accumulate
有的算法有两个版本,可以加入自己的比较函数改变原来算法的执行效果
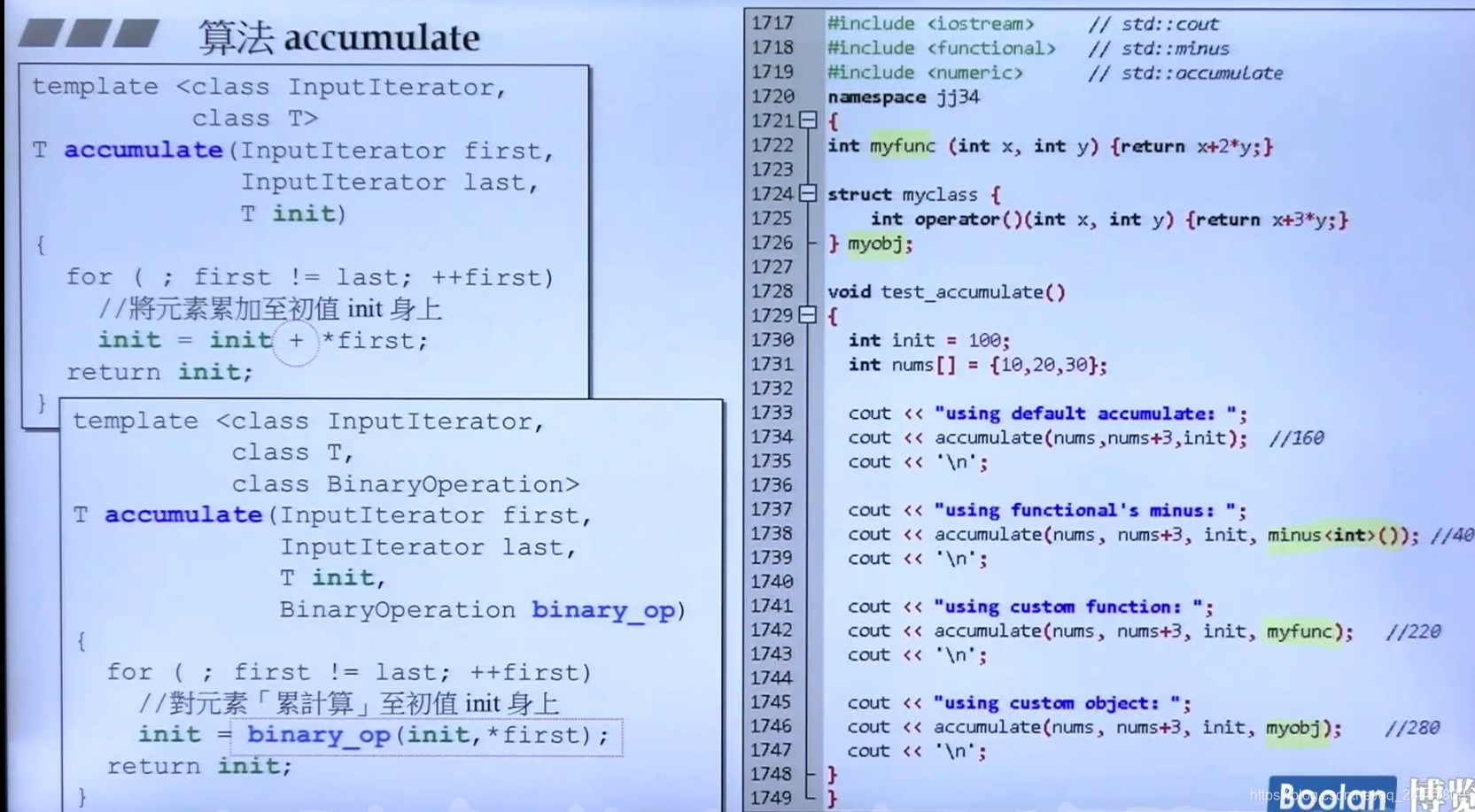
测试函数
#include<iostream>
#include <numeric>
int func(int x, int y)
{
return x + 2 * y;
}
struct testclass {
int operator()(int x, int y) { return x + 3 * y; };
}obj;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 100;
int num[] = { 10,40,60 };
cout << accumulate(num, num + 3,n,func);
return 0;
}
for_each

