s runs %0.2f seconds.' % (name, (end - start)))
if __name__=='__main__':
print('Parent process %s.' % os.getpid())
p = Pool(4)
for i in range(5):
p.apply_async(long_time_task, args=(i,))
print('Waiting for all subprocesses done...')
p.close()
p.join()
print('All subprocesses done.')
Parent process 669.
Waiting for all subprocesses done…
Run task 0 (671)…
Run task 1 (672)…
Run task 2 (673)…
Run task 3 (674)…
Task 2 runs 0.14 seconds.
Run task 4 (673)…
Task 1 runs 0.27 seconds.
Task 3 runs 0.86 seconds.
Task 0 runs 1.41 seconds.
Task 4 runs 1.91 seconds.
All subprocesses done.
11.1.3 子进程
nslookup www.python.org:
import subprocess
print('$ nslookup www.python.org')
r = subprocess.call(['nslookup', 'www.python.org'])
print('Exit code:', r)
$ nslookup www.python.org Server: 192.168.19.4
Address: 192.168.19.4#53Non-authoritative answer: www.python.org canonical name =
python.map.fastly.net. Name: python.map.fastly.net Address:
199.27.79.223Exit code: 0
子进程还需要输入:
import subprocess
print('$ nslookup')
p = subprocess.Popen(['nslookup'], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
output, err = p.communicate(b'set q=mx\npython.org\nexit\n')
print(output.decode('utf-8'))
print('Exit code:', p.returncode)
上面的代码相当于在命令行执行命令nslookup,然后手动输入:
set q=mx
python.org
exit
11.1.4 进程间通信
在父进程中创建两个子进程,一个往Queue里写数据,一个从Queue里读数据:
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import os, time, random
# 写数据进程执行的代码:
def write(q):
print('Process to write: %s' % os.getpid())
for value in ['A', 'B', 'C']:
print('Put %s to queue...' % value)
q.put(value)
time.sleep(random.random())
# 读数据进程执行的代码:
def read(q):
print('Process to read: %s' % os.getpid())
while True:
value = q.get(True)
print('Get %s from queue.' % value)
if __name__=='__main__':
# 父进程创建Queue,并传给各个子进程:
q = Queue()
pw = Process(target=write, args=(q,))
pr = Process(target=read, args=(q,))
# 启动子进程pw,写入:
pw.start()
# 启动子进程pr,读取:
pr.start()
# 等待pw结束:
pw.join()
# pr进程里是死循环,无法等待其结束,只能强行终止:
pr.terminate()
运行结果:
Process to write: 50563
Put A to queue...
Process to read: 50564
Get A from queue.
Put B to queue...
Get B from queue.
Put C to queue...
Get C from queue.
11.2 多线程
启动一个线程:
import time, threading
# 新线程执行的代码:
def loop():
print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
n = 0
while n < 5:
n = n + 1
print('thread %s >>> %s' % (threading.current_thread().name, n))
time.sleep(1)
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name)
print('thread %s is running...' % threading.current_thread().name)
t = threading.Thread(target=loop, name='LoopThread')
t.start()
t.join()
print('thread %s ended.' % threading.current_thread().name)
11.2.1 Lock
创建一个锁:
balance = 0
lock = threading.Lock()
def run_thread(n):
for i in range(100000):
# 先要获取锁:
lock.acquire()
try:
# 放心地改吧:
change_it(n)
finally:
# 改完了一定要释放锁:
lock.release()
11.2.2 多核CPU
11.3 ThreadLocal
import threading
# 创建全局ThreadLocal对象:
local_school = threading.local()
