目录
CORDIC(Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer)算法是一种用于计算三角函数、双曲函数和其他数学函数的迭代算法。它通过简单的移位和加法操作来实现复杂的数学计算,非常适合在FPGA中实现。本文将简要介绍CORDIC算法的原理,以及如何从CORDIC统一的方程式中得到计算sin、cos,反正切,开方,向量模长和相角,
1.CORDIC算法的原理

向量OA与单位圆的交点为 A(xa,ya) , 与正半轴的夹角记为α, xa,ya与α的关系为。
将向量OA逆时针旋转β角得到向量OB,欲求向量OB的坐标有
有
提取cosβ,有
当旋转角度满足条件1
有
向量的旋转进一步转化为转换为移位,相加和相乘。当我们用一系列的满足条件1的角度累加逼近我们输入的角度时候,我们所得到坐标值便逼近输入角度对应的正弦和余弦。满足条件1的角度及对应的正弦值为常数,因此可以将这些值固定在代码中以供算法实现。当我们将向量由相角零旋转至指定相角时,将根据旋转后的角度与指定的角度之间的大小关系确定旋转方向。当我们反过来将向量由指定相角旋转至相角零的时候,则讨论角度的正负。
又因为
因此满足条件1的角度的持续叠加并不能覆盖整个圆周,因此在使用cordic算法对角度进行逼近的时候,需要将角度偏转到能够表示的范围内。记处理至收敛后得到的坐标为(x0,yo), 假设角度范围为0~360,不同角度范围所做的处理及最终的坐标如下:
| 输入角度范围 | 处理方式 | 最终的坐标 |
| [0,90] | 无 | (x0, yo) |
| [90,180] | -90 | (-yo, x0) |
| [180,270] | -270 | (y0, -x0) |
| [270,360] | -360 | (x0, yo) |
2.CORDIC算法的matlab仿真
本小节先对cordic算法进行双精度数的仿真,当旋转角度与输入角度相等的时候,停止迭代
2.1 matlab双精度数仿真
xa = 1;
ya = 0;
theta = 70;
mini_theta = zeros(1024,1);
sin_70= sin(70/180*pi);
cos_70 = cos(70/180*pi);
%正切值为2^-n对应的角度
for i = 1:length(mini_theta)
mini_theta(i) = atan(2^(-(i-1)))/pi*180;
end
%正切值为2^-n对应的角度的余弦值
cos_mini_theta = zeros(1024,1);
for i = 1:length(mini_theta)
cos_mini_theta(i) = cos(mini_theta(i)/180*pi);
end
flag = 1; %方向判定
n = 0;
buffer = zeros(1024,7); %中间计算结果寄存
while(n<=1023)
n=n+1;
buffer(n,1)=theta;
buffer(n,2)=xa;
buffer(n,3)=ya;
cos_theta = cos(theta/180*pi);
buffer(n,4)=cos_theta;
sin_theta = sin(theta/180*pi);
buffer(n,5)=sin_theta;
buffer(n,6) =flag;
buffer(n,7) = cos_mini_theta(n);
%旋转方向判断
if(theta>0)
theta = theta - mini_theta(n);
flag = 1;
else
theta = theta + mini_theta(n);
flag = -1;
end
%坐标计算
xa_buffer = cos_mini_theta(n)*(xa - flag* ya*2^(-(n-1)));
ya_buffer = cos_mini_theta(n)*(ya + flag*xa*2^(-(n-1)));
xa = xa_buffer;
ya = ya_buffer;
dealt_sin = sin_70 - ya;
dealt_cos = cos_70 - xa;
buffer(n,8) = dealt_sin;
buffer(n,9) = dealt_cos;
end

上图显示了角度、正弦值、余弦值在迭代过程中的变化,可以看出当迭代次数到达16的时候,角度、正弦值、余弦值都很接近理论值 。当迭代次数固定的时候,可以将cordic 迭代方程中的cos项提取出来,省去与cos相乘的步骤
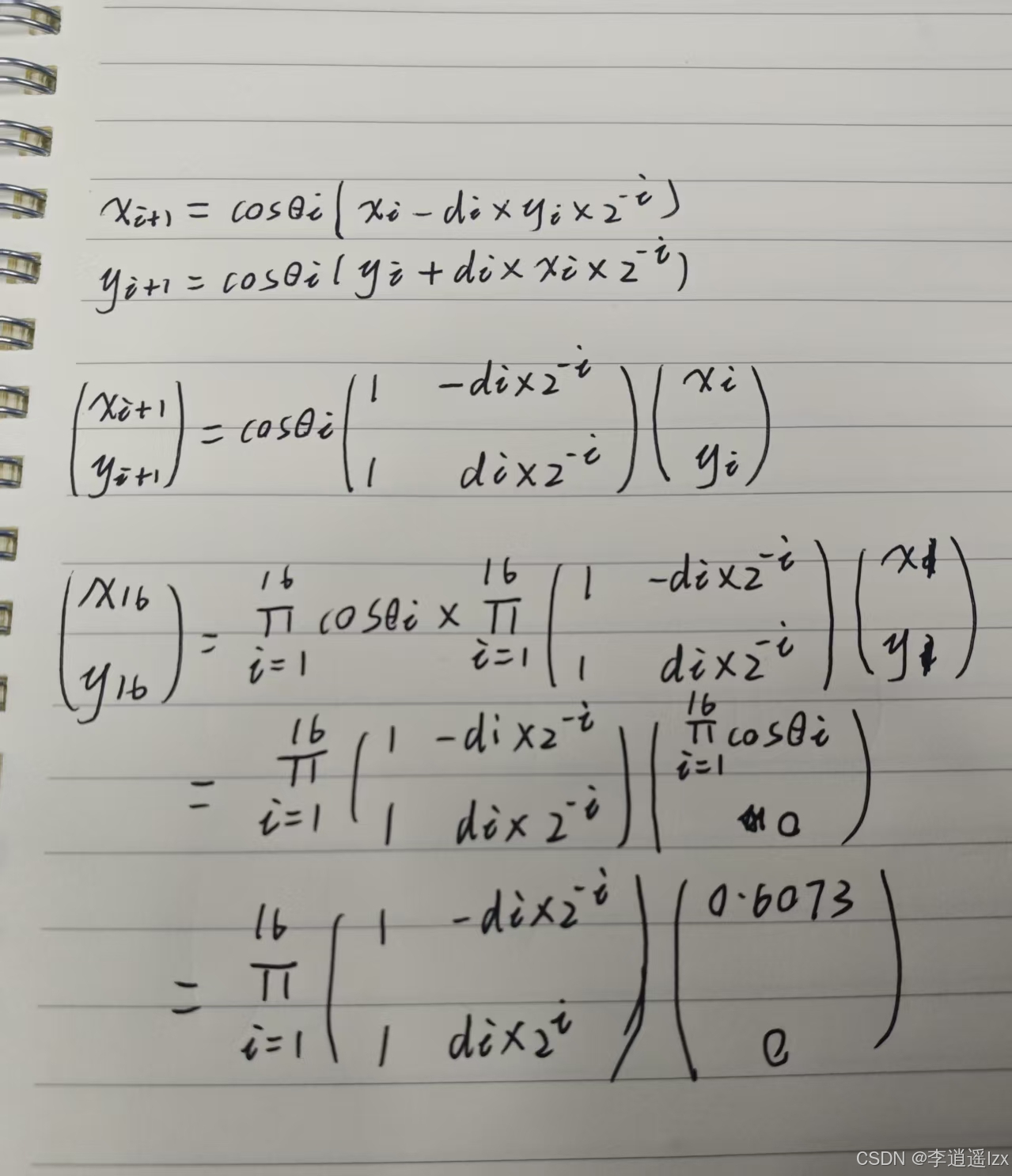
function [sin_o,cos_o] = cordic_cal(deg,num_of_iterration)
%UNTITLED2 此处提供此函数的摘要
% 此处提供详细说明
flag_cordinate = 0;
if deg > 90 && deg <=180
deg = deg - 90;
flag_cordinate = 1;
elseif deg >180 && deg <= 270
deg = deg -270;
flag_cordinate = 2;
elseif deg >270 && deg <= 360
deg = deg -360;
flag_cordinate = 3;
end
theta = zeros(num_of_iterration,1);
cos_theta =zeros(num_of_iterration,1);
for i = 1 :length(theta)
theta(i) = atan(2^(-(i-1)));
cos_theta(i) = cos(theta(i));
