问题:什么是好的决策规划
Behavior planner/Decision making
决定一个车辆动作行为的规划,安全、舒适;
E.g. change lane now or later, stick to left or right lane, stop/go for crosswalk intersection
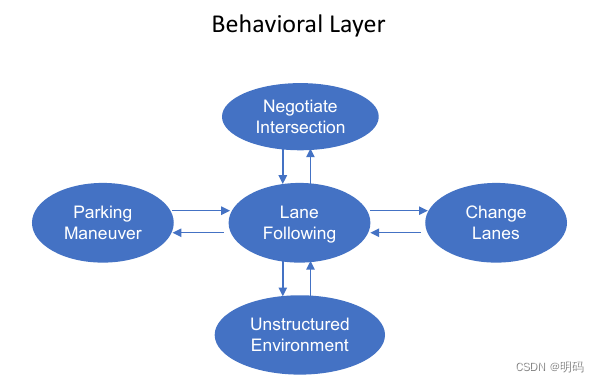
concept
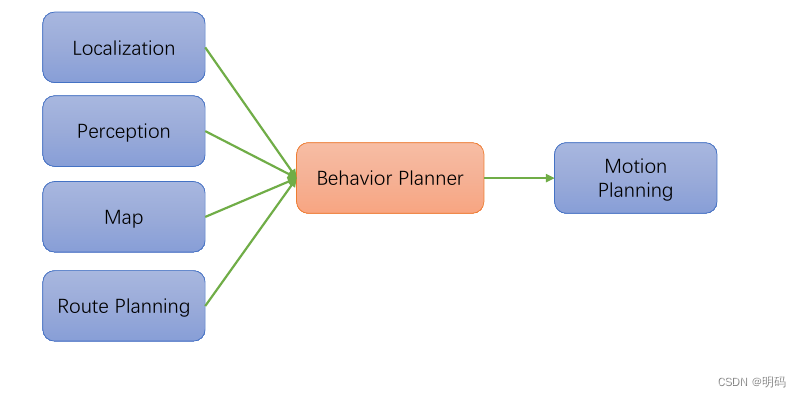
结构图
Mechanisms of enforcing a behavior
●Limit search to subset of feasible configuration space (e.g. c-space only extends to stop sign)
●Set a local goal (e.g. current cycle plan goal to stop at stop sign)
●Set constraints for trajectory optimization (e.g. speed equal to 0 at stop sign)
●Set costs for trajectory selection (e.g. penalize trajectory running a stop sign)
●Set fake obstacles (e.g. virtual obstacle to prevent motion beyond stop sign)
那么如何影响完备性呢?只搜索感知范围内的
Complete with respect to constrained problem, but not searching entire workspace
决策的目标
安全;舒适;操作富有经验
需要注意
Good Decision Attributes:
• Timely
• Account for the effect of our actions
• Account for the actions of others
• Reliable and repeatable
Functionality and Challenges

不确定性三方面
模型,感知,行为的不确定性

Localization
• Where am I now?
Control
• Where will I be later? Tracking error (lateral, longitudinal, speed, heading)
Perception
• Current world state
• Other agent position, size, velocity, type
• Traffic light status
Prediction
• Future world state
• Uncertainty increases dramatically as function of time horizon
Visibility Limitation / Occupancy Likelihood
• Is there someone/something relevant that I can’t see?
