1、Bundle Adjustment
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/penuel/p/13602934.html
BAL(Bundle Adjustment in large)数据集(http://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/bal/)是⼀个⼤型 BA 数据集,它提供了相机与点初始值与观测,你可以⽤它们进⾏ Bundle Adjustment。
1.1、BA问题数学模型
1.1.1、数据集解析
数据集文件为problem-16-22106-pre.txt,数据主要包括4部分分别详细说明。
-
第一部分:第一行:16 22106 83718
有16个相机位姿,22106个路标点(世界坐标系下的三维坐标),83718个观测坐标(两维像素坐标),总体概括及时相机在16个位置下观测22106个路标点,产生83718个对应的像素坐标。每个位置只能观测到部分路标点。 -
第二部分:观测数据,83718个观测坐标(两维像素坐标),共4维分别为
相机位姿编号 路标点编号 对应观测的像素坐标
0 0 -3.859900e+02 3.871200e+02
1 0 -3.844000e+01 4.921200e+02
2 0 -6.679200e+02 1.231100e+02
7 0 -5.991800e+02 4.079300e+02
12 0 -7.204300e+02 3.143400e+02
13 0 -1.151300e+02 5.548999e+01
0 1 3.838800e+02 -1.529999e+01
1 1 5.597500e+02 -1.061500e+02
10 1 3.531899e+02 1.649500e+02
0 2 5.915500e+02 1.364400e+02 -
第三部分:第一类顶点,16个相机位姿,位姿加相机内参共9维,前三维为so3(旋转向量),接下去为t(平移向量3维), f(fx=fy=f), 去畸变参数:k1, k2。注意这里的每个位姿是相对原点的位姿,而不是相对上一个位姿的变化量。
-
第四部分:第二类顶点,22106路标节点的世界坐标,3维。
1.1.2、Ba问题数学描述
已知条件:相机的16个位姿点和22106个路标点(世界坐标系下的三维坐标),这2部分参数认为是不准确的,需要优化;在图像中测量到83718个测量坐标(两维像素坐标)是准确的测量值。
最小二乘法求解问题:16个位姿点和22106个路标点(世界坐标系下的三维坐标)作为变量,已知值作为迭代的初始值,通过相机位姿和路标点世界坐标计算像素坐标,用计算的像素坐标去逼近测量到的83718个对应的像素坐标,不断迭代调整16个位姿点和22106个路标点(世界坐标系下的三维坐标)的值,使得逼近的误差最小。
最小二乘法
最小二乘法问题构建:曲线拟合,捆集调整ba。
最小二乘法求解:计算雅可比矩阵或黑塞矩阵,求解每次迭代的增量△x
1.1.3、g2o的使用步骤
- 创建一个线性求解器LinearSolver;
- 创建BlockSolver,并用上面定义的线性求解器初始化;
- 创建总求解器solver,并从GN/LM/DogLeg 中选一个作为迭代策略,再用上述块求
解器BlockSolver初始化; - 创建图优化的核心:稀疏优化器(SparseOptimizer);
- 定义图的顶点和边,并添加到SparseOptimizer中;
- 设置优化参数,开始执行优化
1.2、后端BA实践
1.2.1、代码实现
主要代码如下,工程代码见gitee链接: link
https://gitee.com/paul126/vslam-learn.git
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "common.h"
#include "sophus/se3.hpp"
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
/// 姿态和内参的结构
struct PoseAndIntrinsics {
PoseAndIntrinsics() {
}
/// set from given data address
explicit PoseAndIntrinsics(double *data_addr) {
rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(data_addr[0], data_addr[1], data_addr[2]));
translation = Vector3d(data_addr[3], data_addr[4], data_addr[5]);
focal = data_addr[6];
k1 = data_addr[7];
k2 = data_addr[8];
}
/* 将9维的估计值输出出去 */
void set_to(double *data_addr) {
auto r = rotation.log();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i] = r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i + 3] = translation[i];
data_addr[6] = focal;
data_addr[7] = k1;
data_addr[8] = k2;
}
SO3d rotation; /* 旋转矩阵 */
Vector3d translation = Vector3d::Zero(); /* 平移向量 */
double focal = 0; /* 相机fx=fy=f */
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0; /* 去畸变参数 */
};
/* g2o本身内部定义了一些常用的顶点类型,
g2o\types\slam3d\vertex_se3.h