end
theta =theta/pi*180;
theta_initial = deg;
xa = 0.6073;
ya = 0;
buffer = zeros(1024,5);
n=1;
flag = 0;
while(n<num_of_iterration)
if theta_initial > 0
theta_initial = theta_initial - theta(n);
flag =1;
else
theta_initial = theta_initial + theta(n);
flag = -1;
end
xb = (xa -flag* ya/2^(n-1));
yb = (ya + flag*xa/2^(n-1));
xa = xb;
ya = yb;
n=n+1;
end
if flag_cordinate == 1
sin_o = xa;
cos_o = -ya;
elseif flag_cordinate == 2
sin_o = -xa;
cos_o = ya;
elseif flag_cordinate == 3
sin_o = ya;
cos_o = xa;
else
sin_o = ya;
cos_o = xa;
end测试
numn_of_iterration = 16;
theta = 0:1:360;
num_of_theta =7;
num_of_cos = 16;
num_of_cordinate = 16;
sin_o = zeros(length(theta),1);
cos_o = zeros(length(theta),1);
sin_standard = zeros(length(theta),1);
cos_standard = zeros(length(theta),1);
dealt_sin_ = zeros(length(theta),1);
dealt_cos = zeros(length(theta),1);
for i = 1 : length(theta)
sin_standard(i) = sin(theta(i)/180*pi);
cos_standard(i) = cos(theta(i)/180*pi);
theta(i) = floor(theta(i)*2^num_of_theta);
[sin_o(i),cos_o(i)] = cordic_cal_fixed_point(theta(i),numn_of_iterration,num_of_theta,num_of_cos,num_of_cordinate);
dealt_sin(i) = sin_standard(i) - sin_o(i)/2^num_of_cordinate;
dealt_cos(i) = cos_standard(i)- cos_o(i)/2^num_of_cordinate;
end
subplot(121);
plot(sin_o/2^num_of_cordinate,'r','LineWidth',0.5);
hold on
plot(cos_o/2^num_of_cordinate,'b','LineWidth',0.5);
xlabel('theta');
ylabel('amplitude');
legend('sin','cos');
grid on;
subplot(122)
plot(dealt_sin,'r','LineWidth',0.5);
hold on
plot(dealt_cos,'b','LineWidth',0.5);
xlabel('theta');
ylabel('amplitude');
legend('dealt\_sin','dealt\_cos');
grid on;
结果

2.2 matlab定点化仿真
function [sin_o,cos_o,buffer] = cordic_cal_fixed_point(deg,num_of_iterration,num_of_theta,num_of_cos,num_of_cordinate)
%UNTITLED2 此处提供此函数的摘要
% 此处提供详细说明
%角度坐标确定及处理
flag_cordinate = 0;
if deg > 90*2^num_of_theta && deg <=180*2^num_of_theta
deg = deg - 90*2^num_of_theta;
flag_cordinate = 1;
elseif deg >= 180*2^num_of_theta && deg < 270*2^num_of_theta
deg = deg - 270 *2^num_of_theta;
flag_cordinate = 2;
elseif deg >=270*2^num_of_theta
deg = deg - 360 *2^num_of_theta;
flag_cordinate = 3;
end
theta = zeros(num_of_iterration,1);
cos_theta =zeros(num_of_iterration,1);
%余弦
for i = 1 :length(theta)
theta(i) = atan(2^(-(i-1)));
cos_theta(i) = floor(cos(theta(i))*2^num_of_cos);
end
%初始化
theta =floor(theta/pi*180*2^num_of_theta);
theta_initial = deg;
xa =floor(0.6073*2^num_of_cordinate);
ya = 0;
buffer = zeros(1024,8);
n=1;
flag = 0;
