* @Author 一一哥Sun
* @Date Created in 2020/4/14
* @Description Description
* EnableCaching启用缓存
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
}
**5. 创建User实体类**
接着创建一个User实体类,封装用户信息。
package com.yyg.boot.domain;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Entity
@Table(name=“user”)
@Data
@ToString
public class User implements Serializable {
//IllegalArgumentException: DefaultSerializer requires a Serializable payload
// but received an object of type [com.syc.redis.domain.User]
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
@Column
private String username;
@Column
private String password;
}
**6. 创建User仓库类**
我们再创建一个JpaRepository,实现对数据库的CRUD操作。
package com.yyg.boot.repository;
import com.yyg.boot.domain.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Long> {
}
**7. 创建Service服务类**
**7.1 定义UserService接口**
package com.yyg.boot.service;
import com.yyg.boot.domain.User;
public interface UserService {
User findById(Long id);
User save(User user);
void deleteById(Long id);
}
**7.2 实现UserServiceImpl类**
package com.yyg.boot.service.impl;
import com.yyg.boot.domain.User;
import com.yyg.boot.repository.UserRepository;
import com.yyg.boot.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
//普通的缓存+数据库查询代码实现逻辑:
//User user=RedisUtil.get(key);
// if(user==null){
// user=userDao.findById(id);
// //redis的key=“product_item_”+id
// RedisUtil.set(key,user);
// }
// return user;
/**
* 注解@Cacheable:查询的时候才使用该注解!
* 注意:在Cacheable注解中支持EL表达式
* redis缓存的key=user_1/2/3…
* redis的缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存预热,缓存更新…
* condition = “#result ne null”,条件表达式,当满足某个条件的时候才进行缓存
* unless = “#result eq null”:当user对象为空的时候,不进行缓存
*/
@Cacheable(value = “user”, key = “#id”, unless = “#result eq null”)
@Override
public User findById(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
/**
* 注解@CachePut:一般用在添加和修改方法中
* 既往数据库中添加一个新的对象,于此同时也往redis缓存中添加一个对应的缓存.
* 这样可以达到缓存预热的目的.
*/
@CachePut(value = “user”, key = “#result.id”, unless = “#result eq null”)
@Override
public User save(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
/**
