| 一、Queue接口(一般队列) 点击此处返回总目录 二、Deque接口(双端队列) 三、PriorityQueue类(优先队列或小根堆) 一、Queue接口 父接口是collection。就是一般的队列,先进先出。 1. boolean add(e) //将指定元素插入队列。成功返回true,失败抛出异常。 boolean offer(e) //同上。成功返回true,失败返回false。 2. E remove() //获取并移除队列的头。为空时抛出异常。 E poll() //同上。为空时返回null。 3. E element() //获取头,但是不移除。为空时,抛出异常。 E peek() //获取头,但是不移除。为空时,返回null。 LinkedList的继承关系如下:  LinkedList实现了Queue接口,我们可以当做队列使用。 初始化: Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 例1:
| package cn.itcast.demo10; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); //false
queue.offer(5);
System.out.println(queue.peek()); //4
queue.poll();
queue.poll();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); //true
}
} |
二、Deque接口(双端队列)
双端队列就是两头都可以进,两头都可以出。
Deque的功能: 1. offerFirst(e)、offerLast(e) //添加元素 2. pollFirst()、pollLast() //移除元素 3. peekFirst()、peekLast() //返回元素 当然Deque继承了Queue的功能,也有offer、poll、peek等函数,但是尽量不要用,因为字面有歧义。比如,虽然知道offer(e)等价于offerLast(e),但是还得记,容易混淆。 LinkedList实现了Deque接口,我们可以当做双端队列使用。 例:
| package cn.itcast.demo11; import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<Integer>();
deque.offerFirst(3); // 3
deque.offerFirst(2); // 2 3
deque.offerLast(4); //2 3 4
System.out.println(deque.peekFirst()); //2
System.out.println(deque.peekLast()); //4
deque.pollFirst(); //3 4
deque.pollLast(); //3
System.out.println(deque.isEmpty()); //false
deque.pollFirst();
System.out.println(deque.isEmpty()); //true
}
} |
三、PriorityQueue<E> 优先队列(就是小根堆)。 1. 一个基于优先级堆的无界优先级队列。优先级队列的元素按照其自然顺序进行排序,或者根据构造队列时提供的Comparator进行排序,具体取决于所使用的构造方法。优先级队列不允许使用 null 元素。依靠自然顺序的优先级队列还不允许插入不可比较的对象(这样做可能导致 ClassCastException)。 2. 此队列的头 是按指定排序方式确定的最小 元素。如果多个元素都是最小值,则头是其中一个元素——选择方法是任意的。队列获取操作 poll、remove、peek 和 element 访问处于队列头的元素。 3. 优先级队列是无界的,但是有一个内部容量,控制着用于存储队列元素的数组大小。它通常至少等于队列的大小。随着不断向优先级队列添加元素,其容量会自动增加。无需指定容量增加策略的细节。 4. 此类及其迭代器实现了Collection和Iterator接口的所有可选 方法。方法iterator()中提供的迭代器不 保证以任何特定的顺序遍历优先级队列中的元素。如果需要按顺序遍历,请考虑使用 Arrays.sort(pq.toArray())。 5. 注意,此实现不是同步的。如果多个线程中的任意线程修改了队列,则这些线程不应同时访问 PriorityQueue 实例。 6. 此实现为排队和出队方法(offer、poll、remove() 和 add)提供 O(log(n)) 时间;为 remove(Object) 和 contains(Object) 方法提供线性时间;为获取方法(peek、element 和 size)提供固定时间。 解释: 1. 优先队列的逻辑结构是一个小根堆,存储结构是一个数组。【例1】 2. 每次拿掉优先队列的队首元素(即小根堆的堆顶元素)之后,其他元素会根据堆排序的方法进行重新排序,确保剩下的优先队列还是一个小根堆。【例1】 3. 可以插入对象。【例2】 例1:
| package cn.itcast.demo01; import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q1 = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
q1.offer(4);
q1.offer(6);
q1.offer(2);
q1.offer(5);
q1.offer(20);
q1.offer(3);
q1.offer(7);
q1.offer(8);
q1.offer(1);
for(int i:q1){
System.out.print(i+" "); //首先看一下队列里面的元素。会发现不是有序排列的。
}