theta1 = theta_initial/2^num_of_theta;
while(n<num_of_iterration)
buffer(n,1) = xa ;
buffer(n,2) = ya ;
buffer(n,3) = theta_initial ;
buffer(n,4) = flag;
if theta_initial< 0
theta_initial = theta_initial + theta(n);
flag =-1;
else
theta_initial = theta_initial - theta(n);
flag = 1;
end
xb = (xa -flag* ya/2^(n-1));
y_shift = ya/2^(n-1);
yb = (ya + flag*xa/2^(n-1));
x_shift = xa/2^(n-1);
buffer(n,5) = theta(n);
buffer(n,6) = y_shift;
buffer(n,7) = x_shift;
xa = xb;
ya = yb;
n=n+1;
buffer(n,8) = n;
end
if flag_cordinate == 0
sin_o = ya;
cos_o = xa;
elseif flag_cordinate == 1
sin_o = xa;
cos_o = -ya;
elseif flag_cordinate == 2
sin_o = -xa;
cos_o = ya;
elseif flag_cordinate ==3
sin_o = ya;
cos_o = xa;
end
测试代码
numn_of_iterration = 16;
theta = 0:1:360;
num_of_theta =7;
num_of_cos = 16;
num_of_cordinate = 16;
sin_o = zeros(length(theta),1);
cos_o = zeros(length(theta),1);
for i = 1 : length(theta)
theta(i) = floor(theta(i)*2^num_of_theta);
[sin_o(i),cos_o(i)] = cordic_cal_fixed_point(theta(i),numn_of_iterration,num_of_theta,num_of_cos,num_of_cordinate)
end
plot(sin_o,'r','LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(cos_o,'b','LineWidth',2);
xlabel('theta');
ylabel('amplitude');
legend('sin','cos');
grid on;
仿真结果

3.CORDIC算法的verilog实现
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module cordic(
input sys_clk ,
input rst ,
input i_theta_vld ,
input [15:0] i_theta ,
output reg signed [17:0] o_sin ,
output reg signed [17:0] o_cos ,
output reg cordic_tvld
);
//theta_in、cos、坐标小数部分位宽分别为7、16、16, 迭代次数为12
reg [17:0] cos_theta [11:0];
reg [15:0] theta [11:0];
//象限判定
reg [1:0] quadrant; //象限
//cordic 迭代
reg signed [15:0] theta_rotate ;
reg cal_en;
reg [3:0] cnt_iteration; //迭代次数
reg signed [17:0] cos_shift;
reg signed [17:0] sin_shift;
reg signed [17:0] sin;
reg signed [17:0] cos;
//输出有效标志
reg cal_en_r1;
wire neg_cal_en;
//固定系数准备
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
cos_theta[0] <= 46340;
cos_theta[1] <= 58617;
cos_theta[2] <= 63579;
cos_theta[3] <= 65029;
cos_theta[4] <= 65408;
cos_theta[5] <= 65504;
cos_theta[6] <= 65528;
cos_theta[7] <= 65534;
cos_theta[8] <= 65535;
cos_theta[9] <= 65535;
cos_theta[10] <= 65535;
cos_theta[11] <= 65535;
cos_theta[12] <= 65535;
end
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
theta[0 ] <= 5760;
theta[1 ] <= 3400;
theta[2 ] <= 1796;
theta[3 ] <= 912;
theta[4 ] <= 457;
theta[5 ] <= 229;
theta[6 ] <= 114;
theta[7 ] <= 57;
theta[8 ] <= 28;
theta[9 ] <= 14;
theta[10] <= 7;
theta[11] <= 3;
