注:成为博客专家之后便不再轻易转发文章了。但最近在研究Linux内核Thermal方面内容时,发现了很好的一篇文章。将我这一阶段已经学到的知识点包括尚存在的疑问点基本都写出来了。因此予以转发推荐(对于格式进行了微调),希望更多的人能够看到。
一、thermal 模块简介
1. Thermal Core(核心)
核心为 thermal_core。可以获取温度的设备抽象为 thermal_zone_device, 如Temp Sensor、NTC(板上的热敏电阻)等。控制温度的设备抽象为 thermal_cooling_device, 如风扇、CPU、DDR、GPU等。温控策略抽象为 thermal_governor,比如 step_wise、bang_bang 等。
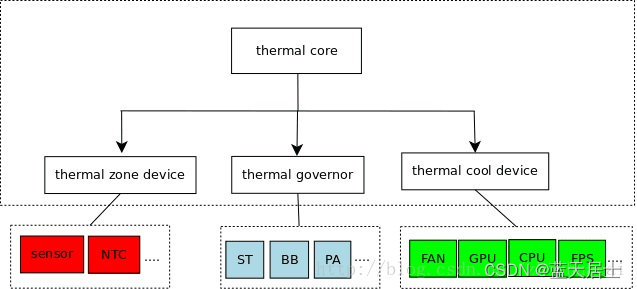
thermal_cooling_device 对应系统实施冷却措施的驱动,是温控的执行者。cooling device 维护一个 cooling 等级,即 state,一般 state 越高即系统的冷却需求越高。cooling device 根据不同等级的冷却需求进行冷却行为。cooling device 只根据 state 进行冷却操作,是实施者,而 state 的计算由 thermal governor 完成。结构 struct cpufreq_cooling_device 和 struct devfreq_cooling_device 作为对 thermal_cooling_device 的扩展,分别主要在 cpufreq_cooling.c 和 devfreq_cooling.c 中使用。
thermal_instance 结构体描述 trip point 与 cooling device 的绑定关系,即当 trip point 触发后由哪个 cooling device 去实施冷却措施。每个 trip point 必须与一个 cooling device 绑定,才有实际意义。
一个 Thermal Zone 可以有多个 Cooling 设备;同时还提供一个核心函数 thermal_zone_device_update 作为 Thermal 中断处理函数和轮询函数,轮询时间会根据不同 Trip Delay 调节。模块流程图如下:
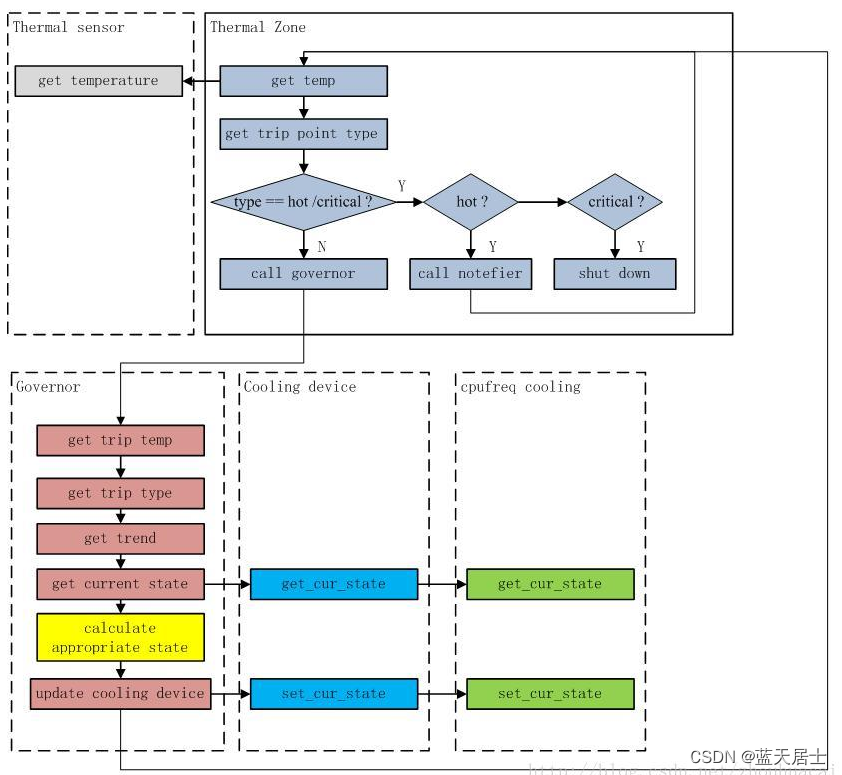
流程:
thermal_zone_device_register --> INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&tz->poll_queue, thermal_zone_device_check) --> thermal_zone_device_check --> thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED)
读取 thermal 温度,然后根据 trip 类型执行 critical 或者 non critical 响应操作。critical 则直接调用 orderly_poweroff; non critical 则调用 governor 的 throttle 函数。
2. Thermal Governor(温控算法)
Thermal Governor即温控算法,解决温控发生时,如何选择 cooling state 的问题,当前可用的governor包括:bang_bang、step_wise、user_space、low_limit、power_allocator
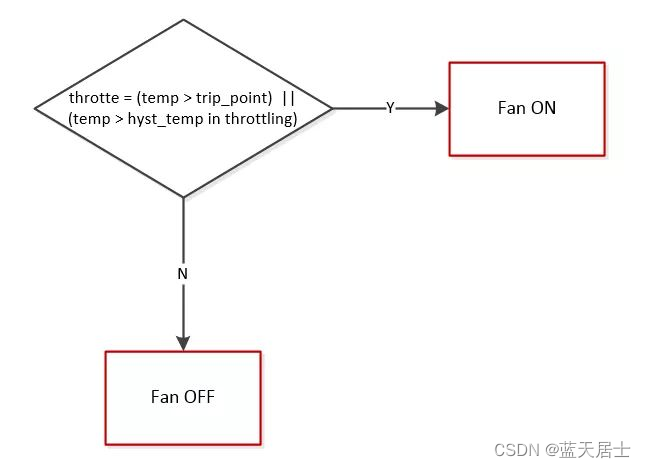
(1) bang_bang governor
由于 bang_bang governor 是用在使用风扇散热的设备中的算法。首先我们需要确定 throttle 即温控是否触发。这包括了两种情况,第一种为当前温度大于温控阈值,第二种为当前温度小于温控阈值但是大于滞后温度(温控解除温度),并且是处于降温的过程中。bang_bang governor的降温策略跟它的名字一样简单,可以用一句话来概括: 当throttle发生,打开风扇;当throttle解除,关闭风扇。