测试函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
void func(int i)
{
cout << i << "\t";
}
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 100;
vector<int> v= { 10,40,60 };
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),func);
return 0;
}
replace

replace_if
 pred是我们要传入的函数指针,名称Predicate暗示我们需要提供一个判断函数
pred是我们要传入的函数指针,名称Predicate暗示我们需要提供一个判断函数
测试函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void display(int i)
{
cout << i << "\t";
}
bool func(int x)
{
if (x % 2 == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n = 10;
vector<int> v = { 10,25,35,40,50 };
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), func, 5); //偶数项全部变为5
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),display);
return 0;
}
count
容器内部自带的count和find查找效率更快

count测试函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 10;
//vector<int> v = { 10,25,35,40,50 };
map<string, int> mp;
mp["qwe"] = 100;
mp["asd"] = 200;
mp["zxc"] = 300;
string s = "qwe";
//cout<<count(mp.begin(), mp.end(),s )<<endl; //此处编译不通过
cout << mp.count(s) << endl; //返回1
return 0;
}
find
 find_if测试函数
find_if测试函数
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
bool func(int& value)
{
return value % 9 == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
int main()
{
int n = 10;
vector<int> v = { 10,25,72,35,40,50 };
cout<<find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), func)-v.begin(); //找到数组中第一个9的整数
return 0;
}
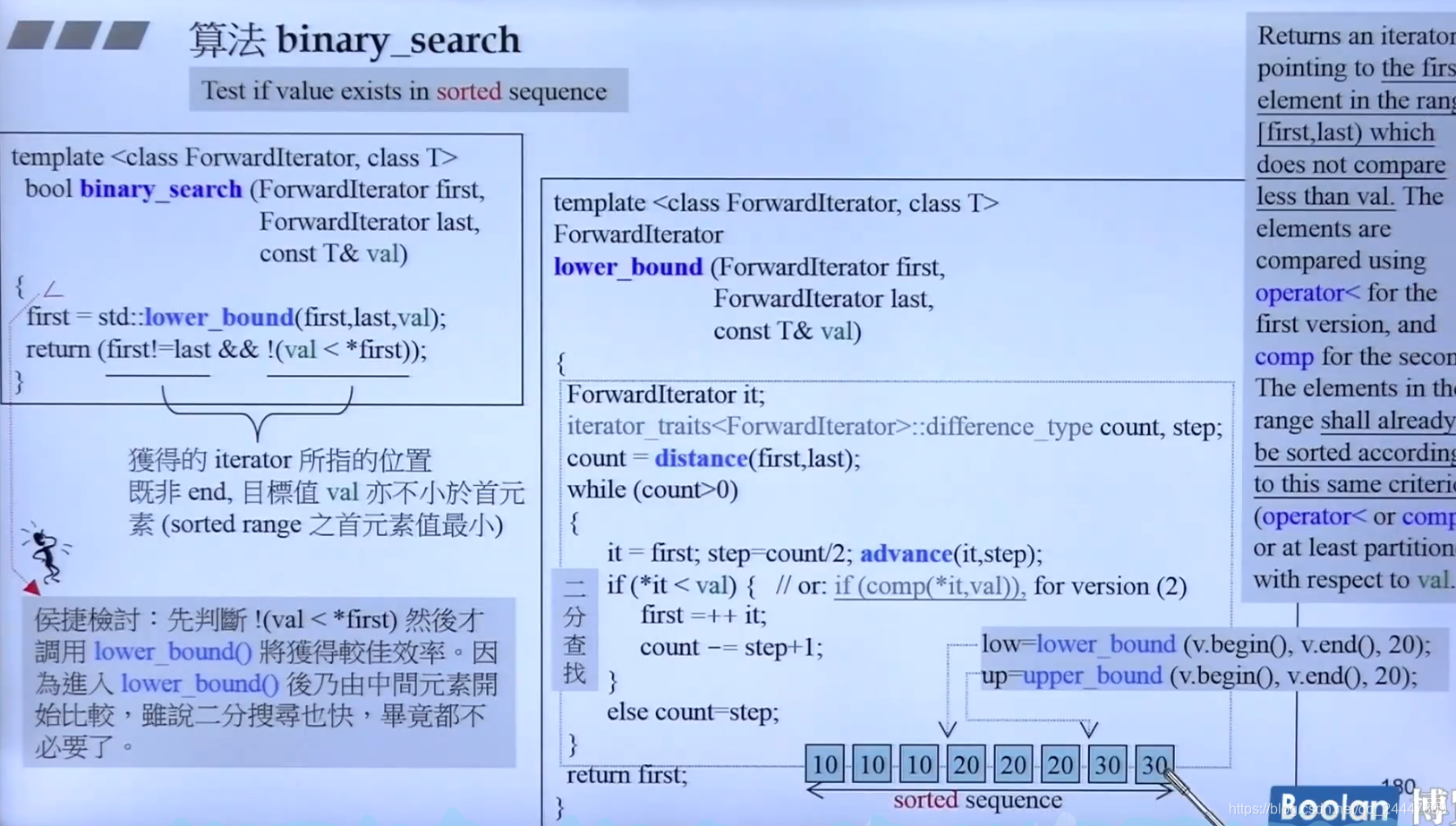
binary_search 二分查找
lower_bound()返回不大于查找value的第一个元素
upper_bound()返回大于查找value的第一个元素
这样的设定可以让两个函数返回的值在另外的算法中满足前闭后开标准。








 本文介绍了C++标准模板库(STL)中的多个实用算法,包括accumulate、for_each、replace_if、count、find及binary_search等,并提供了具体的实现案例。
本文介绍了C++标准模板库(STL)中的多个实用算法,包括accumulate、for_each、replace_if、count、find及binary_search等,并提供了具体的实现案例。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