end
//角度象限判定
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
quadrant <= 'd0;
else if(i_theta_vld)begin
if(i_theta > 11520 && i_theta <=23040 )
quadrant <= 'd1;
else if( i_theta > 23040 && i_theta <= 34560)
quadrant <= 'd2;
else if( i_theta > 34560 )
quadrant <= 'd3;
else
quadrant <= 'd0;
end
end
//-------------------
//cordic 迭代
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
cnt_iteration <= 'd0;
else if(cal_en)
cnt_iteration <= cnt_iteration + 'd1;
else
cnt_iteration <= 'd0;
end
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
cal_en <= 'd0;
else if(i_theta_vld)
cal_en <= 'd1;
else if(cnt_iteration == 'd15)
cal_en <= 'd0;
end
//角度旋转
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
theta_rotate <= 'sd0;
else if(i_theta_vld)begin
if(i_theta > 11520 && i_theta <=23040 )
theta_rotate <= i_theta - 11520;
else if( i_theta > 23040 && i_theta <= 34560 )
theta_rotate <= i_theta - 34560;
else if(i_theta > 34560)
theta_rotate <= i_theta - 46080;
else
theta_rotate <= i_theta;
end
else if(cal_en)begin
if(theta_rotate[15])begin
theta_rotate <= theta_rotate + theta[cnt_iteration];
end
else begin
theta_rotate <= theta_rotate - theta[cnt_iteration];
end
end
else
theta_rotate <= theta_rotate;
end
//三角函数计算
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)begin
sin <= 'sd0;
cos <= 'sd0;
end
else if(i_theta_vld)begin
sin <= 'sd0;
cos <= 'sd39800;
end
else if(cal_en)begin
if(theta_rotate[15])begin
sin <= sin - cos_shift ;
cos <= cos + sin_shift;
end
else begin
sin <= sin + cos_shift ;
cos <= cos - sin_shift;
end
end
end
always@(*)begin
case(cnt_iteration)
0 : cos_shift <= cos;
1 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 1 ;
2 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 2 ;
3 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 3 ;
4 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 4 ;
5 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 5 ;
6 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 6 ;
7 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 7 ;
8 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 8 ;
9 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 9 ;
10 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 10;
11 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 11;
12 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 12;
13 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 13;
14 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 14;
15 : cos_shift <= cos >>> 15;