• Also prediction of non-visible world evolution (other agent, traffic light)
Common method
Rule bases:
•FSM 有限状态机
•Behaviour Tree
•Minimum Violation Planning最小违规
•Formal methods
• etc
Machine Learning based:
•Reinforcement learning;
•CNN
•Deep learning
•Decision Tree
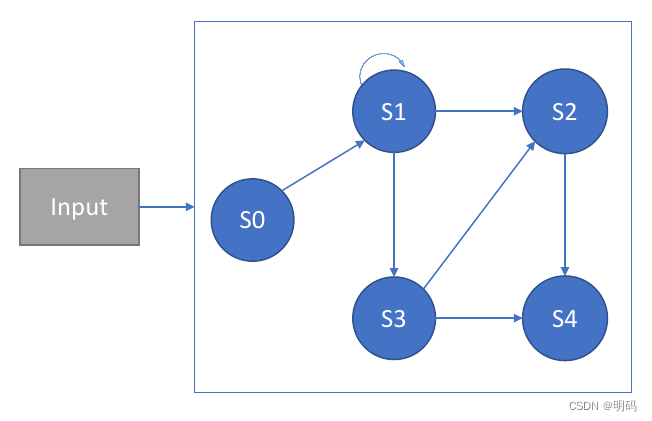
Finite State Machine
• Accepting State:
No transitions to other states
• Transition Function:
Uses input to decide what transition to make
输入组合
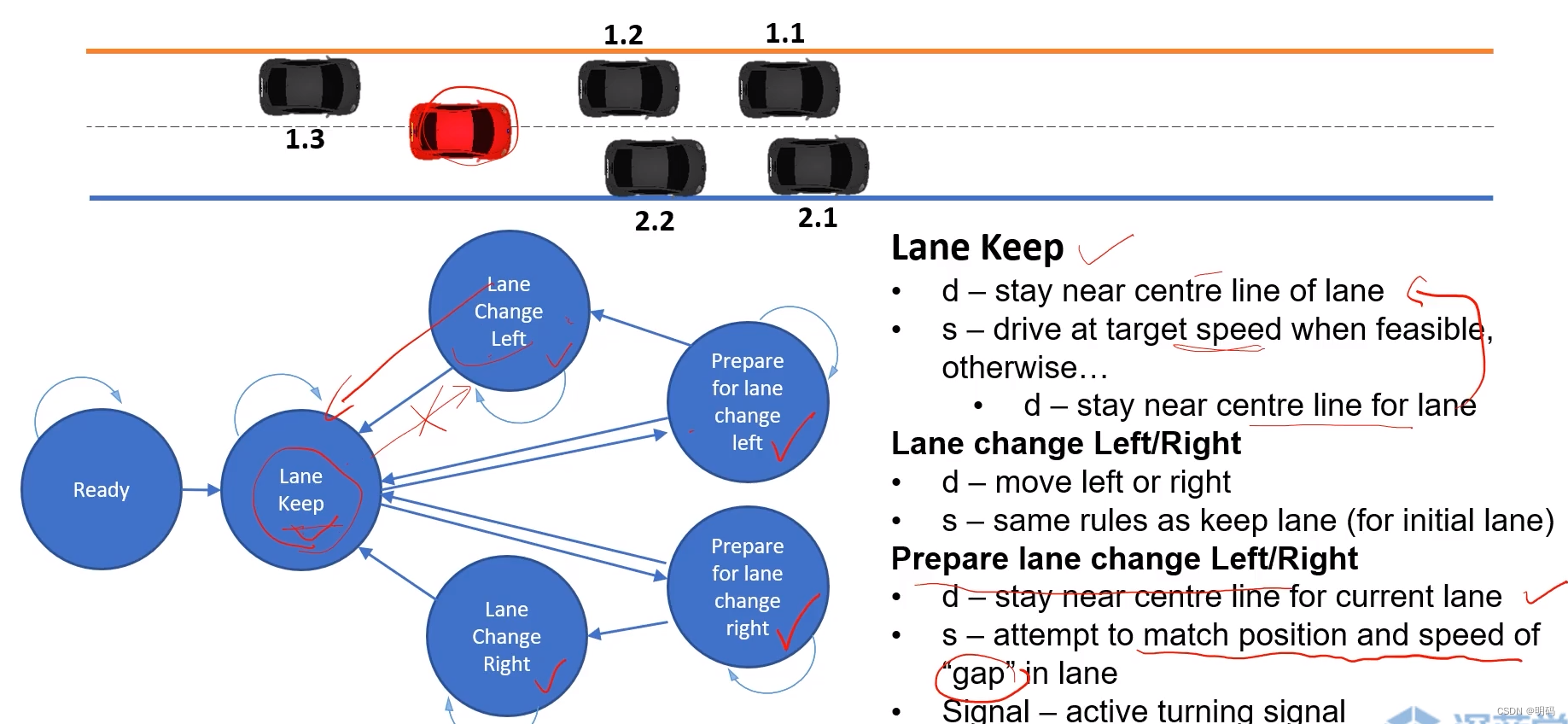
变道与车道保持
完成任务
Finite State Machine to select high level “maneuver”, possibly with dedicated planner
E.g. switch to parking mode to do reverse maneuver for parking
• These may dictate(决定) local goals, or even completely different underlying algorithms
• Important to verify no undesirable properties in large and/or hierarchical (分层)FSM, eg deadlock, livelock, unreachable states