(2) step_wise governor
step_wise 算法在计算 target cooling state 的过程中,除了需要知道是否 throttle,还添加了一个 trend 作为参考条。trend 表示温升趋势,Linux Thermal Framework 定义了五种 trend type,见 enum thermal_trend,即稳定(THERMAL_TREND_STABLE), 上升(THERMAL_TREND_RAISING), 下降(THERMAL_TREND_DROPPING), 最高温线(THERMAL_TREND_RAISE_FULL),最低温线(THERMAL_TREND_DROP_FULL)。
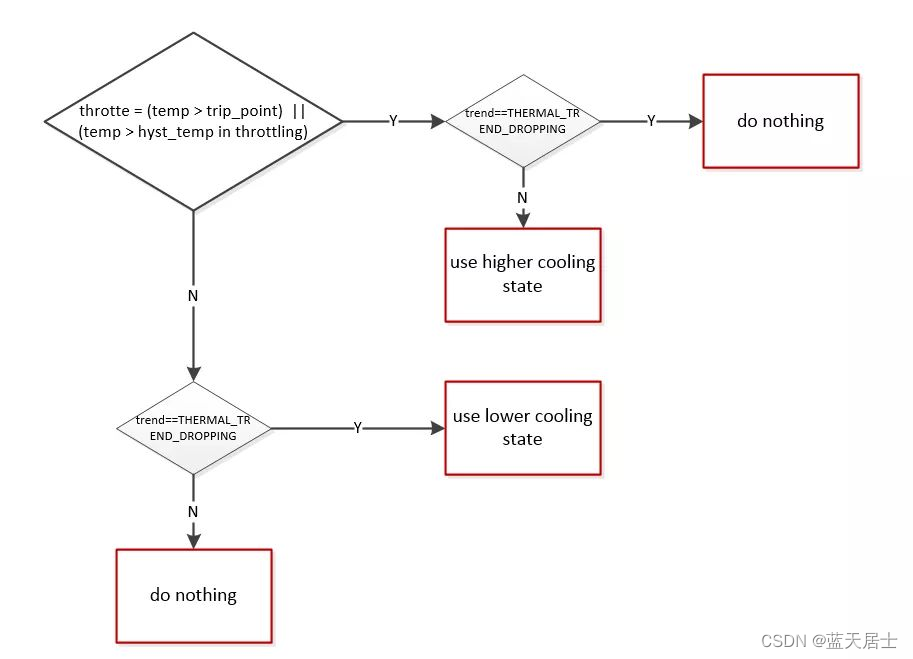
step_wise governor 对于 cooling_state 选择的策略:
a. 当 throttle 发生且温升趋势为上升,使用更高一级的 cooling state;
b. 当 throttle 发生且温升趋势为下降,不改变 cooling state;
c. 当 throttle 解除且温升趋势为下降,不改变 cooling state;
d. 当 throttle 解除且温升趋势为上升,使用更低一级的 cooling state;
step_wise governor 是每个轮询周期逐级提高冷却状态,是一种相对温和的温控策略。
(3) low_limit governor
移动设备在温度比较低的情况下同样会存在诸如无法充电等问题,所以 low_limit governor 应运而生,这个特殊的温控算法用于低温环境下的设备加热。它的温控策略基本上就是反向的 step_wise,在这里就不进一步展开叙述了,感兴趣的同学可以自行查看kernel源码,内核5.10中已经将其移除。
(4) user_space governor
user_space governor 是通过 uevent 将温区当前温度,温控触发点等信息上报到用户空间,由用户空间软件制定温控的策略。
(5) power_allocator governor
power_allocator governor 即 IPA 算法,是由 ARM 在2015年提交及纳入 Linux kernel mainline。IPA(Intelligent Power Allocator)模型的核心是利用 PID 控制器,ThermalZone 的温度作为输入,可分配功耗值作为输出,调节 Allocator 的频率和电压值。
3. Thermal Governor Section
各个governor是通过 __section() 属性配合链接器脚本链接到一起的。
//drivers/thermal/gov_step_wise.c
THERMAL_GOVERNOR_DECLARE(thermal_gov_step_wise);
//drivers/thermal/thermal_core.h
#define THERMAL_TABLE_ENTRY(table, name) \
static typeof(name) *__thermal_table_entry_##name \
__used __section("__" #table "_thermal_table") = &name
#define THERMAL_GOVERNOR_DECLARE(name) THERMAL_TABLE_ENTRY(governor, name)
//展开后为:
static struct thermal_governor *__thermal_table_entry_thermal_gov_step_wise \
