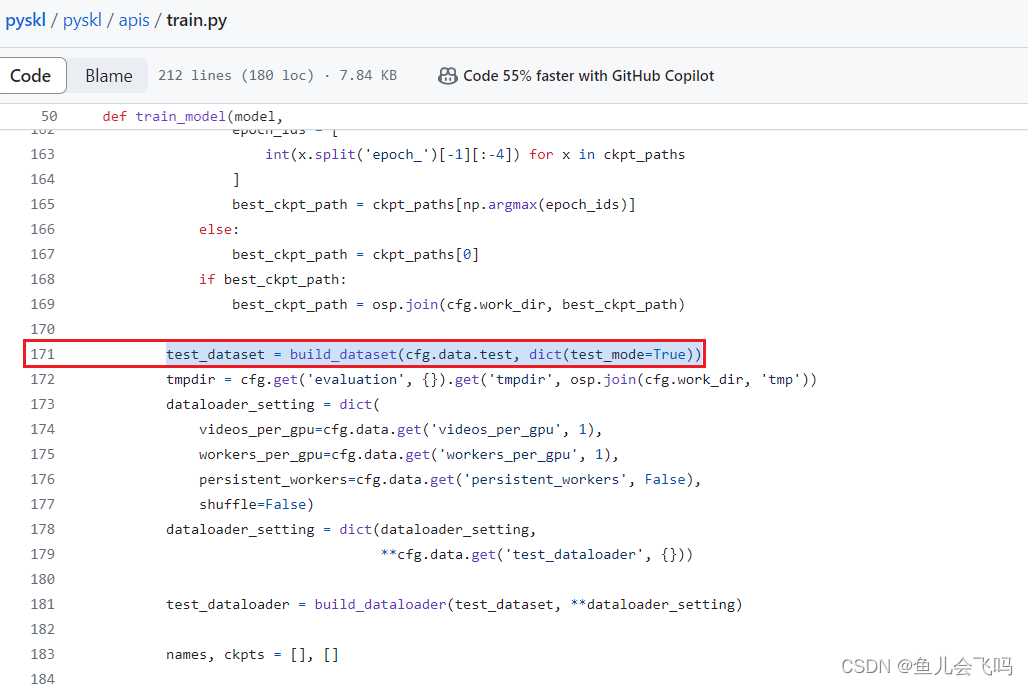
build_dataset 是一个函数,它接受两个参数:cfg.data.test 和 dict(test_mode=True)。它返回一个名为 test_dataset 的数据集对象。
根据函数的命名和参数推测,build_dataset 函数用于构建测试数据集。它使用 cfg.data.test 参数来配置测试数据集的相关设置,并使用 dict(test_mode=True) 参数来设置测试模式为真(True)。
具体的数据集构建过程和返回的数据集对象的类型会根据实际实现而有所不同。通常情况下,数据集对象可能是一个自定义的数据集类的实例,该类继承自 PyTorch 中的 torch.utils.data.Dataset 类,或者是其他类似的数据集对象。
通过执行提供的代码,将使用相应的参数配置构建测试数据集,并将结果存储在 test_dataset 变量中,以供后续使用。
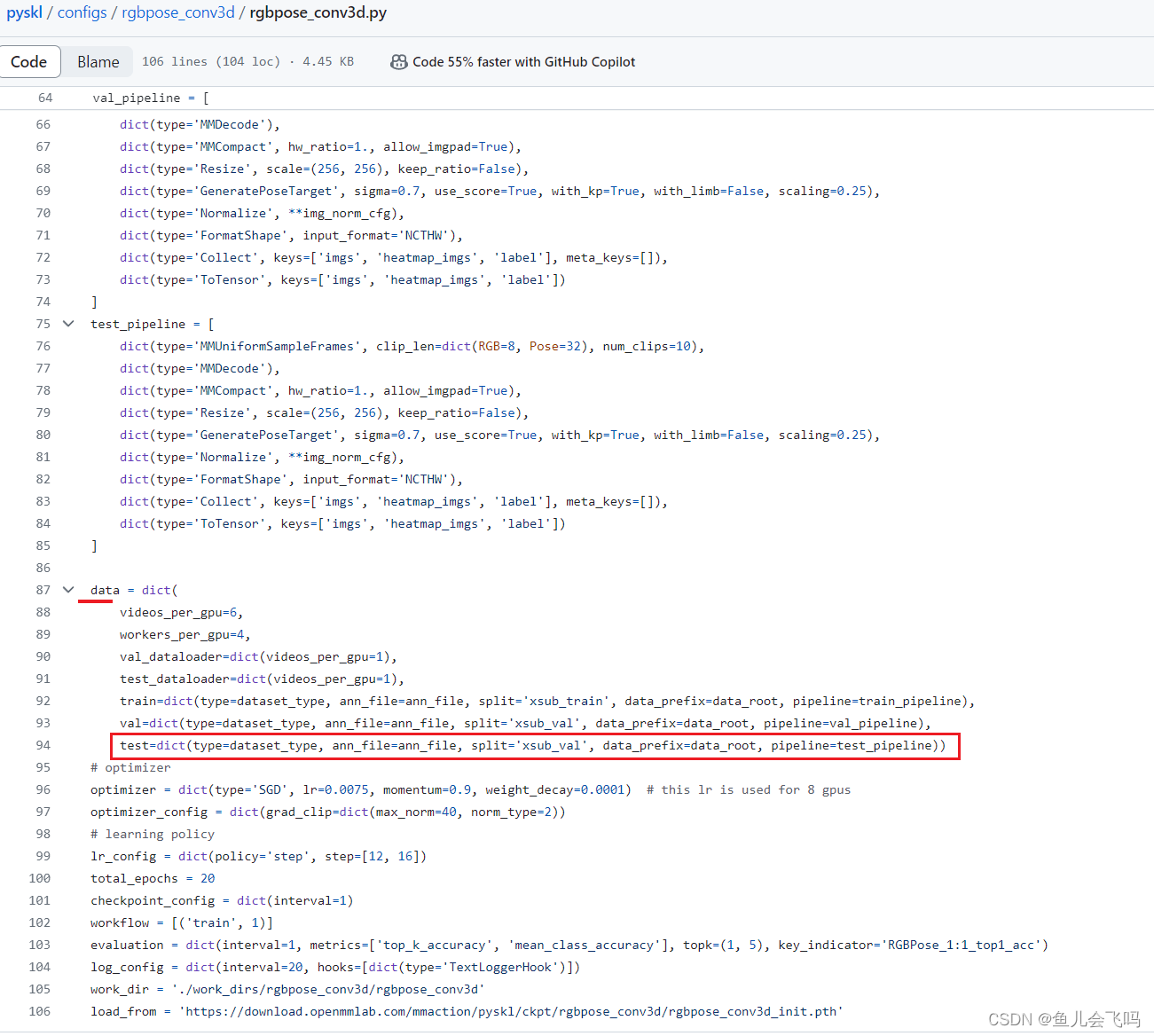
这行代码定义了一个名为 test 的字典,包含了一些用于测试的配置信息。这些配置信息包括:
type:数据集类型,存储在变量dataset_type中。ann_file:注释文件的路径,存储在变量ann_file中。split:数据集的划分方式,这里设置为'xsub_val'。data_prefix:数据集文件的前缀路径,存储在变量data_root中。pipeline:数据处理的管道,存储在变量test_pipeline中。
