因为本期使用C语言来实现代码,由于C语言不支持栈,所以我们要先实现栈的模拟。
栈的结构特点和实现
栈的结构特点:只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除的操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的元素遵循先进后出的原则。
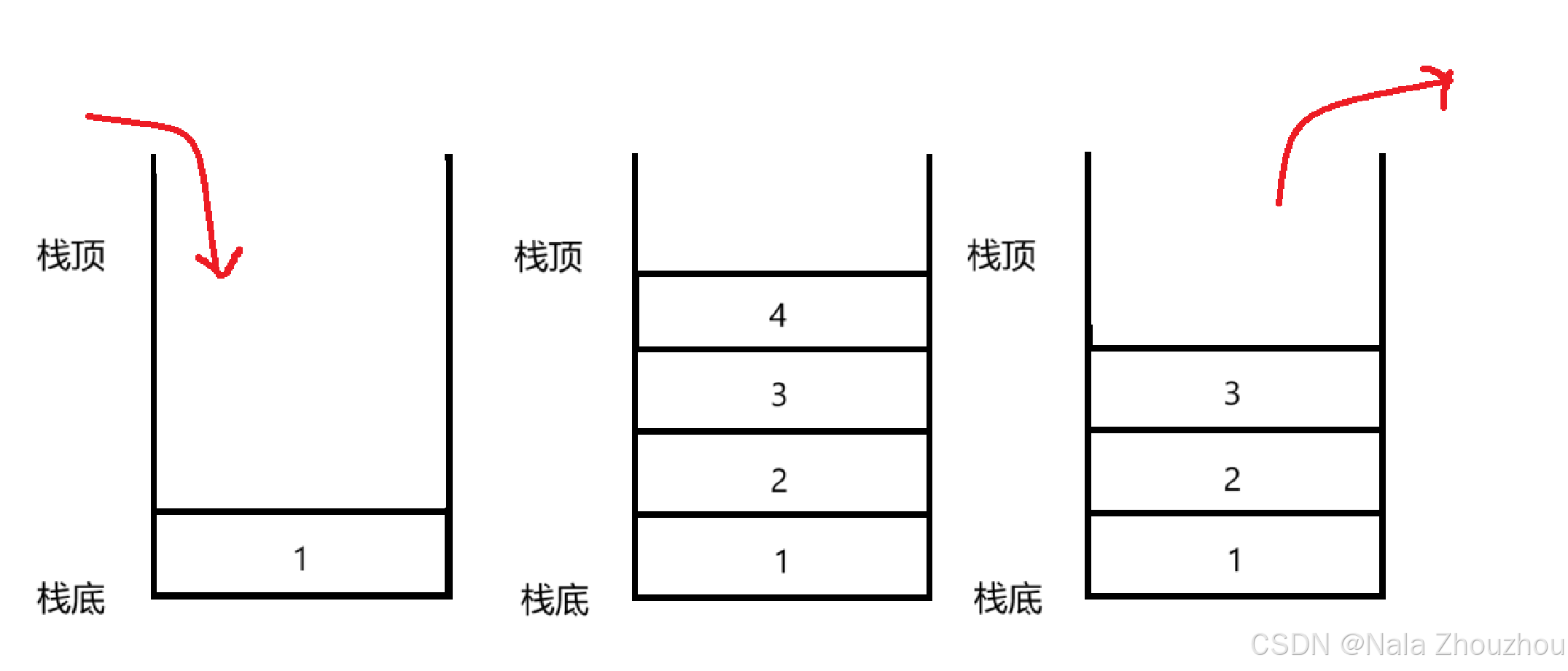
栈的实现:栈的实现可以用数组和链表来实现,如果用数组来实现栈,入栈就在数组尾上插入数据,出栈就在数组尾上删除数据,很容易实现效率高;如果用链表实现栈,将链表头作为栈顶,入栈就是头插,出栈就是尾删,效率没有用数组实现高,所以我选择用数组实现栈的结构。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
int* a;
int top;
int capacity;
} ST;
void STInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void STDestroy(ST* ps);//销毁栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//入栈
void STPop(ST* ps);//出栈
int STSize(ST* ps);//获取栈的有效元素个数
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);//检查栈是否为空
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素
