蚁群算法
基本原理
蚁群算法是对自然界蚂蚁的寻径方式进行模拟而得出的一中仿生算法:蚂蚁在运动过程中,能够在它所经过的路径上留下信息素的物质进行信息传递,而且蚂蚁在运动过程中能够感知这种物质,并以此指导自己的运动方向。
基本流程
在ACO算法中,人工蚂蚁实际上代表的是一个解得随机结构过程,从最初的空解开始,通过不断地向部分解添加解得成分而构建出一个完整的解
AS算法对TSP的求解主要有两大步骤:
1、路径构建
2、信息素更新
代码实现
%% 旅行商问题(TSP)优化
%% 清空环境变量
clear all
clc
%% 导入数据
load citys_1.mat
%citys=round(rand(31,2)*3000)+1000;
%save citys_1 citys;
%% 计算城市间相互距离
fprintf('Computing Distance Matrix... \n');
n = size(citys,1);
D = zeros(n,n);
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:n
if i ~= j
D(i,j) = sqrt(sum((citys(i,:) - citys(j,:)).^2));
else
D(i,j) = 1e-4;
end
end
end
%% 初始化参数
fprintf('Initializing Parameters... \n');
m = 50; % 蚂蚁数量
alpha = 1; % 信息素重要程度因子
beta = 5; % 启发函数重要程度因子
rho = 0.1; % 信息素挥发因子
Q = 1; % 常系数
Eta = 1./D; % 启发函数
Tau = ones(n,n); % 信息素矩阵
Table = zeros(m,n); % 路径记录表
iter = 1; % 迭代次数初值
iter_max = 150; % 最大迭代次数
Route_best = zeros(iter_max,n); % 各代最佳路径
Length_best = zeros(iter_max,1); % 各代最佳路径的长度
Length_ave = zeros(iter_max,1); % 各代路径的平均长度
%% 迭代寻找最佳路径
figure;
while iter <= iter_max
fprintf('迭代第%d次\n',iter);
% 随机产生各个蚂蚁的起点城市
start = zeros(m,1);
for i = 1:m
temp = randperm(n);
start(i) = temp(1);
end
Table(:,1) = start;
% 构建解空间
citys_index = 1:n;
% 逐个蚂蚁路径选择
for i = 1:m
% 逐个城市路径选择
for j = 2:n
tabu = Table(i,1:(j - 1)); % 已访问的城市集合(禁忌表)
allow_index = ~ismember(citys_index,tabu);
allow = citys_index(allow_index); % 待访问的城市集合
P = allow;
% 计算城市间转移概率
for k = 1:length(allow)
P(k) = Tau(tabu(end),allow(k))^alpha * Eta(tabu(end),allow(k))^beta;
end
P = P/sum(P);
% 轮盘赌法选择下一个访问城市
Pc = cumsum(P);
target_index = find(Pc >= rand);
target = allow(target_index(1));
Table(i,j) = target;
end
end
% 计算各个蚂蚁的路径距离
Length = zeros(m,1);
for i = 1:m
Route = Table(i,:);
for j = 1:(n - 1)
Length(i) = Length(i) + D(Route(j),Route(j + 1));
end
Length(i) = Length(i) + D(Route(n),Route(1));
end
% 计算最短路径距离及平均距离
if iter == 1
[min_Length,min_index] = min(Length);
Length_best(iter) = min_Length;
Length_ave(iter) = mean(Length);
Route_best(iter,:) = Table(min_index,:);
else
[min_Length,min_index] = min(Length);
Length_best(iter) = min(Length_best(iter - 1),min_Length);
Length_ave(iter) = mean(Length);
if Length_best(iter) == min_Length
Route_best(iter,:) = Table(min_index,:);
else
Route_best(iter,:) = Route_best((iter-1),:);
end
end
% 更新信息素
Delta_Tau = zeros(n,n);
% 逐个蚂蚁计算
for i = 1:m
% 逐个城市计算
for j = 1:(n - 1)
Delta_Tau(Table(i,j),Table(i,j+1)) = Delta_Tau(Table(i,j),Table(i,j+1)) + Q/Length(i);
end
Delta_Tau(Table(i,n),Table(i,1)) = Delta_Tau(Table(i,n),Table(i,1)) + Q/Length(i);
end
Tau = (1-rho) * Tau + Delta_Tau;
% 迭代次数加1,清空路径记录表
% figure;
%最佳路径的迭代变化过程
[Shortest_Length,index] = min(Length_best(1:iter));
Shortest_Route = Route_best(index,:);
plot([citys(Shortest_Route,1);citys(Shortest_Route(1),1)],...
[citys(Shortest_Route,2);citys(Shortest_Route(1),2)],'o-');
pause(0.3);
iter = iter + 1;
Table = zeros(m,n);
% end
end
%% 结果显示
[Shortest_Length,index] = min(Length_best);
Shortest_Route = Route_best(index,:);
disp(['最短距离:' num2str(Shortest_Length)]);
disp(['最短路径:' num2str([Shortest_Route Shortest_Route(1)])]);
%% 绘图
figure(1)
plot([citys(Shortest_Route,1);citys(Shortest_Route(1),1)],...
[citys(Shortest_Route,2);citys(Shortest_Route(1),2)],'o-');
grid on
for i = 1:size(citys,1)
text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)]);
end
text(citys(Shortest_Route(1),1),citys(Shortest_Route(1),2),' 起点');
text(citys(Shortest_Route(end),1),citys(Shortest_Route(end),2),' 终点');
xlabel('城市位置横坐标')
ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')
title(['蚁群算法优化路径(最短距离:' num2str(Shortest_Length) ')'])
figure(2)
plot(1:iter_max,Length_best,'b',1:iter_max,Length_ave,'r:')
legend('最短距离','平均距离')
xlabel('迭代次数')
ylabel('距离')
title('各代最短距离与平均距离对比')结果分析
一、alpha(信息素重要程度因子)影响分析:
1、alpha=1 beta=5 rho=0.1

