1.赋值运算符重载
1.1运算符重载
1.运算符用于类类型时是不能直接使用的,C++语⾔允许我们通过运算符重载的形式指定新的含义。
2.运算符重载是具有特殊名字的函数,他的名字是由operator和后⾯要定义的运算符共同构成。和其
他函数⼀样,它也具有其返回类型和参数列表以及函数体。
3.重载运算符函数的参数个数和该运算符作⽤的运算对象数量⼀样多。⼀元运算符有⼀个参数(自增,自减),⼆元
运算符有两个参数,⼆元运算符的左侧运算对象传给第⼀个参数,右侧运算对象传给第⼆个参数。但是如果⼀个重载
运算符函数是成员函数,则它的第⼀个运算对象默认传给隐式的this指针,因此运算符重载作为成员函数时,参数⽐
运算对象少⼀个。
4.运算符重载以后,其优先级和结合性与对应的内置类型运算符保持⼀致。
5.不能通过连接语法中没有的符号来创建新的操作符:⽐如operator@。
6.(.* :: sizeof ?: .) 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。 重载操作符⾄少有⼀个类类型参数,不能通过运算符重载
改变内置类型对象的含义,如: int operator+(int x, int y)。
int operator+(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
int main()
{
int a, b = 3;
//error C2803: “operator +”必须至少有一个类类型的形参
a + b;
return 0;
}
class A
{
public:
void func()
{
cout << "func" << endl;
}
};
typedef void(A::* pf)();//成员函数指针类型
int main()
{
pf p = &A::func;// C++规定成员函数要加&才能取到函数指针
A obj;
(obj.*p)();// 对象调⽤成员函数指针时,使⽤.*运算符
return 0;
}
7.重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是operator++,⽆法很好的区分。
C++规定,后置++重载时,增加⼀个int形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,⽅便区分。
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
//private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
// 重载为全局的⾯临对象访问私有成员变量的问题
// 有⼏种⽅法可以解决:
// 1、成员放公有
// 2、Date提供getxxx函数
// 3、友元函数
// 4、重载为成员函数
bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{
return d1._year == d2._year
&& d1._month == d2._month
&& d1._day == d2._day;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2025, 7, 1);
Date d2(2025, 7, 1);
// 运算符重载函数可以显⽰调⽤
operator==(d1, d2);
// 编译器会转换成 operator==(d1, d2);
d1 == d2;
return 0;
}
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
//重载成成员函数
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
Date& operator++()
{
cout << "前置++" << endl;
//...
return *this;
}
//这返回的是临时变量不能引用返回
Date operator++(int)
{
Date tmp;
cout << "后置++" << endl;
//...
return tmp;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2025, 7, 1);
Date d2(2025, 7, 1);
// 运算符重载函数可以显⽰调⽤
d1.operator == (d2);
// 编译器会转换成 d1.operator==(d2);
d1 == d2;
// 编译器会转换成 d1.operator++();
++d1;
// 编译器会转换成 d1.operator++(0);
d1++;
return 0;
}
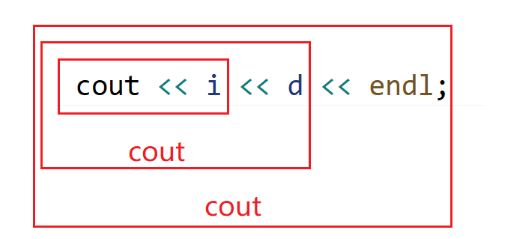
8.重载<<和>>时,需要重载为全局函数,因为重载为成员函数,this指针默认抢占了第⼀个形参位
置,第⼀个形参位置是左侧运算对象,调⽤时就变成了对象<<cout,不符合使⽤习惯和可读性。
重载为全局函数把ostream/istream放到第⼀个形参位置就可以了,第⼆个形参位置当类类型对
象。
class Data
{
public:
Data(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_mouth = month;
_day = day;
}
//private:
int _year;
int _mouth;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream & out, const Data& d)
{
out << d._year << " " << d._mouth << " " << d._day;
return out;//每次 << 操作返回一个 ostream 对象的引用,允许下一个 << 操作继续使用同一个流对象。
}
int main()
{
Data d1(2025, 7, 1);
cout << d1;
}
如果重载成成员函数
class Data
{
public:
Data(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_mouth = month;