* CacheEvict:一般用在删除方法中
*/
@CacheEvict(value = “user”, key = “#id”)
@Override
public void deleteById(Long id) {
userRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
**8. 创建Controller接口方法**
然后创建一个Controller,定义几个URL接口进行测试。
package com.yyg.boot.web;
import com.yyg.boot.domain.User;
import com.yyg.boot.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(“/user”)
@Slf4j
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping
public User saveUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.save(user);
}
@GetMapping(“/{id}”)
public ResponseEntity getUserById(@PathVariable(“id”) Long id) {
User user = userService.findById(id);
log.warn(“user=”+user.hashCode());
HttpStatus status = user == null ? HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND : HttpStatus.OK;
return new ResponseEntity<>(user, status);
}
@DeleteMapping(“/{id}”)
public String removeUser(@PathVariable(“id”) Long id) {
userService.deleteById(id);
return “ok”;
}
}
#### **9. 创建入口类**
最后创建一个项目入口类,启动项目。
package com.yyg.boot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
#### **10. 项目代码结构**
## 总结:绘上一张Kakfa架构思维大纲脑图(xmind)
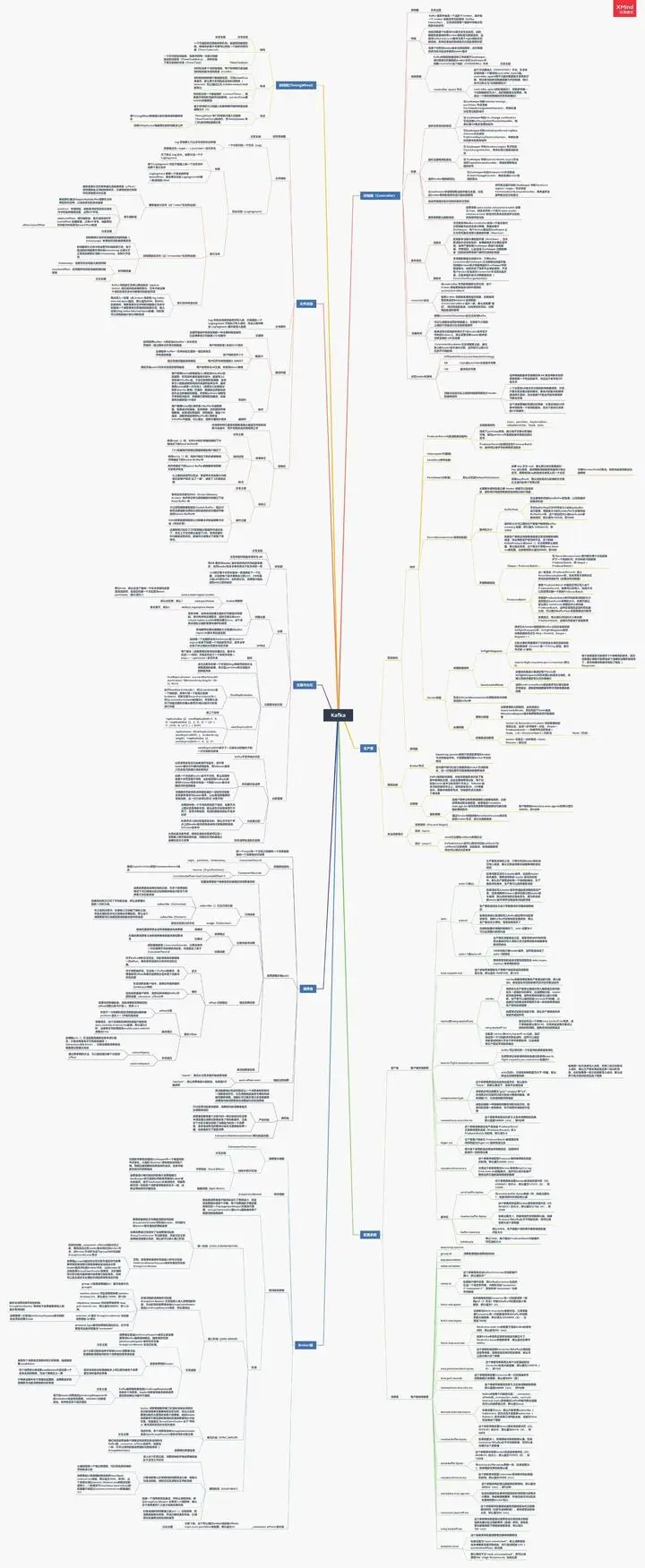
其实关于Kafka,能问的问题实在是太多了,扒了几天,最终筛选出44问:基础篇17问、进阶篇15问、高级篇12问,个个直戳痛点,不知道如果你不着急看答案,又能答出几个呢?
若是对Kafka的知识还回忆不起来,不妨先看我手绘的知识总结脑图(xmind不能上传,文章里用的是图片版)进行整体架构的梳理
梳理了知识,刷完了面试,如若你还想进一步的深入学习解读kafka以及源码,那么接下来的这份《手写“kafka”》将会是个不错的选择。
* Kafka入门
* 为什么选择Kafka
* Kafka的安装、管理和配置
* Kafka的集群
* 第一个Kafka程序
* Kafka的生产者
* Kafka的消费者
* 深入理解Kafka
* 可靠的数据传递
* Spring和Kafka的整合
* SpringBoot和Kafka的整合
* Kafka实战之削峰填谷
* 数据管道和流式处理(了解即可)

Kafka的集群
* 第一个Kafka程序
* Kafka的生产者
* Kafka的消费者
* 深入理解Kafka
* 可靠的数据传递
* Spring和Kafka的整合
* SpringBoot和Kafka的整合
* Kafka实战之削峰填谷
* 数据管道和流式处理(了解即可)
[外链图片转存中...(img-ndqNbzaa-1714756391022)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-4vY3Myv7-1714756391022)]
> **本文已被[CODING开源项目:【一线大厂Java面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+最新讲解视频+实战项目源码】](https://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/618154847)收录**





















 1256
1256

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