default : cos_shift <= cos;
endcase
end
always@(*)begin
case(cnt_iteration)
0 : sin_shift <= sin ;
1 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 1 ;
2 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 2 ;
3 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 3 ;
4 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 4 ;
5 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 5 ;
6 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 6 ;
7 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 7 ;
8 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 8 ;
9 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 9 ;
10 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 10;
11 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 11;
12 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 12;
13 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 13;
14 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 14;
15 : sin_shift <= sin >>> 15;
default : sin_shift <= sin;
endcase
end
//output
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
cal_en_r1 <= cal_en;
end
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)begin
o_sin <= 'sd0;
o_cos <= 'sd0;
end
else if(neg_cal_en)begin
case(quadrant)
0 : begin
o_sin <= sin;
o_cos <= cos;
end
1 : begin
o_sin <= cos;
o_cos <= -sin;
end
2 : begin
o_sin <= -cos;
o_cos <= sin;
end
3 : begin
o_sin <= sin;
o_cos <= cos;
end
default : begin
o_sin <= 'sd0;
o_cos <= 'sd0;
end
endcase
end
end
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
cordic_tvld <= neg_cal_en;
end
assign neg_cal_en = cal_en_r1 & ~cal_en;
endmodule
仿真
module tb_cordic(
);
reg sys_clk;
reg rst;
wire i_theta_vld;
wire [15:0] i_theta;
reg [8:0] theta;
// cordic Outputs
wire [17:0] o_sin;
wire [17:0] o_cos;
wire cordic_tvld;
initial begin
sys_clk = 0;
rst = 1;
#100
rst = 0;
end
reg [7:0] cnt ;
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
cnt <= 'd0;
else
cnt <= cnt + 'd1;
end
assign i_theta_vld = cnt == 8'hff;
always@(posedge sys_clk)begin
if(rst)
theta <= 'd0;
else if(i_theta_vld)begin
if(theta == 360)
theta <= 'd0;
else
theta <= theta + 'd1;
end
end
assign i_theta = theta*128;
always #10 sys_clk = ~sys_clk;
cordic u_cordic (
.sys_clk ( sys_clk ),
.rst ( rst ),
.i_theta_vld ( i_theta_vld ),
.i_theta ( i_theta ),
.o_sin ( o_sin ),
.o_cos ( o_cos ),
.cordic_tvld ( cordic_tvld )
);仿真结果

























 2406
2406

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