System.out.println();
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(q1.poll()+" "); //每次先把第一个元素拿掉,
System.out.println();
for(int i:q1){
System.out.print(i+" "); //然后看看剩下的元素是怎么排列的。
}
System.out.println();
}
}
} |
运行结果: 1 2 3 5 20 4 7 8 6
1
2 5 3 6 20 4 7 8
2
3 5 4 6 20 8 7
3
4 5 7 6 20 8
4
5 6 7 8 20
5
6 8 7 20
6
7 8 20
7
8 20
8
20
20 分析: 首先输出的是:1 2 3 5 20 4 7 8 6 。 说明,优先队列存储上不是有序的。但是逻辑上是有序的,而且逻辑结构是一个小根堆。因为看做把这个数组看成一个树的话, 为: 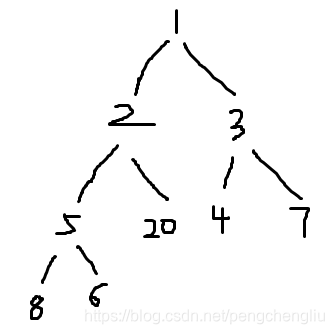 刚好是一个小根堆。 这个小根堆是怎么得来的呢? 是输入一个之后,调整为小根堆。然后输入第二个,再调整为小根堆。。。这样得来的。整个过程如下图所示: 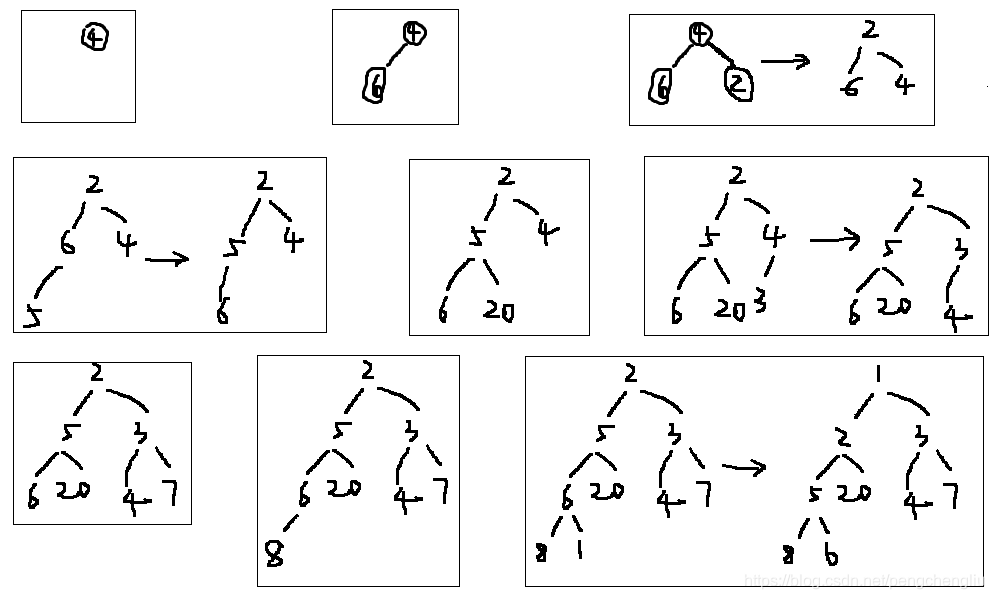
注意,并不是全部输入之后,再一下子调整成小根堆。而是输入一个就调整一下。因为它也不知道什么时候输入完呀,是吧。 删除的过程也是,删除一个就调整成小根堆。过程如下: 然后拿掉队首1,之后优先队列的数据为:
2 5 3 6 20 4 7 8 而不是"2 3 5 20 4 7 8 6",说明拿到堆顶元素之后,又重新调整了。调整的方式就是堆排序,即:把堆尾的元素放到堆顶,然后堆顶下沉。 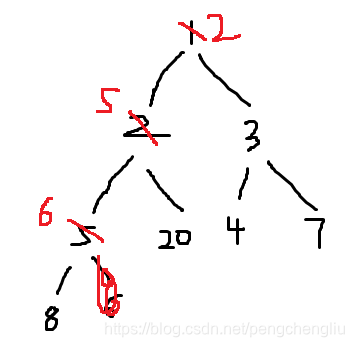
再拿掉2之后,为:
3 5 4 6 20 8 7 即: 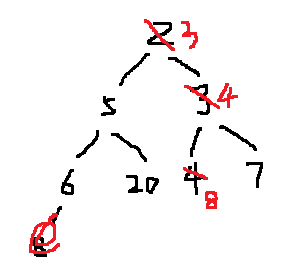
拿掉3之后,得到:
4 5 7 6 20 8 即: 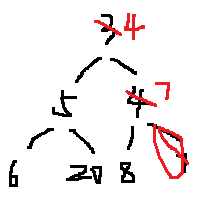
拿掉4之后,得到:
5 6 7 8 20 即: 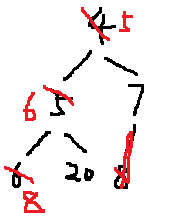
拿掉5之后,得到:
6 8 7 20 即: 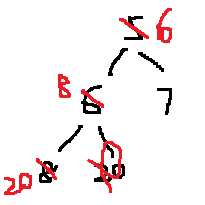
拿到6之后,得到:
7 8 20 即: 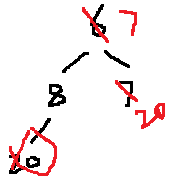
拿到7之后,得到:
8 20 即: 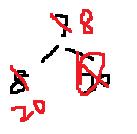
拿到8之后,得到:
20 即:  最后,拿到20。 例2: //Student.java
| package cn.itcast.demo02; public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ //继承Comparable接口。
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public int getScore() {
return score;
} public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public int compareTo(Student p){ //重写compareTo方法。
return this.score - p.score;
}
} |
//Test.java
| package cn.itcast.demo02; import java.util.PriorityQueue; public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> heap = new PriorityQueue<Student>();
heap.offer(new Student("no1",22,4));
heap.offer(new Student("no2",22,6));
heap.offer(new Student("no3",22,2));
heap.offer(new Student("no4",22,5));
heap.offer(new Student("no5",22,20));
heap.offer(new Student("no6",22,3));
heap.offer(new Student("no7",22,7));
heap.offer(new Student("no8",22,8));
heap.offer(new Student("no9",22,1));
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(heap.poll().getName()+" ");
}
}
} |
结果: no9 no3 no6 no1 no4 no2 no7 no8 no5 | 







 本文深入探讨了Java集合框架中的Queue接口,包括其基本概念、常用方法以及在实际编程中的应用。通过实例解析了offer、poll、peek等操作,并讨论了Queue接口与其他集合类型的区别,帮助读者掌握如何高效地使用队列数据结构。
本文深入探讨了Java集合框架中的Queue接口,包括其基本概念、常用方法以及在实际编程中的应用。通过实例解析了offer、poll、peek等操作,并讨论了Queue接口与其他集合类型的区别,帮助读者掌握如何高效地使用队列数据结构。



























 742
742

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








