2.2 类体内定义成员函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time
{
public:
void set_time(){
cin>>hour>>minute>>sec;
}
void show_time(){
cout<<hour<<':'<<minute<<':'<<sec<<endl;
}
private:
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
};
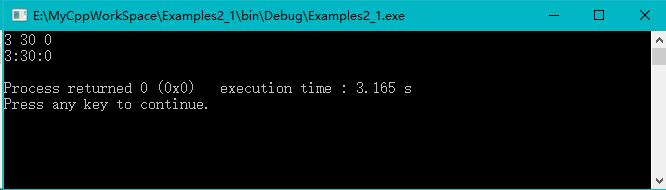
int main()
{
Time t;
t.set_time();
t.show_time();
return 0;
}
2.3 改写2.2:类体内声明成员函数,类外定义成员函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time
{
public:
void set_time();
void show_time();
private:
int hour;
int minute;
int sec;
};
void Time::set_time(){
cin>>hour>>minute>>sec;
}
void Time::show_time(){
cout<<hour<<':'<<minute<<':'<<sec<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Time t;
t.set_time();
t.show_time();
return 0;
}
2.4 在本章第2.3.3节中分别给出了包含类定义的头文件student.h,包含成员函数定义的源文件student.cpp以及包含主函数的源文件main.cpp。请完善该程序,在类中增加一个对数据成员赋初值的成员函数set_value。
1.先创建student.h头文件

#ifndef STUDENT_H_INCLUDED
#define STUDENT_H_INCLUDED
//student.h头文件。在这里只进行声明变量和函数,不进行定义
class Student
{
public:
void display( );
void set_value();
private:
int num;
char name[20];
char sex;
};
#endif // STUDENT_H_INCLUDED
2.创建student.cpp
#include <E:\MyCppWorkSpace\Examples2_4\student.h>//导入student.h头文件,切记,需加上绝对地址
#include <iostream>
//输入变量和函数定义
using namespace std; //不要漏写此行
void Student::display( )
{
cout<<"num:"<<num<<endl;
cout<<"name:"<<name<<endl;
cout<<"sex:"<<sex<<endl;
}
void Student::set_value()
{
cin>>num;
cin>>name;
cin>>sex;
}
student.h的绝对地址:

3.创建main函数
#include <iostream>
#include <E:\MyCppWorkSpace\Examples2_4\student.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Student stud;
stud.set_value();
stud.display();
return 0;
}
文件关系图:

运行结果:

2.6 需要求3个长方柱的体积,请编一个基于对象的程序。数据成员包括length、width、height。要求用成员函数实现以下功能:
1. 由键盘分别输入3个长方柱的长、宽、高;
2. 计算长方柱的体积;
3. 输出3个长方柱的体积。
请编程序,上机调试并运行。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class cubeVolume
{
private:
int length;//长
int width;//宽
int height;//高
int volume;//体积
public:
void set_volume();
void cal_volume();
void show_colume();
};
void cubeVolume::set_volume()
{
cout << "L:"; cin >> length;
cout << "W:"; cin >> width;
cout << "H:"; cin >> height;
}
void cubeVolume::cal_volume()
{
volume = length * height * width;
}
void cubeVolume::show_colume()
{
cout << "The volume is " << volume << endl;
}
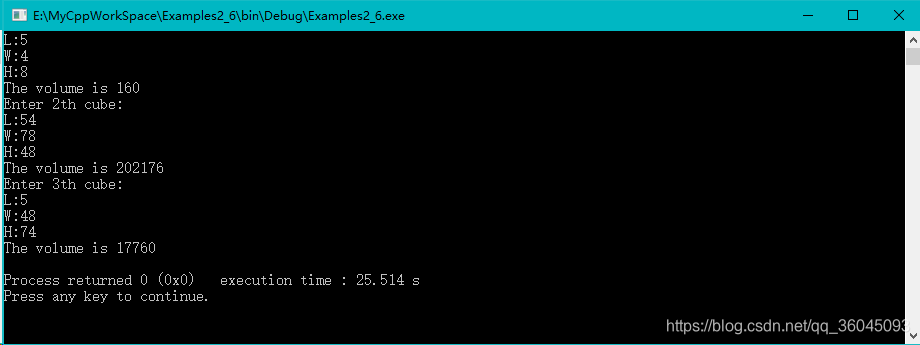
int main()
{
cubeVolume cube[3];
int i;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
{
cout << "Enter " << i+1 << "th cube:" << endl;
cube[i].set_volume();
cube[i].cal_volume();
cube[i].show_colume();
}
return 0;
}








 本文详细介绍C++中类的定义与使用,包括成员函数的内联与外联定义,通过实例展示如何创建并操作类对象,实现数据的输入、显示及计算功能。
本文详细介绍C++中类的定义与使用,包括成员函数的内联与外联定义,通过实例展示如何创建并操作类对象,实现数据的输入、显示及计算功能。

















 1703
1703

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