void STInit(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0; // 栈顶元素的下一个位置
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) {
assert(ps);
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) {
STDataType* tmp =
(STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc");
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
void STPop(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}题目:用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
思路
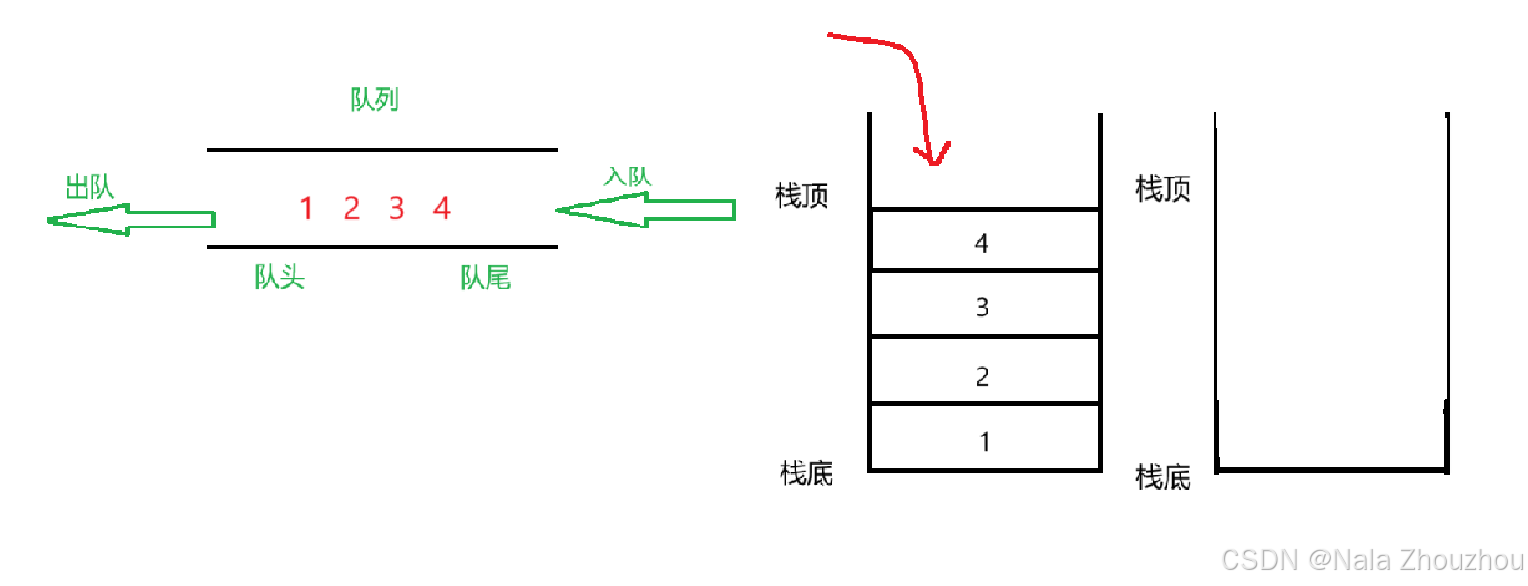
用栈实现入队操作很容易,由于栈只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作,而队列只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,如果我们想要出队删除元素1,相当于第一个栈的栈底元素1,就要把1上面的其他元素都移动到第二个栈中,
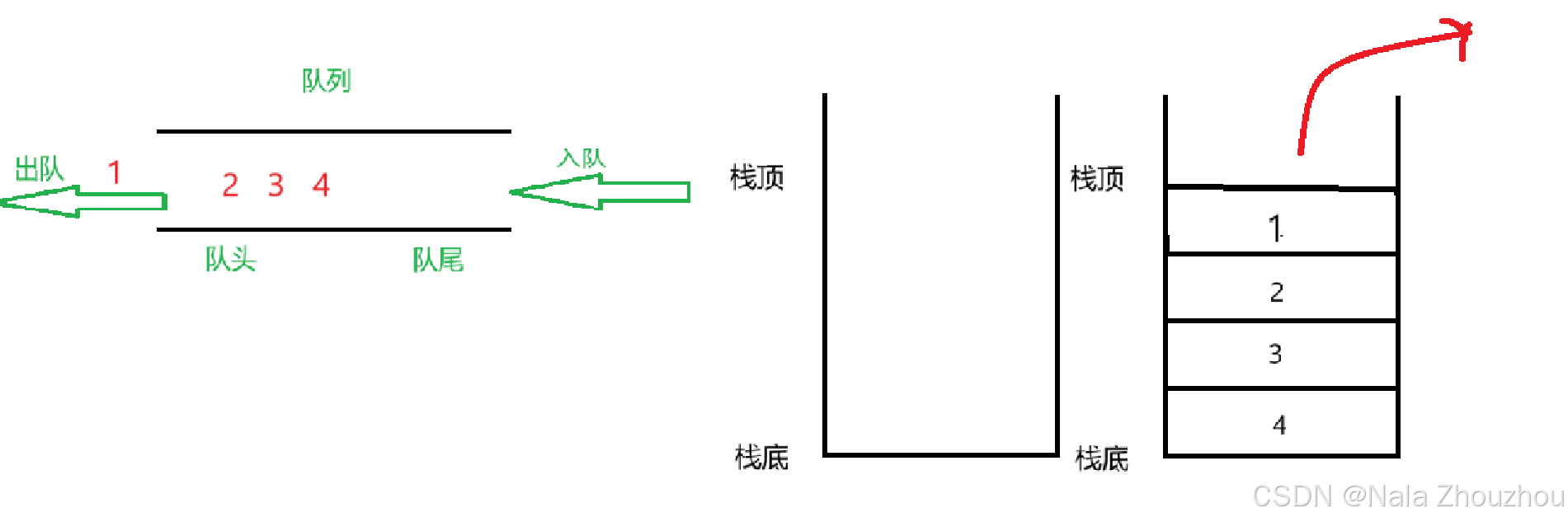
如果我们想要继续插入元素,应该该如何插入?