2、alpha=3 beta=5 rho=0.1

3、alpha=5 beta=5 rho=0.1
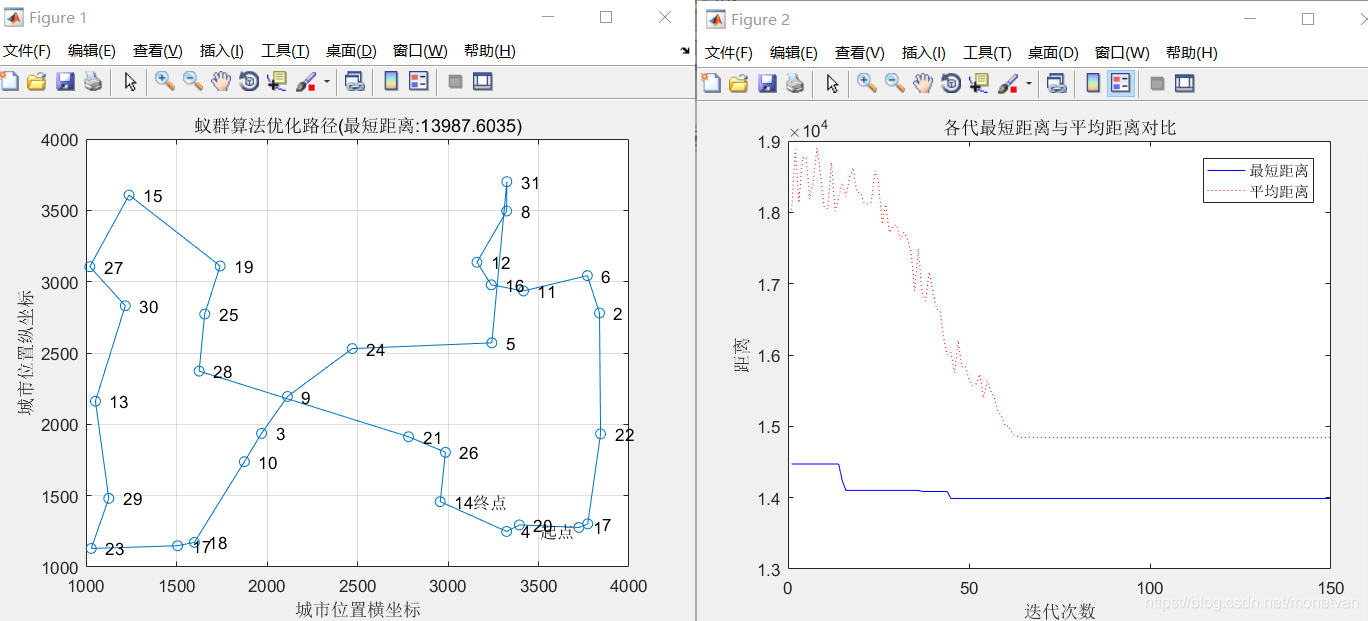 总结:alpha值(反映蚂蚁在运动过程中所积累的信息量在指导蚁群搜索中的相对重要程度)对算法性能有较大影响,alpha值越大,蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大,搜索路径的随机性减弱,算法会出现过早收敛;alpha值越小,蚁群搜索范围就会减少,收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部最优。
总结:alpha值(反映蚂蚁在运动过程中所积累的信息量在指导蚁群搜索中的相对重要程度)对算法性能有较大影响,alpha值越大,蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大,搜索路径的随机性减弱,算法会出现过早收敛;alpha值越小,蚁群搜索范围就会减少,收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部最优。
二、beta(启发函数重要程度因子)影响分析:
1、alpha=1 beta=2 rho=0.1

