题目描述:
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
题目分析:
这道题是在上一道题“Linked List Cycle”的扩充,也就是当链表存在“环”的时候,要找到“环”开始的位置。所以判断是否有环的实现不再赘述,重点分析一下确定链表有环之后,如何判断环的起始位置。
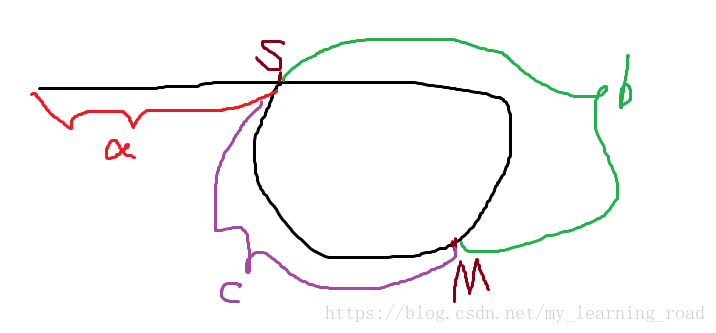
上图中,S表示的是环的起始位置,也就是我们最终要找的起始结点;M代表的是p1和p2相遇的位置,也就是它们相遇的结点;a、b、c代表的是指针走过的距离。
因为p2的速度是p1的2倍,二者在M点相遇,所以我们很容易得出,当二者在M点相遇时:p1走过的距离为(a+b),p2走过的距离为(a+b+c+b)=(a+2b+c);又因为p2速度为p1的两倍,且二者走的时间相同,所以有距离公式(s=v*t)可得,a+2b+c=2(a+b),所以可以得出a==c。此时,重新定义一个新的指向头结点的指针slow,当slow在头结点开始以每一次走一步的速度向前扫描,p1在M点开始也已每一次走一步的速度向前扫描,二者会在同时到达S点,也就是我们最终需要的位置!
Java实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null ||head.next.next==null)
return null;
ListNode p1=head;
ListNode p2=head;
while(p2!=null && p2.next!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next.next;
if(p1==p2){
ListNode slow=head;
while(slow!=p1){
slow=slow.next;
p1=p1.next;
}
return p1;
}
}
return null;
}
}




 本文介绍了一种高效算法来确定链表中环的起始节点。通过快慢指针定位相遇点后,利用数学原理找到环的入口。
本文介绍了一种高效算法来确定链表中环的起始节点。通过快慢指针定位相遇点后,利用数学原理找到环的入口。
















 475
475

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