如果我们直接向第二个栈中插入元素,就会导致元素的顺序不对,那如果我们向第一个栈中插入元素,我们是否需要将第二个栈中的元素移动回来?
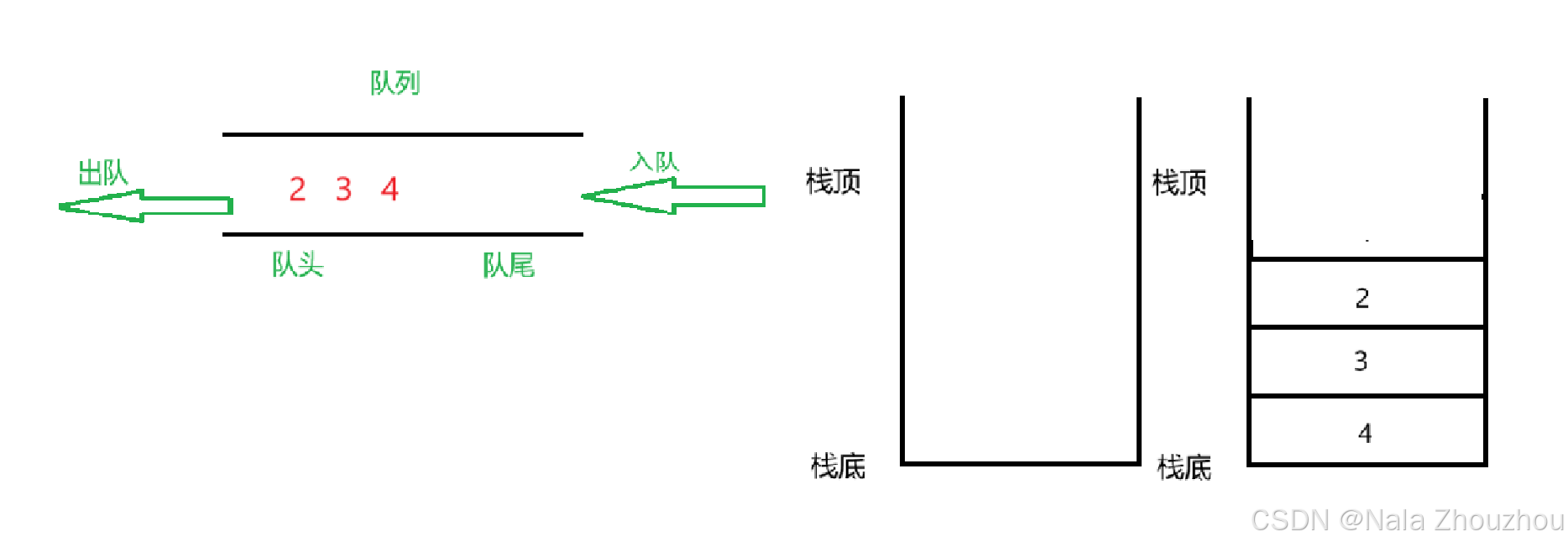
经过观察我们发现,如果此时继续出队删除元素,出队的顺序第二个栈出栈的顺序相同,即我们不需要将第二个栈中的数据倒回到第一个栈中,只需要将新入队的元素放在第一个栈中即可,如果需要出栈,就从第二个栈中直接获取栈顶元素。
总的来说就是,第一个栈负责入队,第二个栈负责出队,如果出队的时候第二个栈为空,就将第一个栈中的元素倒到第二个栈中。
如果想要判断队列是否为空,就要判断两个栈是否都为空。
代码(C语言版)
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack {
int* a;
int top;
int capacity;
} ST;
void STInit(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return;
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0; // 栈顶元素的下一个位置
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) {
assert(ps);
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity) {
STDataType* tmp =
(STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc");
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
void STPop(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
typedef struct {
ST stpush;
ST stpop;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* queue = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if (queue == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
STInit(&queue->stpush);
STInit(&queue->stpop);
return queue;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->stpush, x);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if (STEmpty(&obj->stpop)) {
// 倒数据
while (!STEmpty(&obj->stpush)) {
STPush(&obj->stpop, STTop(&obj->stpush));
STPop(&obj->stpush);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->stpop);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int ret = myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->stpop);
return ret;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->stpush) && STEmpty(&obj->stpop);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->stpush);
STDestroy(&obj->stpop);
free(obj);
}持续更新,下期见
























 2534
2534

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