这些配置信息通常用于指定要使用的数据集、注释文件以及数据处理的方式。具体的数据集类型、注释文件路径、数据集划分、数据前缀路径和数据处理管道的内容将根据实际设置进行相应的配置。
通过将这些配置信息放在 test 字典中,可以方便地将其传递给其他函数或方法,以便构建和处理测试数据集。
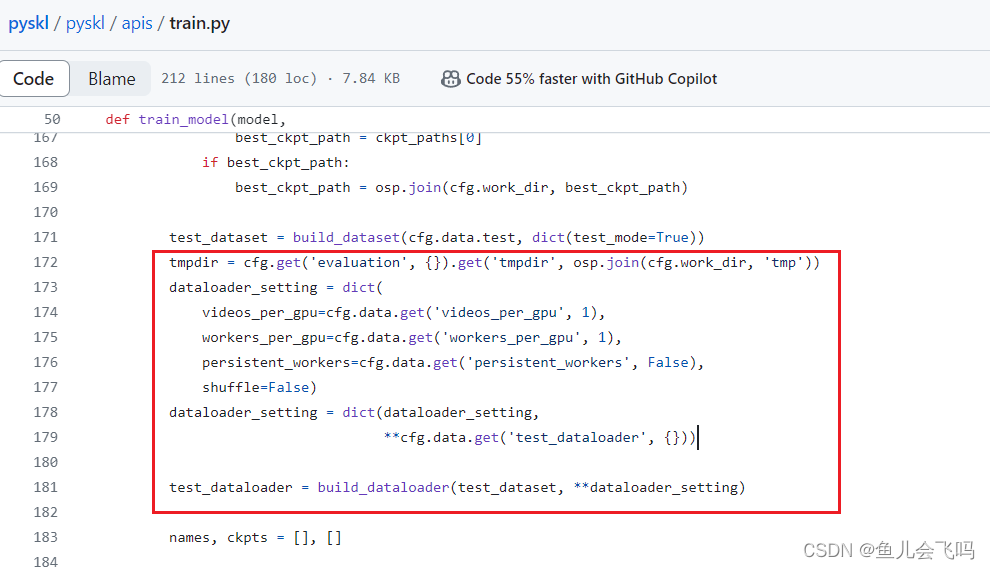
逐行解释:
-
tmpdir = cfg.get('evaluation', {}).get('tmpdir', osp.join(cfg.work_dir, 'tmp')):
从配置文件cfg中获取evaluation对应的字典,然后获取其中的tmpdir键对应的值。如果没有找到该键,则使用默认值osp.join(cfg.work_dir, 'tmp'),即将工作目录路径与'tmp'字符串拼接作为临时目录的路径,并将结果存储在tmpdir变量中。 -
dataloader_setting = dict(videos_per_gpu=cfg.data.get('videos_per_gpu', 1), workers_per_gpu=cfg.data.get('workers_per_gpu', 1), persistent_workers=cfg.data.get('persistent_workers', False), shuffle=False):