通过代价函数评判是否启动状态转移
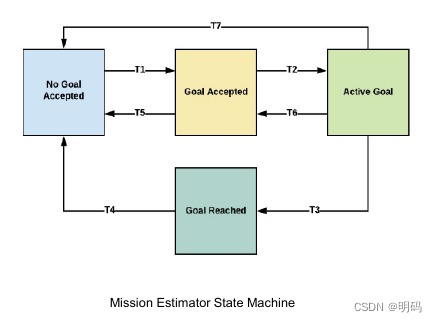
Stanford’s DUC 2007 Behavior FSM (link)
并行FSM
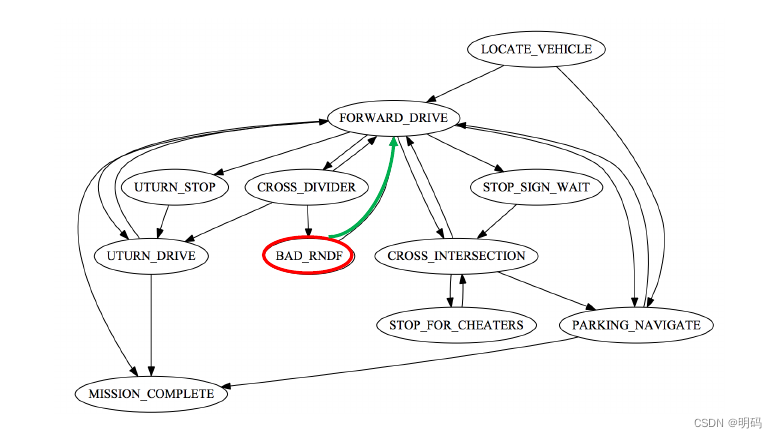
UTURN_STRO ,U形掉头时暂停
BAD_RNDF: 如果CROSS_DIVIDER失败时调用,使用hybrid A*在结构化道路进行导航
分层FSM
同一类型状态机组合成一个大类(超级状态)
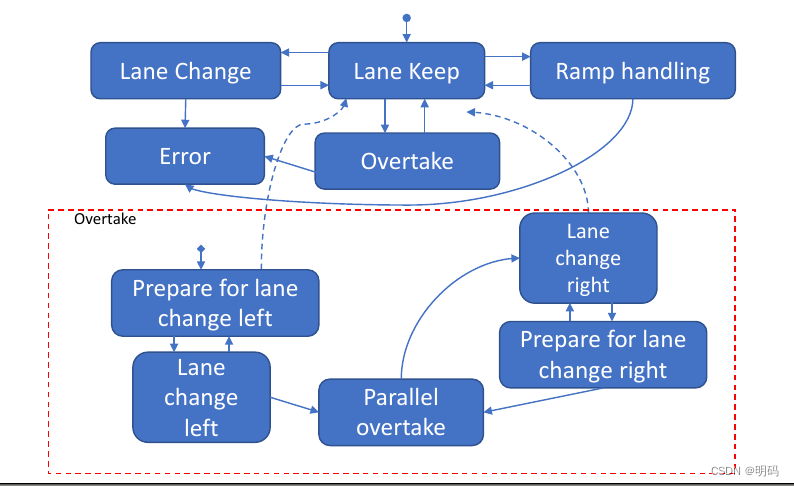
有时状态很多的时候,难以理解为何这样做
可维护性差,当需要对FSM改动时,其他状态变换可能改变
由于状态有明确的定义,这导致其可移值性变差。
Behavior Tree
T
行为树被表述为具有树结构的有向图,并具有以下内容特征:
行为树是树:它们从根节点开始,被设计为按照一个特定顺序进行遍历,直到达到最终状态(成功或失败)。
叶节点是可执行的行为:每个叶都会做一些事情,无论是简单的检查或复杂的操作,并会输出一个状态(成功、失败或运行)。换句话说,叶节点是 BT 连接特定应用底层代码的地方。
内部节点控制树遍历:树的内部(非叶子)节点将接受他们孩子的结果状态,并应用他们自己的规则来决定哪个节点应该是接下来被扩展。
• There are 6 basic types of nodes that make up behaviour trees and they are represented
graphically:
• Behavior trees execute in discrete update steps known as ticks.
• After a node ticks, it returns a status to its parent, which can be Success, Failure, or Running.