_day = day;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out)
{
out << _year << " " << _mouth << " " << _day;
return out;
}
private:
int _year;
int _mouth;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Data d1(2025, 7, 1);
d1 << cout;
}
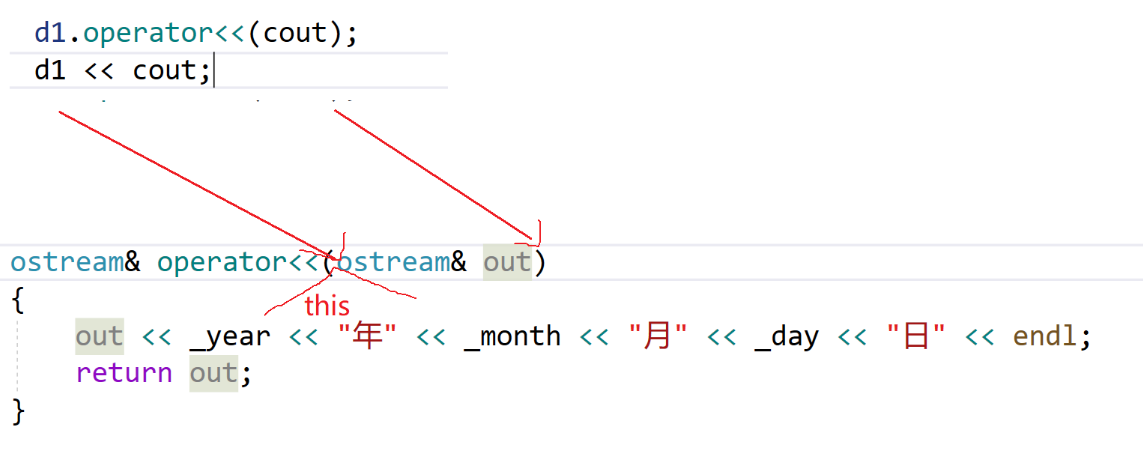
可读性会变差
1.2赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是⼀个默认成员函数,⽤于完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷⻉赋值,这⾥要注意跟
拷⻉构造区分,拷⻉构造⽤于⼀个对象拷⻉初始化给另⼀个要创建的对象。
赋值运算符重载的特点
- 赋值运算符重载是⼀个运算符重载,规定必须重载为成员函数。赋值运算重载的参数建议写成
const当前类类型引⽤,否则会传值传参会有拷⻉。 - 有返回值,且建议写成当前类类型引⽤,引⽤返回可以提⾼效率,有返回值⽬的是为了⽀持连续赋
值场景。 - 没有显式实现时,编译器会⾃动⽣成⼀个默认赋值运算符重载,默认赋值运算符重载⾏为跟默认拷
⻉构造函数类似,对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷⻉/浅拷⻉(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷⻉),对⾃定义
类型成员变量会调⽤他的赋值重载函数。 - 像Date这样的类成员变量全是内置类型且没有指向什么资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载就
可以完成需要的拷⻉,所以不需要我们显⽰实现赋值运算符重载。像Stack这样的类,虽然也都是
内置类型,但是_a指向了资源,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载完成的值拷⻉/浅拷⻉不符合我
们的需求,所以需要我们⾃⼰实现深拷⻉(对指向的资源也进⾏拷⻉)。像MyQueue这样的类型内部
主要是⾃定义类型Stack成员,编译器⾃动⽣成的赋值运算符重载会调⽤Stack的赋值运算符重载,
也不需要我们显⽰实现MyQueue的赋值运算符重载。
class Data
{
public:
Data(int year = 1, int mouth = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_mouth = mouth;
_day = day;
}
Data(const Data& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_mouth = d._mouth;
_day = d._day;
}
Data& operator=(const Data& d)
{
if(this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_mouth = d._mouth;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
private:
int _year;
int _mouth;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Data d1(2025, 7, 1);
Data d2(d1);//拷贝构造
Data d3(2025, 7, 2);
d1 = d3;//赋值运算符重载
// 需要注意这⾥是拷⻉构造,不是赋值重载
// 请牢牢记住赋值重载完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷⻉赋值
// ⽽拷⻉构造⽤于⼀个对象拷⻉初始化给另⼀个要创建的对象
Data d4 = d1;
}
2.取地址运算符重载
2.1 const成员函数
• 将const修饰的成员函数称之为const成员函数,const修饰成员函数放到成员函数参数列表的后
⾯。
• const实际修饰该成员函数隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进⾏修改。
const修饰Date类的Print成员函数,Print隐含的this指针由 Date* const this 变为 const Date* const this
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
// void Print(const Date* const this) const
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
// 这⾥⾮const对象也可以调⽤const成员函数是⼀种权限的缩⼩
Date d1(2024, 7, 5);
d1.Print();
const Date d2(2024, 8, 5);
d2.Print();
return 0;
}
2.2 取地址运算符重载
取地址运算符重载分为普通取地址运算符重载和const取地址运算符重载,⼀般这两个函数编译器⾃动⽣成的就可以够我们⽤了,不需要去显⽰实现。除⾮⼀些很特殊的场景,⽐如我们不想让别⼈取到当前类对象的地址,就可以⾃⼰实现⼀份,胡乱返回⼀个地址。
class Date
{
public :
Date* operator&()
{
return this;
// return nullptr;
}
const Date* operator&()const
{
return this;
// return nullptr;
}
private :
int _year ; // 年
int _month ; // ⽉
int _day ; // ⽇
};






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