__used __section("__governor_thermal_table") = &thermal_gov_step_wise //__section()中应该会自动去掉中间的空格
//include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h
#define THERMAL_TABLE(name) \
. = ALIGN(8); \
__##name##_thermal_table = .; \
KEEP(*(__##name##_thermal_table)) \
__##name##_thermal_table_end = .;
#define INIT_DATA \
...
THERMAL_TABLE(governor) \
...
//展开后为:
#define THERMAL_TABLE(governor) \
. = ALIGN(8); \
__governor_thermal_table = .; \
KEEP(*(__governor_thermal_table)) \
__governor_thermal_table_end = .;
使用遍历方法:
/* Init section thermal table */
extern struct thermal_governor *__governor_thermal_table[];
extern struct thermal_governor *__governor_thermal_table_end[];
#define for_each_governor_table(__governor) \
for (__governor = __governor_thermal_table; __governor < __governor_thermal_table_end; __governor++)
二、设备树配置
1. 除了SOC里面的温度传感器分别监控各个子系统的当前温度外。同样在PCB上还包含有多个热敏电阻(NTC), 这些NTC通过算法的计算后可以获得手机主板上各个区域的温度。软件上将这些 tsensor 及 ntc 等可以获取温度的设备描述为 thermal zone, 在代码中以 dts 的形式来描述。
//thermal_zones 下每一个子节点都是一个 thermal, 在 /sys/class/thermal 下对应一个 thermal_zoneX 目录,ntc的也在里面。
thermal_zones: thermal-zones {
...
soc_max {
polling-delay = <0>; /* /* 温控未发生时(超过阈值时)轮询周期(ms) */ */
polling-delay-passive = <0>; /* 温控发生时(未超过阈值时)的轮询周期(ms) 配置为0,代表不使用轮询方式,通过tsensor中断触发温控。*/
thermal-governor = "step_wise"; /* 补充的,该温区发生温控时所使用的算法*/
thermal-sensors = <&lvts 0>; /* 对应的sensor,表示使用 lvts 这个温度传感器的通道0 */
trips { /* 温控触发点 */
soc_max_crit: soc_max_crit@0 {
/* 触发温度为(116500)/1000 = 116.5 度发生温控,对应 trip_point_0_temp 文件 */
temperature = <116500>;
/* 滞后温度,表示当下降到(116.5 – 2000/1000) = 114.5 度时解除温控,对应 trip_point_0_hyst 文件 */
hysteresis = <2000>;
/*
* "critical"表示触发温控后立刻重启,若配置为”passive”,表示当温控发生后由governor控制,
* 轮询周期改为使用 polling-delay-passive,对应 trip_point_0_type 文件
*/
type = "critical";
};
};
};
...