节点分为两大类,控制与执行
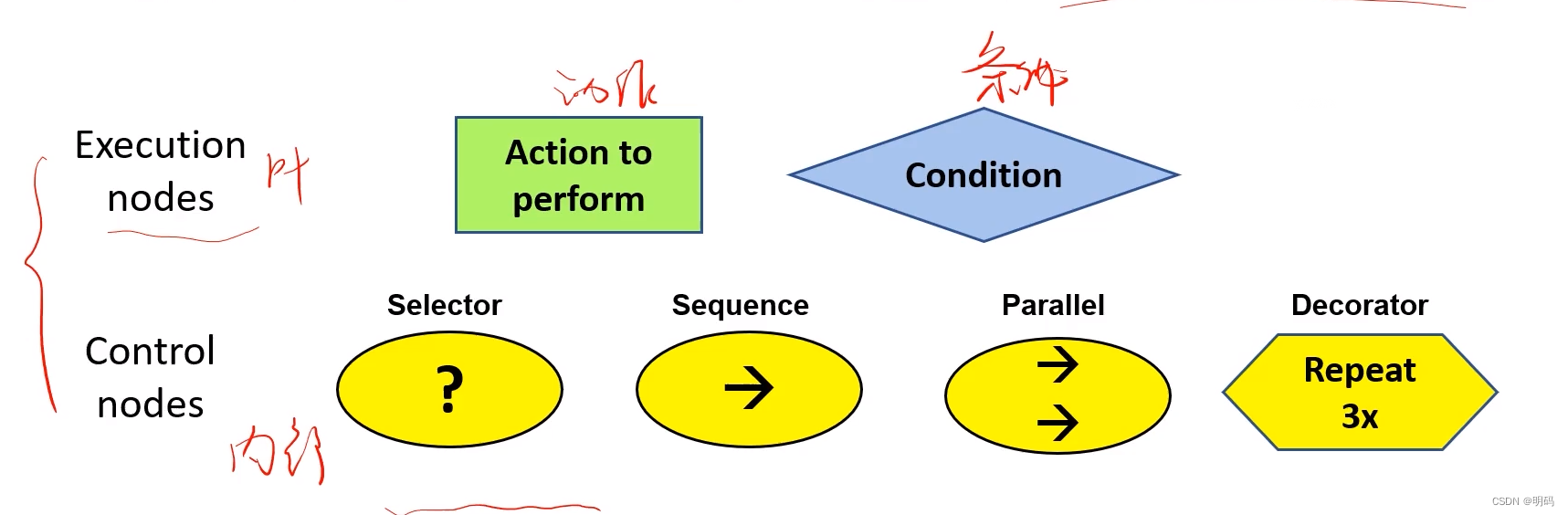
• Action nodes are the leaves of the trees
• It performs a task and returns Success if the action is completed, Failure if the task could not be completed, and Running while the task is being performed.
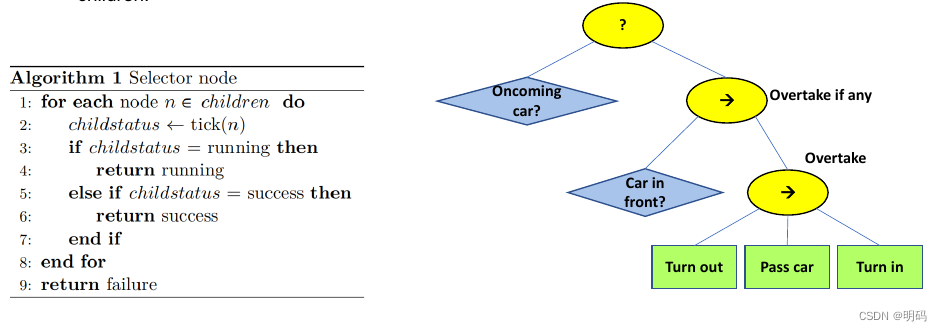
超车e.g
动作顺序
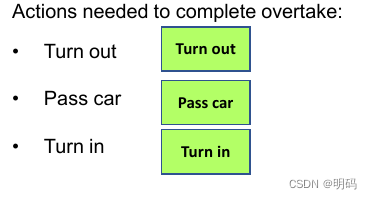
Sequence node
Y:确保子节点按顺序执行
A sequence node ticks its children in sequence, trying to ensure that a number of sequential tasks are all performed.