2、alpha=1 beta=3 rho=0.1

3、alpha=1 beta=4 rho=0.1

总结:beta(反映了启发式信息在指导蚁群搜索过程中的相对重要程度)值过小,蚁群陷入随机的局部搜索,难以找到最优解;值过大,算法收敛性能有变差的趋势,蚁群搜索最优路径的随机性减弱,容易陷入局部最优。
三、rho(信息素挥发因子)影响分析:
1、alpha=1 beta=5 rho=0.1

2、alpha=1 beta=5 rho=0.5

3、alpha=1 beta=5 rho=0.9
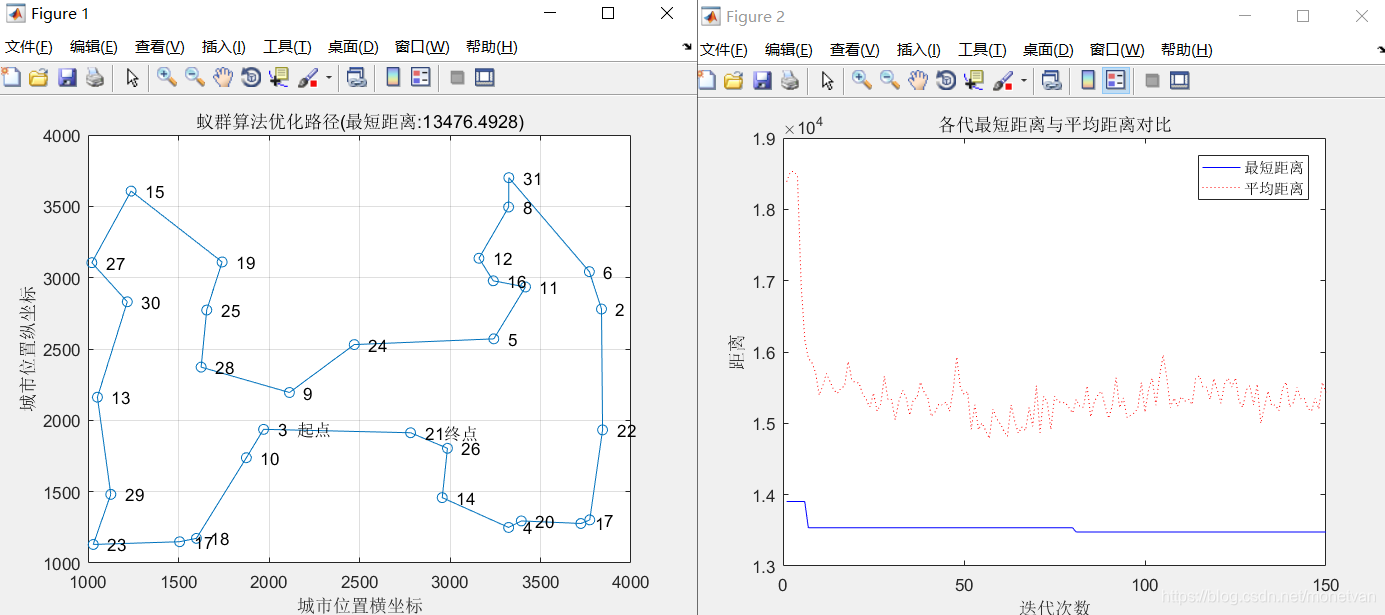
总结:当rho值过小时,在各路径上残留的信息素过多,导致无效的路径会继续被搜索,影响到算法的收敛速率;rho过大,无效的路径虽然可以被排除搜索,但是不能保证有效的路径也会被放弃搜索,影响到最优值的搜索。




 本文详细介绍了蚁群算法的基本原理和流程,包括路径构建和信息素更新两个关键步骤。通过代码实现展示了算法在解决旅行商问题中的应用,并深入分析了alpha、beta和rho三个参数对算法性能的影响,探讨了如何平衡全局搜索和局部最优的问题。
本文详细介绍了蚁群算法的基本原理和流程,包括路径构建和信息素更新两个关键步骤。通过代码实现展示了算法在解决旅行商问题中的应用,并深入分析了alpha、beta和rho三个参数对算法性能的影响,探讨了如何平衡全局搜索和局部最优的问题。
















 506
506

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








