1 问题
之前的案例都是线线性的,但实际情况常面临很多非线性问题,比如:
假设平面上有一飞行器,初始坐标为(x0,y0)(x_0,y_0)(x0,y0),需要该飞行器基于该平面完成一个圆形运动,模型如下;
(1)建模
xt+1=xt+vx∗dt∗cos(w)x_{t+1} = x_t+v_x*dt*cos(w)xt+1=xt+vx∗dt∗cos(w)
yt+1=yt+vy∗dt∗sin(w)y_{t+1} = y_t+v_y*dt*sin(w)yt+1=yt+vy∗dt∗sin(w)
wt+1=wt+Δ(w)∗dtw_{t+1} = w_t+\Delta(w)*dtwt+1=wt+Δ(w)∗dt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
"""
速度:X = X0 + V_X * t * cos(w)
位置:Y = Y0 + V_Y * t * sin(w)
角速度:W = W0 + Dw * t
"""
DT = 0.1
SIM_TIME = 500.0
H = np.array([[1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0]])
def calc_input():
v = 1.0 # [m/s]
yawrate = 0.1 # [rad/s]
u = np.array([[v], [yawrate]])
return u
def motion_model(x,u):
A = np.array([[1.0, 0.0,0.0],
[0.0, 1.0,0.0],
[0.0, 0.0,1.0]])
B = np.array([[DT * np.cos(x[2, 0]), 0],
[DT * np.sin(x[2, 0]), 0],
[0.0, DT]])
x = A @ x +B @ u
return x
def observation_model(x):
H = np.array([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0]])
z = H @ x
return z
time=0
x_array = []
y_array = []
xTrue = np.zeros((3, 1))
u = np.array([[1. ],
[0.01]])
while SIM_TIME >= time:
xTrue = motion_model(xTrue,u)
x_array.append(xTrue[0,0])
y_array.append(xTrue[1,0])
time += DT
plt.figure(0)
plt.plot(x_array,y_array,'g')
plt.show()
然而现实总存在各种噪声,以至于模型并不会像设计那样得到想要的结构,在上述模型的输入和观测加入噪声。可以得到观测模型
def observation(x, xd, u):
x = motion_model(x, u)
z = observation_model(xTrue) + NOISE_OP @ np.random.randn(2, 1)
ud = u + NOISE_INPUT @ np.random.randn(2, 1)
xd = motion_model(xd, ud)
return x, z, xd, ud
运行后能的到如下结果:
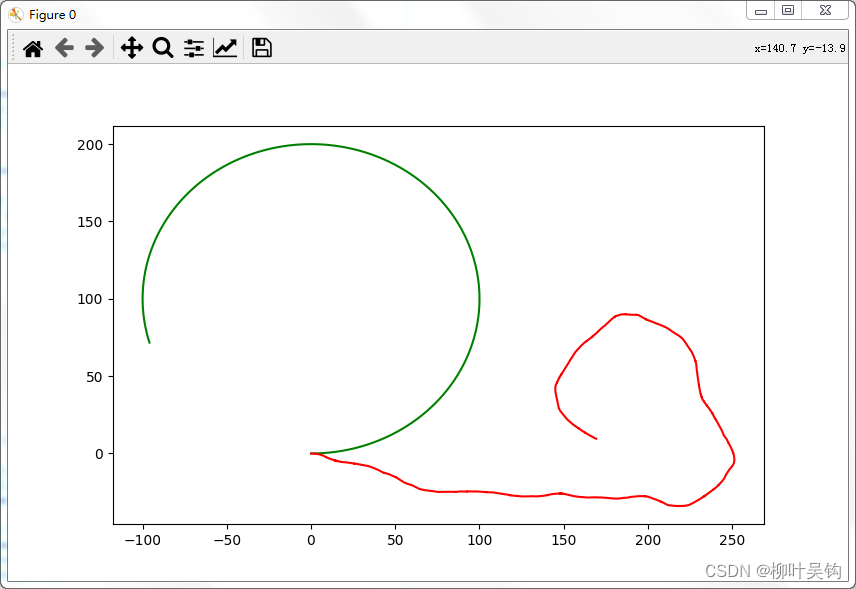
可见失之毫厘谬以千里,如果不加以滤波和修正,该飞行器将不会按理想的运行轨迹运行。
由于所构建的模型引入了三角函数,该模型将不是一个线性模型,卡尔曼滤波将不再适用,因此引入了扩展卡尔曼滤波。
首先需要构建雅克比矩阵:
有模型函数可得:
(2)状态空间方程
略




 文章探讨了在飞行器模型中遇到的非线性问题,如圆形运动的建模,模型包含速度、位置和角速度的动态变化。由于现实中的噪声影响,模型预测与实际运行轨迹产生偏差。为解决这一问题,文章提到了扩展卡尔曼滤波,它是对线性卡尔曼滤波的扩展,适用于处理非线性系统。通过构建雅克比矩阵,实现对飞行器状态的估计和校正,以减小噪声带来的误差。仿真结果显示,扩展卡尔曼滤波对于非线性模型的滤波效果显著。
文章探讨了在飞行器模型中遇到的非线性问题,如圆形运动的建模,模型包含速度、位置和角速度的动态变化。由于现实中的噪声影响,模型预测与实际运行轨迹产生偏差。为解决这一问题,文章提到了扩展卡尔曼滤波,它是对线性卡尔曼滤波的扩展,适用于处理非线性系统。通过构建雅克比矩阵,实现对飞行器状态的估计和校正,以减小噪声带来的误差。仿真结果显示,扩展卡尔曼滤波对于非线性模型的滤波效果显著。
















 2300
2300

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








