215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
输出: 5
示例 2:
输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4
输出: 4
说明:
你可以假设 k 总是有效的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组的长度。
解题:
思路1:python自带的函数
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
return sorted(nums)[-k]
思路2:冒泡法:用python写冒泡法是和耗时的
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums)
t = n
if n/2>k:
for i in range(k):
for j in range(1,t):
if nums[j-1]>nums[j]:
nums[j-1],nums[j]=nums[j],nums[j-1]
t-=1
return nums[-k]
else:
for i in range(n-k+1):
print(t,nums)
for j in range(1,t):
if nums[j-1]<nums[j]:
nums[j-1],nums[j]=nums[j],nums[j-1]
t-=1
return nums[-n+k-1]
结果:执行用时: 1792 ms, 在Kth Largest Element in an Array的Python3提交中击败了11.04% 的用户
其他思路:用快速选择算法会更加减少空间和时间复杂度
88. 合并两个有序数组
给定两个有序整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,将 nums2 合并到 nums1 中,使得 num1 成为一个有序数组。
说明:
初始化 nums1 和 nums2 的元素数量分别为 m 和 n。
你可以假设 nums1 有足够的空间(空间大小大于或等于 m + n)来保存 nums2 中的元素。
示例:
输入:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
输出: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
解题:
思路1,直接利用python自带的排序函数
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1, m, nums2, n):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type m: int
:type nums2: List[int]
:type n: int
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
if n>0:
nums1[:] = sorted(nums1[:-n]+nums2)
结果:执行用时: 48 ms, 在Merge Sorted Array的Python3提交中击败了82.77% 的用户
思路2:
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1, m, nums2, n):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type m: int
:type nums2: List[int]
:type n: int
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums1 in-place instead.
"""
i =m+n-1
i1=m-1
i2=n-1
while i1>=0 and i2>=0:
while i1>=0 and nums1[i1]>=nums2[i2]:
nums1[i]=nums1[i1]
i1-=1
i-=1
if i1>=0:
while i2>=0 and nums2[i2]>=nums1[i1]:
nums1[i]=nums2[i2]
i2-=1
i-=1
if i1>=0:
nums1[:i+1] = nums1[:i1+1]
if i2>=0:
nums1[:i+1] = nums2[:i2+1]
结果:执行用时: 44 ms, 在Merge Sorted Array的Python3提交中击败了99.73% 的用户
80:删除排序数组中的重复项 II
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素最多出现两次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
示例 1:
给定 nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3],
函数应返回新长度 length = 5, 并且原数组的前五个元素被修改为 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 。
解题:
思路1:与题26相似,只是多了一个计算重复次数的标志
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n=len(nums)
if n<=2:
return n
else:
k=0
c1=True
for i in range(1,n):
if nums[i]==nums[k]:
if c1:
k+=1
nums[k]=nums[i]
c1=False
else:
k+=1
nums[k]=nums[i]
c1=True
return k+1
思路2:这是我参考的,很巧妙,只要是和前面第二个不同则为新的值
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
i = 0
for e in nums:
if i < 2 or e != nums[i - 2]:
nums[i] = e
i += 1
return i
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
26:删除排序数组中的重复项
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
示例 1:
给定数组 nums = [1,1,2],
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且原数组 nums 的前两个元素被修改为 1, 2。
你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
解题:已经是排好序的数列,则不担心[1,1,2,1]的情况,按顺序如果不和前面的数相等,则为新值
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n=len(nums)
if n==0:
return 0
else:
k=0
for i in range(1,n):
if nums[i] >nums[k]:
k+=1
nums[k]=nums[i]
return k+1
704:二分查找
给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
输出: 4
解释: 9 出现在 nums 中并且下标为 4
解题,二分查找思想
class Solution:
def search(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
l = len(nums)
if l==0:
return -1
head = 0
tail = l-1
while tail>=head:
i = (head+tail)//2
if nums[i]==target:
return i
elif nums[i]<target:
head = i+1
else:
tail = i-1
return -1
75:颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 n 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
此题中,我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
注意:
不能使用代码库中的排序函数来解决这道题。
示例:
输入: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
输出: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
解题:
思路一,顺序遍历,如果为2,往后放,为0 ,往前放,,执行用时56 ms
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
tail = len(nums)-1
head = 0
i = 0
while i<=tail:
if nums[i]<1:
if i ==head:
i+=1
continue
else:
nums[i],nums[head]=nums[head],nums[i]
head+=1
elif nums[i]>1:
nums[i],nums[tail]=nums[tail],nums[i]
tail-=1
else:
i+=1
思路2,摇摆遍历,执行用时44 ms
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
l =len(nums)
if l>1:
tail = l-1
head = 0
i = l//2
while head<tail and i<=tail:
if nums[i]<1:
nums[i],nums[head]=nums[head],nums[i]
head+=1
elif nums[i]>1:
nums[i],nums[tail]=nums[tail],nums[i]
tail-=1
else:
i+=1
i = l//2-1
while head<tail and i>=head:
if nums[i]<1:
nums[i],nums[head]=nums[head],nums[i]
head+=1
elif nums[i]>1:
nums[i],nums[tail]=nums[tail],nums[i]
tail-=1
else:
i-=1
27:移除元素
给定一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度。不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 1:
给定 nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
函数应该返回新的长度 2, 并且 nums 中的前两个元素均为 2。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
给定 nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
函数应该返回新的长度 5, 并且 nums 中的前五个元素为 0, 1, 3, 0, 4。
注意:这五个元素可为任意顺序。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以“引用”方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参作任何拷贝
int len = removeElement(nums, val);
// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中该长度范围内的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
解题:
代码如下:
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
i =len(nums)
while i>0:
if nums[-i]==val:
del nums[-i]
i-=1
283:移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
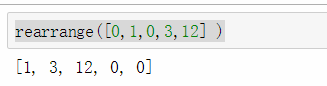
输入: [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
说明: 必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。 尽量减少操作次数。
代码:
def rearrange(l):
n= len(l)
k=0
for i in l:
if i:
l[k]=i
k+=1
for i in range(k,n):
l[i]=0
return l
结果如下:





















 1625
1625

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