If any child return failure, the sequence has failed and it will propagate up.
The sequence node only returns success if all children succeed.

Condition node
蓝色节点,确定是否满足超车条件
检查是否安全执行
• The Condition node is analogous to a simple if-statement.
• If the conditional check is true, the node returns Success and Failure if false.
• A Condition node will never return a Running status.
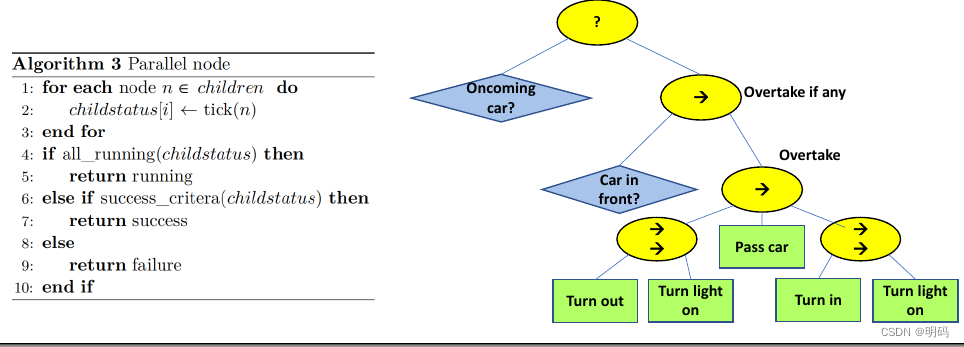
Parallel node
并行执行子节点
A parallel node ticks all its children at the same time, allowing several Action nodes to enter a running state at the same time.
The requirement for how many children need to succeed before the Parallel node itself reports success/failure can be customized on a per-instance basis.
Decorator node
• The decorator node wraps(封装) the functionality of the underlying(底层) child or subtree.
• It can for example influence the behavior of the underlying node(s) or modify the return state.
• E.g.
• Inverter: flip the return status of its child from Success to Failure and vice versa.
• Repeat: repeat the task multiple times
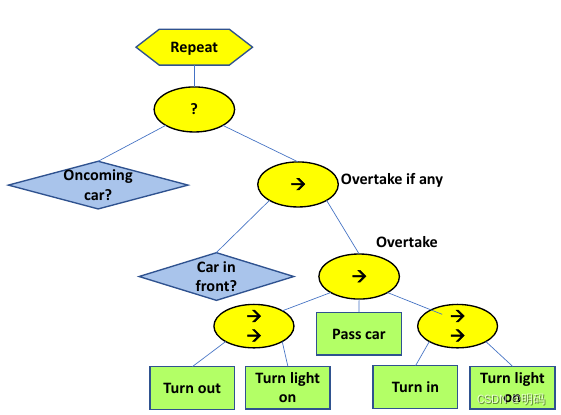
整个超车行为树
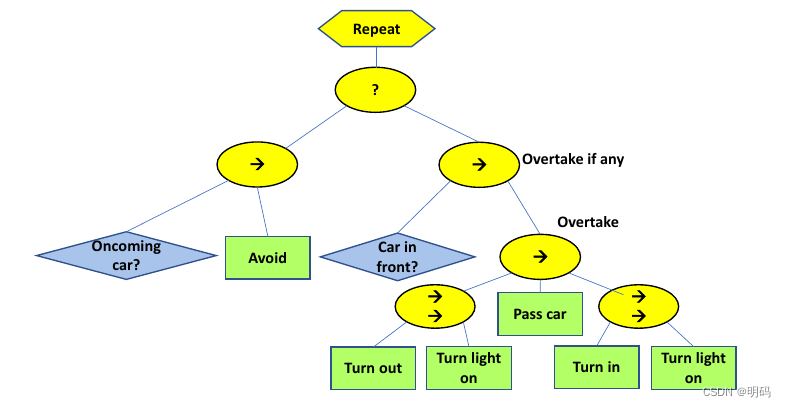
Behavior Trees vs. Finite State Machine
• In theory, it is possible to express anything as a BT, FSM, one of the other abstractions, or as plain code. However, each model has its own advantages and disadvantages in their intent to aid design at larger scale.