class G2O_TYPES_SLAM3D_API VertexSE3 : public BaseVertex<6, Isometry3>
其他的列举出来出来为:
VertexSE2 : public BaseVertex<3, SE2> //2D pose Vertex, (x,y,theta)
VertexSE3 : public BaseVertex<6, Isometry3> //6d vector (x,y,z,qx,qy,qz) (note that we leave out the w part of the quaternion)
VertexPointXY : public BaseVertex<2, Vector2>
VertexPointXYZ : public BaseVertex<3, Vector3>
VertexSBAPointXYZ : public BaseVertex<3, Vector3>
VertexSE3Expmap : public BaseVertex<6, SE3Quat>
VertexCam : public BaseVertex<6, SBACam>
VertexSim3Expmap : public BaseVertex<7, Sim3>
自定义顶点:重新定义顶点一般需要考虑重写如下函数:
virtual bool read(std::istream& is);
virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const;
// 顶点更新函数。非常重要的一个函数,主要用于优化过程中增量△x 的计算。我们根据增量方程计算出增量之后,就是通过这个函数对估计值进行调整的。
virtual void oplusImpl(const number_t* update);
// 顶点参数创建函数,创建顶点参数的空间,并将地址传递给g2o库中的 _estimate。
virtual void setToOriginImpl();
自定义顶点需要提供2个参数:
相机位姿参数作为顶点,共9维,前三维为so3(旋转向量),接下去为t(平移向量3维), f(fx=fy=f), 去畸变参数:k1, k2;
第一是顶点参数维度:9
第二是参数的模板类型:后续会创建此类型空间,并将地址传递给 _estimate
*/
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
/* 此宏定义在Eigen库中定义,确保了Eigen对象能够在内存中对齐。需要对齐的原因是为了最大限速的提升运算效率,
Eigen库的一些对象(矩阵和向量)需要特别的内存对齐,提升数学运算效率。
在c++中使用new分配对象是不会保证这种共对齐,此宏定义可以确保new为Eigen对象分配内存是满足对齐要求。 */
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() {
}
/* 创建顶点参数的结构体空间,并将地址传递给g2o库中的 _estimate */
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
/* 这里只是显示调用构造函数,创建 PoseAndIntrinsics 结构体空间,元素并没有初始化,后面会进行初始化 */
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
/* 顶点更新函数,我们根据增量方程计算出增量△x (对应 update)之后,此函数根据迭代的增量对估计值进行调整,是估计值更加准确 */
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate.rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation;
_estimate.translation += Vector3d(update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
/* 从函数不是g2o库要求完成的,而是根据实际需求新增的一个结构,根据估计值投影一个点 */
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
/* 将世界坐标转换为相机坐标 */
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation;
/* 相机坐标归一化平面 */
pc = -pc / pc[2];
/* 归一化平面的坐标去畸变的到相机的像素坐标 */
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm();
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2);
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0],
_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {
}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {
}
};
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() {
}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {
}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {
}
};
/* 定义边的方法
边的类型:BaseUnaryEdge,BaseBinaryEdge,BaseMultiEdge 分别表示一元边,两元边,多元边。
一元边你可以理解为一条边只连接一个顶点,两元边理解为一条边连接两个顶点,也就是我们常见的边啦,多元边理解为一条边可以连接多个(3个以上)顶点
virtual bool read(std::istream& is);
virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const;
// 使用当前顶点的值计算的测量值与真实的测量值之间的误差,注意是 _error = _measurement - proj,但是 _error = _proj - measurement 也可以,只是雅可比矩阵需要对应起来。
virtual void computeError();
// 在当前顶点的值下,该误差对优化变量的偏导数,也就是我们说的Jacobian;这里不实现雅可比计算方式,g2o自己会计算,此时_error用上述2种方式都可以。
virtual void linearizeOplus();
*/
class EdgeProjection :
public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
/* 使用当前顶点的值计算的测量值与真实的测量值之间的误差 */
virtual void computeError() override {
auto v0 = (VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *) _vertices[0];
auto v1 = (VertexPoint *) _vertices[1];
/* 计算估计值二维像素坐标,根据三维的相机坐标计算二维的像素坐标 */
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate());
/* 测量值减去估计值 */
_error = _measurement - proj;
}
// use numeric derivatives
virtual bool read(istream &in) {
}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {
}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_g2o bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* 将problem-16-22106-pre.txt文件数据解析出来 */
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize();
/* 给路标点坐标,相机位姿添加干扰 */
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
/* 路标点世界坐标地址,3维 */
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
/* 相机参数地址,9维 */
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
/* 第1步:创建一个线性求解器LinearSolver */
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
/* 第2步:创建BlockSolver。并用上面定义的线性求解器初始化 */
/* 第3步:use LM创建总求解器solver。并从GN, LM, DogLeg 中选一个,再用上述块求解器BlockSolver初始化 */
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
/* std::make_unique就是对智能指针的封装,std::unique_ptr */
std::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(std::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
/* 第4步:创建终极大boss 稀疏优化器(SparseOptimizer) */
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
/* build g2o problem,获取观测的像素坐标,二维变量 */
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
// vertex
/* 第5步:定义图的顶点和边。并添加到SparseOptimizer中 */
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
v->setId(i);
/* void setEstimate(const EstimateType& et) {
_estimate = et;
updateCache();
} g2o\core\base_vertex.h
*/
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera));
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras());
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2]));
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点,Marginalized边缘化求解
v->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
// edge
/* 第5步:定义图的顶点和边。并添加到SparseOptimizer中 */
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
/* 设置此边连接的顶点,二元边连接2个顶点的参数:第m个相机位姿下观测第n个路标点产生的测量值保存到 _measurement 中:测量值是2维像素坐标 */
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]);
