什么是GSL?
The GNU Scientific Library (GSL) is a numerical library for C and C++ programmers.
The library provides a wide range of mathematical routines such as random number generators, special functions and least-squares fitting. There are over 1000 functions in total with an extensive test suite.
The complete range of subject areas covered by the library includes,
| Complex Numbers | Roots of Polynomials |
| Special Functions | Vectors and Matrices |
| Permutations | Sorting |
| BLAS Support | Linear Algebra |
| Eigensystems | Fast Fourier Transforms |
| Quadrature | Random Numbers |
| Quasi-Random Sequences | Random Distributions |
| Statistics | Histograms |
| N-Tuples | Monte Carlo Integration |
| Simulated Annealing | Differential Equations |
| Interpolation | Numerical Differentiation |
| Chebyshev Approximation | Series Acceleration |
| Discrete Hankel Transforms | Root-Finding |
| Minimization | Least-Squares Fitting |
| Physical Constants | IEEE Floating-Point |
| Discrete Wavelet Transforms | Basis splines |
| Running Statistics | Sparse Matrices and Linear Algebra |
以上摘自http://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/
可见里面还是有不少干货的。
我们知道计算机产生的随机数都是伪随机数,需要一个种子,种子不同,产生的随机数序列才不同,这个种子可以是时间,因为系统的时间一直都在变。通常,我们用c标准库里的函数rand产生的随机数是均匀分布的,那么要产生高斯分布的(钟形)随机数就需要一个算法,在GSL库中实现了两个这样的算法。
这里解读其随机数产生的实现,我使用的源码是gsl-2.4.tar.gz,gsl_ran_gaussian函数就是产生高斯分布随机数。
其代码在gsl-2.4/randist/gauss.c中
double
gsl_ran_gaussian (const gsl_rng * r, const double sigma)
{
double x, y, r2;
do
{
/* choose x,y in uniform square (-1,-1) to (+1,+1) */
x = -1 + 2 * gsl_rng_uniform_pos (r);
y = -1 + 2 * gsl_rng_uniform_pos (r);
/* see if it is in the unit circle */
r2 = x * x + y * y;
}
while (r2 > 1.0 || r2 == 0);
/* Box-Muller transform */
return sigma * y * sqrt (-2.0 * log (r2) / r2);
}
这是Box-Muller方法实现的,在Knuth的The Art Of Computer Programming Vol.2, 3rd edition里有讲到。
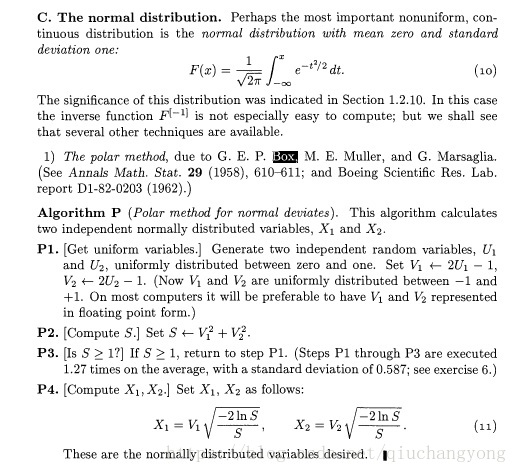
另一个方法是Kinderman-Monahan方法,有相关论文,这里不讲。
上面那个函数中的gsl_rng_uniform_pos就是产生均匀分布的随机数,范围是(0, 1)
其实现在gsl-2.4/rng/gsl_rng.h中,
INLINE_FUN double
gsl_rng_uniform_pos (const gsl_rng * r)
{
double x ;
do
{
x = (r->type->get_double) (r->state) ;
}
while (x == 0) ;
return x ;
}
如果要在深挖下去,就到了gsl_rng_type *gsl_rng_mt19937
get_double就是gsl_rng_mt19937的成员函数,具体实现在gsl-2.4/rng/mt.c中。
它也可以用rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0)代替,那样就要在产生随机数之前用srand设置一个随机数种子。
附:
#define RAND_MAX 0x7fff
static double
mt_get_double (void * vstate)
{
return mt_get (vstate) / 4294967296.0 ;
}
可以看出还是有点不同,后者除以(0xFFFFFFFF+1)










 本文详细介绍了GNU科学库(GSL)的功能和应用范围,特别聚焦于随机数生成算法,包括Box-Muller和Kinderman-Monahan方法,以及GSL如何实现高斯分布随机数的生成。
本文详细介绍了GNU科学库(GSL)的功能和应用范围,特别聚焦于随机数生成算法,包括Box-Muller和Kinderman-Monahan方法,以及GSL如何实现高斯分布随机数的生成。
















 854
854

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