• Specific to BTs vs. FSMs, there is a tradeoff between modularity(模块化) and reactivity(反应性). Generally , BTs are easier to compose and modify while FSMs have their strength in designing reactive behaviors
以超车为例
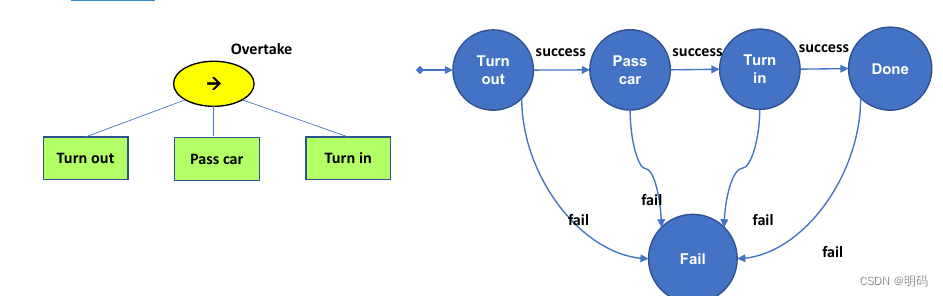
如果我们需要判断被超车车辆是否够快行为
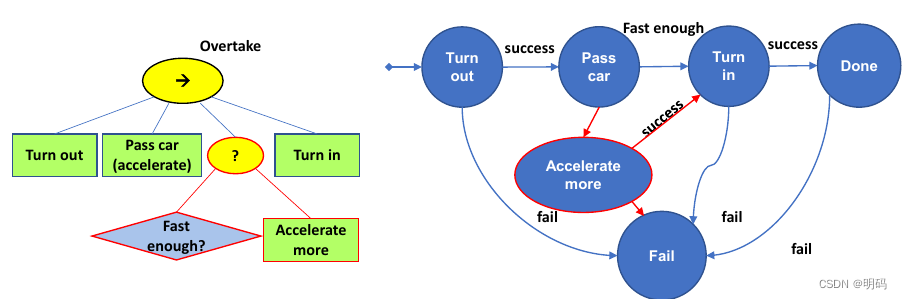
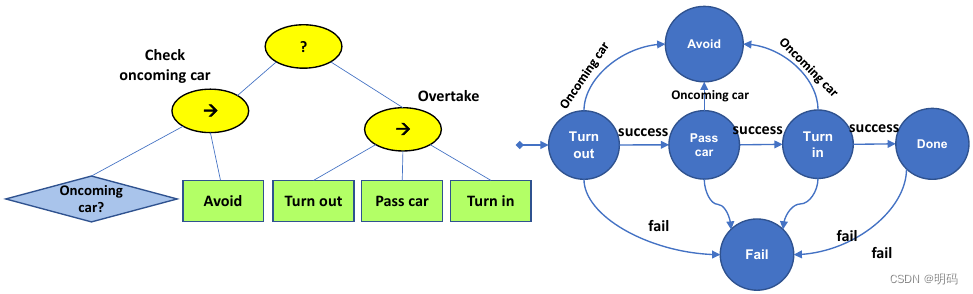
行为树的修改更加方便
但不够reactive, 比如如果判断能够超车,那行为树直接跳到overtake 节点,后面没有再去检查后车,而FSM能够方便地进行判断








 本文探讨了自动驾驶车辆的决策规划,强调安全和舒适性的重要性。介绍了行为规划的机制,如限制配置空间搜索、设定局部目标和约束等。同时,提到了决策的及时性、对自身和他人行动的考虑以及可靠性和可重复性。文章对比了有限状态机(FSM)和行为树(Behavior Tree)在处理复杂决策时的优缺点,指出行为树在修改和组合行为时更具优势,而FSM则擅长于设计反应性行为。超车行为作为案例,说明了行为树的修改便利性。关键词涉及自动驾驶、决策规划、行为树、有限状态机和安全性。
本文探讨了自动驾驶车辆的决策规划,强调安全和舒适性的重要性。介绍了行为规划的机制,如限制配置空间搜索、设定局部目标和约束等。同时,提到了决策的及时性、对自身和他人行动的考虑以及可靠性和可重复性。文章对比了有限状态机(FSM)和行为树(Behavior Tree)在处理复杂决策时的优缺点,指出行为树在修改和组合行为时更具优势,而FSM则擅长于设计反应性行为。超车行为作为案例,说明了行为树的修改便利性。关键词涉及自动驾驶、决策规划、行为树、有限状态机和安全性。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








