Intersection
Time Limit: 4000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 512000/512000 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 206 Accepted Submission(s): 86
Problem Description
Matt is a big fan of logo design. Recently he falls in love with logo made up by rings. The following figures are some famous examples you may know.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.
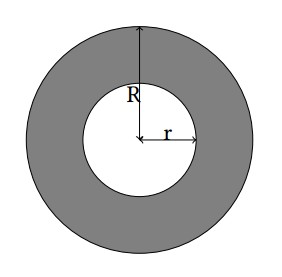
Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.

A ring is a 2-D figure bounded by two circles sharing the common center. The radius for these circles are denoted by r and R (r < R). For more details, refer to the gray part in the illustration below.

Matt just designed a new logo consisting of two rings with the same size in the 2-D plane. For his interests, Matt would like to know the area of the intersection of these two rings.
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T ≤ 105), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, the first line contains two integers r, R (0 ≤ r < R ≤ 10).
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Each of the following two lines contains two integers xi, yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 20) indicating the coordinates of the center of each ring.
Output
For each test case, output a single line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the area of intersection rounded to 6 decimal places.
Sample Input
2 2 3 0 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 5 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 15.707963 Case #2: 2.250778
题意:已经说完了,求两个圆环的相交面积。
题解:如图所示,两圆环相交面积即使外圆相交面积S1减去两倍外圆和内圆相交面积S2加上内圆相交面积S3.
求两圆相交面积可根据余弦定理求出两扇形面积减去四边形面积即可。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#define LL __int64
#define eps 1e-8
#define pi acos(-1)
using namespace std;
struct point{
double x,y;
};
struct circle{
point c;
double r;
};
double CS(circle a,circle b){ //求两圆相交面积
double d=sqrt((a.c.x-b.c.x)*(a.c.x-b.c.x)+(a.c.y-b.c.y)*(a.c.y-b.c.y));
if (a.r<b.r){
circle g;
g=a;
a=b;
b=g;
}
if (a.r+b.r<=d) return 0; //两圆相离
if (a.r-b.r>=d){
return (pi*b.r*b.r);
} //大圆包含小圆
double a1=acos((d*d+a.r*a.r-b.r*b.r)/(2*a.r*d));
double b1=acos((d*d+b.r*b.r-a.r*a.r)/(2*b.r*d));
double s=a1*a.r*a.r+b1*b.r*b.r;
double s1=a.r*d*sin(a1);
return s-s1;
}
int main(){
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
for (int cas=1;cas<=T;cas++){
circle a,b;
scanf("%lf%lf",&a.r,&b.r);
scanf("%lf%lf",&a.c.x,&a.c.y);
scanf("%lf%lf",&b.c.x,&b.c.y);
circle c=a;
c.r=b.r;
circle d=b;
d.r=a.r;
double s1=CS(c,b);
double s2=CS(a,b);
double s3=CS(a,d);
printf("Case #%d: %f\n",cas,s1-2*s2+s3);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一种计算两个相同大小圆环相交面积的方法,通过分解为外圆相交面积、内外圆相交面积及内圆相交面积进行求解,并提供了具体的算法实现。
本文介绍了一种计算两个相同大小圆环相交面积的方法,通过分解为外圆相交面积、内外圆相交面积及内圆相交面积进行求解,并提供了具体的算法实现。
















 1414
1414

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