创建一个字典dataloader_setting,包含用于配置数据加载器的设置。这些设置包括:videos_per_gpu:每个GPU加载的视频数量,默认为1。workers_per_gpu:每个GPU分配的数据加载器线程数,默认为1。persistent_workers:是否持续使用加载器线程,默认为False。shuffle:是否对数据进行洗牌,默认为False(即不洗牌)。
-
dataloader_setting = dict(dataloader_setting, **cfg.data.get('test_dataloader', {})):
从配置文件cfg的data字典中获取test_dataloader对应的字典,将其与dataloader_setting合并为一个新的字典,并将结果重新赋值给dataloader_setting。这样可以通过配置文件覆盖默认的数据加载器设置。 -
test_dataloader = build_dataloader(test_dataset, **dataloader_setting):
使用build_dataloader函数构建测试数据加载器。它接受一个数据集对象test_dataset和一系列关键字参数dataloader_setting,这些参数将被传递给数据加载器构造函数。最终,构建的数据加载器将存储在test_dataloader变量中。
通过执行上述代码,根据配置文件中的设置和默认值,构建了用于测试的数据加载器,并将其存储在 test_dataloader 变量中,以供后续使用。
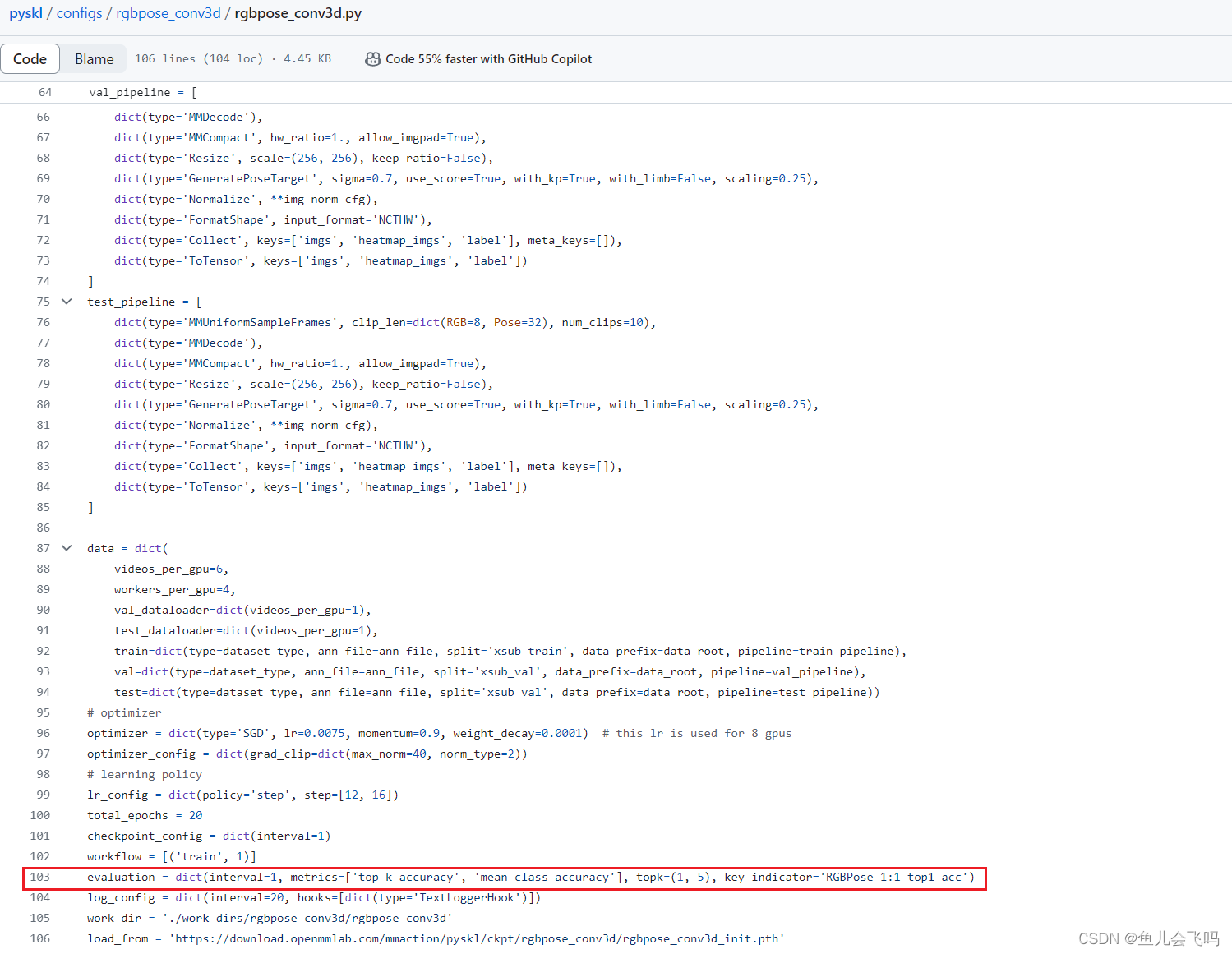

videos_per_gpu=cfg.data.get('videos_per_gpu', 1),发现data字典,里面videos_per_gpu键的值是6
videos_per_gpu 的值是从配置文件的 data 字典中获取的,如果该键不存在,则默认值为 1。然而,你提到在 data 字典中,videos_per_gpu 键的值为 6。
因此,在这段代码中,videos_per_gpu 的值将是 6,因为它是从配置文件的 data 字典中获取的。这意味着每个 GPU 将加载并处理 6 个视频。
这种配置方式允许你在配置文件中灵活地调整每个 GPU 处理的视频数量,以适应你的计算资源和模型训练需求。在这种情况下,使用了配置文件中的值 6 来覆盖默认值 1。
https://github.com/kennymckormick/pyskl/blob/main/pyskl/apis/train.py























 1387
1387

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