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1]));
/* 信息矩阵,他是协方差矩阵之逆,在图优化中通过setInformation设置信息矩阵对边加权,也就是对改变在总体优化问题的重要性进行加权。
Matrix2d::Identity()是一个2*2的单位矩阵,意味着该约束的所有维度都具有相同的权重 */
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity());
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
/* 第6步:设置优化参数,开始执行优化 */
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
/* 两个入参:第一个是 iterations 设置优化过程的最大迭代次数,当迭代次数达到指定最大迭代次数或达到收敛条件则退出迭代。
第二个参数是 online 表示是否在线优化,在线优化通常用于实时系统中,意味着在优化过程中可以实时的向图中添加新的顶点和边,
在每次迭代后都会增量式更新图的结构,以便立即处理新的顶点和边。
我们使用时 online 一般默认为false,一次性将顶点和边添加完成后再进行求解。
g2o\core\sparse_optimizer.h:int optimize(int iterations, bool online = false);
g2o\core\sparse_optimizer.cpp:int SparseOptimizer::optimize(int iterations, bool online) */
optimizer.optimize(40);
/* 将迭代求解优化之后的参数更新到 cameras 的空间 */
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate();
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k];
}
}
1.2.2、Meshlab安装
- 添加第三方软件源
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:zarquon42/meshlab - 有时候会需要update一下
sudo apt-get update - 安装MeshLab
sudo apt-get install meshlab - 卸载MeshLab
sudo apt-get remove meshlab - 删除添加的第三方软件源,在 Ubuntu Linux 中移除或删除 PPA
sudo apt-get install ppa-purge /* 安装ppa管理的工具 */
sudo ppa-purge ppa:zarquon42/meshlab
PPA,英文全称为 Personal Package Archives,即个人软件包档案。是 Ubuntu Launchpad 网站提供的一项源服务,允许个人用户上传软件源代码,通过 Launchpad 进行编译并发布为二进制软件包,作为 apt / 新立得(Synaptic)源供其他用户下载和更新。
推荐资料:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_38364548/article/details/122129843
1.2.3、测试结果
执行命令:xb@ukylin:~/learn/practice/p7-ba/build/bin$ ./ba_g2o problem-16-22106-pre.txt
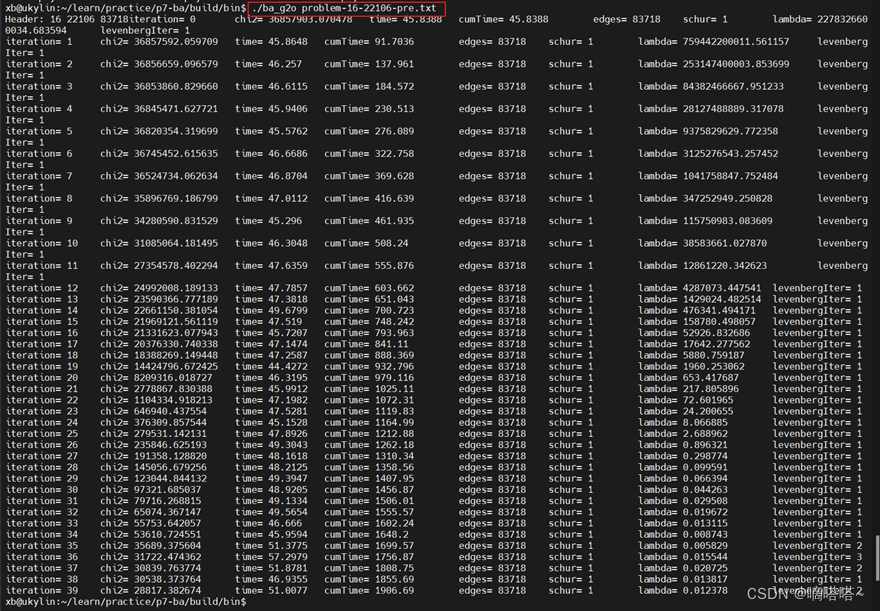
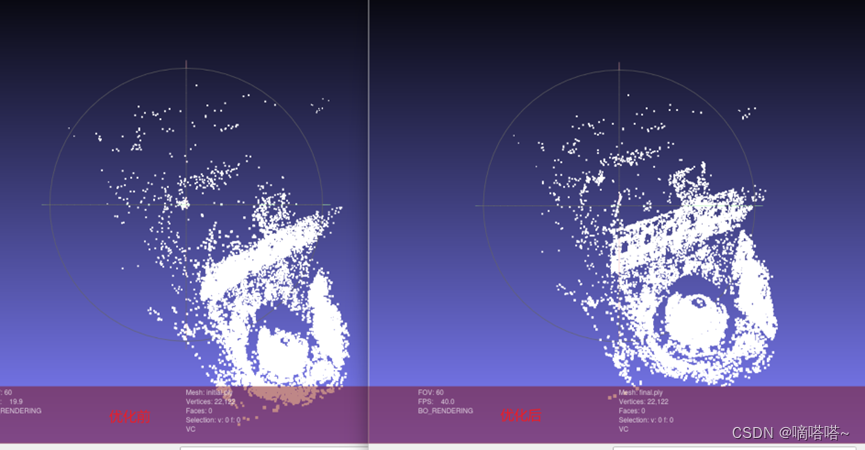
生成点云文件(相机16个位姿的世界坐标以及22106个路标点的世界坐标,三维):

使用mashlab可视化点云文件
xb@ukylin:~/learn/practice/p7-ba/build/bin$ meshlab initial.ply
xb@ukylin:~/learn/practice/p7-ba/build/bin$ meshlab final.ply
1.2.4、问题记录
- 使用旋转向量进行坐标变换问题
下面2个函数我没法理解这两个函数有什么作用,为什么需要这两个函数。c = -R’t这个是什么公式?
void BALProblem::CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(const double *camera,
double *angle_axis, double *center) const {
VectorRef angle_axis_ref(angle_axis, 3);
if (use_quaternions_) {
QuaternionToAngleAxis(camera, angle_axis);
} else {
/* ConstVectorRef 保证参数不会被改变 */
angle_axis_ref = ConstVectorRef(camera, 3




 博客围绕Bundle Adjustment展开,介绍了其数学模型、后端实践,包括数据集解析、最小二乘法求解等。还阐述了直接法的Bundle Adjustment,涉及数学模型和实践中的问题。此外,详细讲解了ceres库和G2o库的使用,如流程、代价函数、顶点和边的创建等。
博客围绕Bundle Adjustment展开,介绍了其数学模型、后端实践,包括数据集解析、最小二乘法求解等。还阐述了直接法的Bundle Adjustment,涉及数学模型和实践中的问题。此外,详细讲解了ceres库和G2o库的使用,如流程、代价函数、顶点和边的创建等。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1869
1869

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








