Fibonacci
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 14845 Accepted: 10442
Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
 .
.
Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000).
Sample Input
0
9
999999999
1000000000
-1
Sample Output
0
34
626
6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
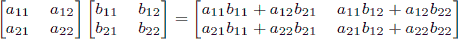 .
.
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
 .
.
Source
#include <stdio.h>
const int mod=10000;
struct matrix
{
int a[2][2];
}origin,res;
struct matrix multiply(struct matrix x,struct matrix y)
{ int i,j,k;
struct matrix temp;
memset(temp.a, 0, sizeof(temp.a));
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
for(k=0;k<2;k++)
temp.a[i][j]+=(x.a[i][k]%mod)*(y.a[k][j]%mod)%mod;
return temp;
}
void init()
{
memset(res.a, 0, sizeof(res.a));
res.a[0][0]=res.a[1][1]=1;
}
void calc(long long n)
{
while(n)
{
if(n&1)
res=multiply(res, origin);
n>>=1;
origin=multiply(origin, origin);
}
printf("%d\n",res.a[1][0]%10000);
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
long long n;
while(scanf("%lld",&n) && n!=-1)
{ origin.a[0][0]=1,origin.a[0][1]=1,origin.a[1][0]=1,origin.a[1][1]=0;
init();
calc(n);
init();
}
return 0;
}
通过这个题目学习到了矩阵快速幂~~~,感觉萌萌大~~~
顺便贴一下快速幂代码
int pw(int a, int b)
{
int r = 1, base = a;
while (b != 0)
{
if (b & 1)
r *= base;
base *= base;
b >>= 1;
}
return r;
}
比较一下,其实矩阵快速幂只是将乘法变为了一种函数,其实想想普通的a*b中乘法也是一种函数,类比一下吧
再来一个矩阵快速幂
#include <stdio.h>
#define mod 9973
struct matrix
{
int a[10][10];
}res,origin;
struct matrix multiply(struct matrix x,struct matrix y)
{ int i,j,k;
struct matrix temp;
memset(temp.a, 0, sizeof(temp.a));
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
for(j=0;j<10;j++)
for(k=0;k<10;k++)
temp.a[i][j]+=(x.a[i][k]%mod)*(y.a[k][j]%mod)%mod;
return temp;
}
void calc(long long n)
{
while(n)
{
if(n&1)
res=multiply(res, origin);
n>>=1;
origin=multiply(origin, origin);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
int n,k,t,i,j,g,sum;
scanf("%d",&t);
for(i=0;i<t;i++)
{ sum=0;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
memset(res.a, 0, sizeof(res.a));
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
res.a[j][j]=1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
for(g=0;g<n;g++)
scanf("%d",&origin.a[j][g]);
calc(k);
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
sum+=res.a[j][j]%mod;
sum%=mod;
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#define mod 10000007
long long n,m;
struct matrix
{
long long a[15][15];
}origin,res;
struct matrix multiply(struct matrix x,struct matrix y,long long q,long long w)
{
long long i,j,k;
struct matrix temp;
memset(temp.a,0,sizeof(temp.a));
for(i=0;i<q;i++)
for(j=0;j<w;j++)
for(k=0;k<w;k++)
temp.a[i][j]+=(x.a[i][k])*(y.a[k][j])%mod;//通过i判断,则为矩阵x*y;
return temp;
}
void init()
{
long long i,k;
memset(origin.a,0,sizeof(origin.a));
memset(res.a,0,sizeof(res.a));
for(i=0;i<=n+1;i++)
{
origin.a[0][i]=10;
origin.a[i][n+1]=0;
origin.a[n+1][i]=1;
res.a[i][i]=1;
}
origin.a[0][n+1]=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(k=i;k<=n;k++)
origin.a[i][k]=1;
}
void calc()
{
while(m)
{
if(m&1)
res=multiply( res,origin,n+2,n+2);
m>>=1;
origin=multiply(origin, origin,n+2,n+2);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
long long i;
struct matrix c;
memset(c.a,0,sizeof(c.a));
while(~scanf("%lld %lld",&n,&m))
{
getchar();
c.a[0][0]=23,c.a[0][n+1]=3;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lld",&c.a[0][i]);
init();
calc();
c=multiply(c, res, 1,n+2);
printf("%lld\n",c.a[0][n]%mod);
}
return 0;
}
都是一个模块,可以学习一下





 本文介绍了如何使用矩阵快速幂技术解决特定数学问题,包括求解斐波那契数列的高效算法及矩阵幂运算的应用。
本文介绍了如何使用矩阵快速幂技术解决特定数学问题,包括求解斐波那契数列的高效算法及矩阵幂运算的应用。

















 7416
7416

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