def process_student():
# 获取当前线程关联的student:
std = local_school.student
print('Hello, %s (in %s)' % (std, threading.current_thread().name))
def process_thread(name):
# 绑定ThreadLocal的student:
local_school.student = name
process_student()
t1 = threading.Thread(target= process_thread, args=('Alice',), name='Thread-A')
t2 = threading.Thread(target= process_thread, args=('Bob',), name='Thread-B')
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
Hello, Alice (in Thread-A)
Hello, Bob (in Thread-B)
11.4 进程 vs. 线程
11.4.1 线程切换
11.4.2 计算密集型 vs. IO密集型
11.4.3 异步IO
11.5 分布式进程
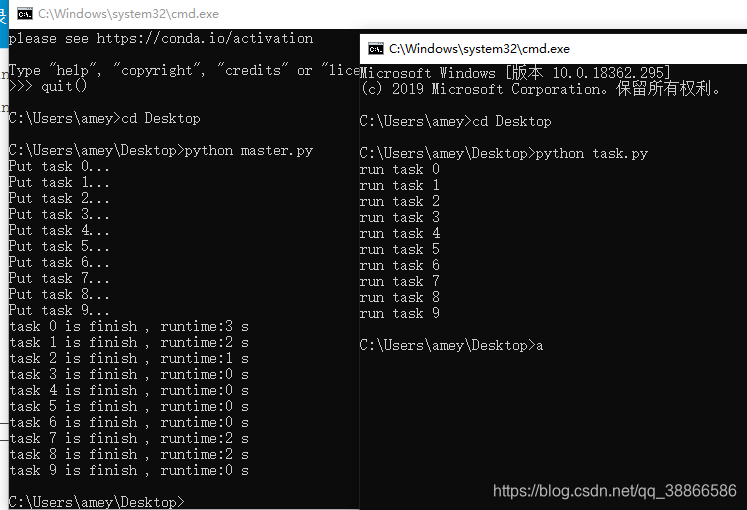
服务进程,服务进程负责启动Queue,把Queue注册到网络上,然后往Queue里面写入任务:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding : utf-8 -*-
# master.py for windows
import time, queue
from multiprocessing.managers import BaseManager
from multiprocessing import freeze_support
# 任务个数
task_number = 10;
# 定义收发队列
task_queue = queue.Queue(task_number);
result_queue = queue.Queue(task_number);
def gettask():
return task_queue;
def getresult():
return result_queue;
def test():
# windows下绑定调用接口不能使用lambda,所以只能先定义函数再绑定
BaseManager.register('get_task', callable=gettask);
BaseManager.register('get_result', callable=getresult);
# 绑定端口并设置验证码,windows下需要填写ip地址,linux下不填默认为本地
manager = BaseManager(address=('192.168.3.163', 5002), authkey=b'123');
# 启动
manager.start();
try:
# 通过网络获取任务队列和结果队列
task = manager.get_task();
result = manager.get_result();
# 添加任务
for i in range(task_number):
print('Put task %d...' % i)
task.put(i);
# 每秒检测一次是否所有任务都被执行完
while not result.full():
time.sleep(1);
for i in range(result.qsize()):
ans = result.get();
print('task %d is finish , runtime:%d s' % ans);
except:
print('Manager error');
finally:
# 一定要关闭,否则会爆管道未关闭的错误
manager.shutdown();
if __name__ == '__main__':
# windows下多进程可能会炸,添加这句可以缓解
freeze_support()
test();
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding : utf-8 -*-
# task.py for windows
import time, sys, queue, random
from multiprocessing.managers import BaseManager
BaseManager.register('get_task')
BaseManager.register('get_result')
conn = BaseManager(address=('192.168.3.163', 5002), authkey=b'123');
try:
conn.connect();
except:
print('连接失败');
sys.exit();
task = conn.get_task();
result = conn.get_result();
while not task.empty():
n = task.get(timeout=1);
print('run task %d' % n);
sleeptime = random.randint(0, 3);
time.sleep(sleeptime);
rt = (n, sleeptime);
result.put(rt);
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass;








 本文深入探讨了Python中进程和线程的实现方式,包括多进程的创建与管理,线程的启动与同步,以及进程间通信的方法。通过具体代码示例,详细讲解了multiprocessing模块的使用,如Pool的批量任务处理,子进程的调用,以及Queue的进程间数据传递。同时,介绍了多线程环境下Lock的使用和ThreadLocal的作用。
本文深入探讨了Python中进程和线程的实现方式,包括多进程的创建与管理,线程的启动与同步,以及进程间通信的方法。通过具体代码示例,详细讲解了multiprocessing模块的使用,如Pool的批量任务处理,子进程的调用,以及Queue的进程间数据传递。同时,介绍了多线程环境下Lock的使用和ThreadLocal的作用。
















 2056
2056

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