}
trips 即触发点,每个 thermal zone 可以维护多个 trip point,其 type 为 trip point类型,沿袭PC散热方式,分为四种类型 passive、active、hot、critical,在内核中由 enum thermal_trip_type 描述,若是 critical,温度触发后直接触发重启,非 critical 类型由 governor 的温控策略来降温。
2. 现在我们已经将 tsensor 跟 NTC 以 thermal_zone 的形式注册到系统中,可以实时的监控设备各个子系统的发热状况。当温度超过所设阈值时,将会上报中断,接下来就是冷却设备起作用的时刻了。这些通过控制自己的状态达到降温效果的设备,操作系统将其抽象为 cooling_device(冷却设备)。像 cpufreq, devfreq 等driver在初始化的时候会调用 of_thermal.c 提供的接口在 thermal_core 中注册 cooling device。
gpu2 {
polling-delay = <100>; /* milliseconds */
polling-delay-passive = <12>; /* milliseconds */
thermal-sensors = <&lvts 14>;
trips {
gpu_throttle: trip-point@0 {
temperature = <95000>;
hysteresis = <2000>;
type = "passive";
};
};
/* 该温区对应到的冷却设备列表 */
cooling-maps {
map0 {
/* 该冷却设备对应的温区温控触发点 */
trip = <&gpu_throttle>;
/* 对应的真正执行冷却操作的设备及最大/最小状态,格式为< phandle of device, min_state,max_state> */
cooling-device = <&mali THERMAL_NO_LIMIT THERMAL_NO_LIMIT>;
contribution = <1024>;
};
};
};
注:MTK 5.10内核的 cooling device 没有再按这个设备树格式了,检索 #cooling-cells 来查找 cooling device 的设备树节点配置。
三、文件接口
1. /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zoneX/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0 # ls -l
-r--r--r-- available_policies //可选的温控governor,如 power_allocator user_space step_wise --w------- emul_temp //模拟设置thermal的温度,单位毫摄氏度,设置后 update_temperature()中可获取到这个温度,和实际达到这个温度同效果。只有其为0,读取的才是真正的温度值,否则就是echo的模拟值 -rw-r--r-- integral_cutoff -rw-r--r-- k_d -rw-r--r-- k_i -rw-r--r-- k_po -rw-r--r-- k_pu -rw-r--r-- mode //此thermalzone是否使能了,若是为disabled,对其sys文件的操作不生效,可以echo enabled使能 -rw-r--r-- offset -rw-r--r-- passive -rw-r--r-- policy //当前使用的governor是哪个 -rw-r--r-- slope -rw-r--r-- sustainable_power -r--r--r-- temp //该温区的当前温度,测试时往 emul_temp 中写的值也会体现在这里。 -rw-r--r-- trip_point_0_hyst //滞后温度,来自设备树 hysteresis 字段,此例中为 2000。有 trips 节点才会有此文件。 -rw-r--r-- trip_point_0_temp //触发温度,来自设备树 temperature字段,此例中为 116500,可以通过sysfs更改。 -r--r--r-- trip_point_0_type //触发点0的类型,来自设备树 type 字段,此例中为"critical" -r--r--r-- type //该温区的名称,对应于设备树 thermal_zones 下子节点的名字,此例中为"soc_max" -rw-r--r-- uevent
不同 thermal_zoneX 下的文件不完全相同,取决于在设备树中是否指定了trips成员,以及指定了几个。
2. /sys/class/thermal/cooling_deviceX
/sys/class/thermal/cooling_device0 # ls -l -rw-r--r-- cur_state //该 cooling_device 的当前 cooling state -r--r--r-- max_state //该 cooling_device 的最大 cooling state drwxr-xr-x stats -r--r--r-- type //该cooling device的名称 -rw-r--r-- uevent /sys/class/thermal/cooling_device0 # ls -l stats/ --w------- reset //对统计状态进行复位 -r--r--r-- time_in_state_ms //在每个state下停留的时间 -r--r--r-- total_trans //不同state之间转换的次数 -r--r--r-- trans_table //各个state状态转换表,最大只能显示1个页的内容
type 为 thermal-cpufreq-X 的 cool device 控制 CPU ClusterX 的频点,比如向 cur_state 中写入 max_state 的值,对应Cluster的 scaling_max_freq 文件将显示被限制到了最小频点。
type 为 thermal-cpufreq-X 的是通过 cpufreq_cooling.c 注册的 cool device,type 为 thermal-devfreq-X 的是通过 devfreq_cooling.c 注册的 cool device。







 文章详细介绍了Linux内核的Thermal模块,包括ThermalCore的组成部分,如thermal_zone_device和thermal_cooling_device,以及不同的温控策略如bang_bang和step_wise。ThermalGovernor部分解析了各种算法的工作原理,如如何选择冷却状态。此外,还讨论了设备树配置和文件接口在温控系统中的作用。
文章详细介绍了Linux内核的Thermal模块,包括ThermalCore的组成部分,如thermal_zone_device和thermal_cooling_device,以及不同的温控策略如bang_bang和step_wise。ThermalGovernor部分解析了各种算法的工作原理,如如何选择冷却状态。此外,还讨论了设备树配置和文件接口在温控系统中的作用。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








