子图工具Subplottool类概述
matplotlib部件(widgets)提供了子图工具(Subplottool类)用于调整子图的相关参数(边距、间距)。
子图工具实现定义为matplotlib.widgets.Subplottool类,继承关系为:Widget->AxesWidget->Subplottool。
Subplottool类的签名为class matplotlib.widgets.SubplotTool(targetfig, toolfig)。
Subplottool类构造函数的参数为:
targetfig:子图工具控制的图像,类型为matplotlib.figure.Figure的实例。toolfig:子图工具所在的图像,类型为matplotlib.figure.Figure的实例。
子图工具由6个滑动条和1个重置按钮构成。
Subplottool类通过6个滑动条调整图像子图的边距、间距等参数。Subplottool类通过将targetfig.subplots_adjust()方法与滑动条的on_changed(func)方法绑定实现对图像子图参数的调整。Subplottool类的重置按钮回调函数的基本功能其实就是滑动条的reset()方法
plt.subplot_tool()原理
pyplot模块提供了subplot_tool()函数用于快速构造子图工具。
subplot_tool()函数的签名为def subplot_tool(targetfig=None) -> SubplotTool(targetfig, toolfig)
subplot_tool()函数的参数为targetfig,即需要调整子图的图像,类型为matplotlib.figure.Figure的实例,默认值为None。
subplot_tool()函数的返回值为SubplotTool(targetfig, toolfig)。
根据subplot_tool()函数可知,如果targetfig参数为None,那么targetfig = gcf(),即当前图像。subplot_tool()函数随后创建一个没有工具栏的图像toolfig,完成SubplotTool()实例的构造。
案例:官方示例
https://matplotlib.org/gallery/subplots_axes_and_figures/subplot_toolbar.html
Figure2为直接使用Subplottool类创建的工具,Figure3为使用subplot_tool函数创建的工具。
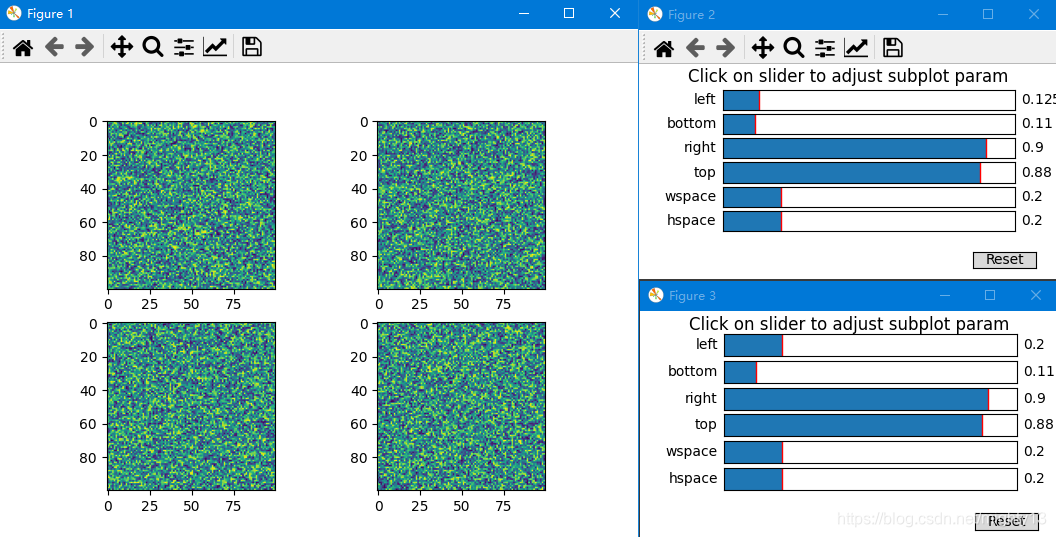
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.widgets import SubplotTool
np.random.seed(19680801)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2)
axs[0, 0].imshow(np.random.random((100, 100)))
axs[0, 1].imshow(np.random.random((100, 100)))
axs[1, 0].imshow(np.random.random((100, 100)))
axs[1, 1].imshow(np.random.random((100, 100)))
# 使用SubplotTool类创建工具
fig_tool = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
tool = SubplotTool(fig,fig_tool)
# 使用subplot_tool函数创建工具
plt.subplot_tool()
plt.show()
源码
plt.subplot_tool()源码
def subplot_tool(targetfig=None):
"""
Launch a subplot tool window for a figure.
A :class:`matplotlib.widgets.SubplotTool` instance is returned.
"""
if targetfig is None:
targetfig = gcf()
with rc_context({'toolbar': 'None'}): # No nav toolbar for the toolfig.
toolfig = figure(figsize=(6, 3))
toolfig.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
if hasattr(targetfig.canvas, "manager"): # Restore the current figure.
_pylab_helpers.Gcf.set_active(targetfig.canvas.manager)
return SubplotTool(targetfig, toolfig)
Subplottool类部分源码
self._sliders = []
names = ["left", "bottom", "right", "top", "wspace", "hspace"]
# The last subplot, removed below, keeps space for the "Reset" button.
for name, ax in zip(names, toolfig.subplots(len(names) + 1)):
ax.set_navigate(False)
slider = Slider(ax, name,
0, 1, getattr(targetfig.subplotpars, name))
slider.on_changed(self._on_slider_changed)
self._sliders.append(slider)
with cbook._setattr_cm(toolfig.subplotpars, validate=False):
self.buttonreset.on_clicked(self._on_reset)
def _on_slider_changed(self, _):
self.targetfig.subplots_adjust(
**{slider.label.get_text(): slider.val
for slider in self._sliders})
if self.drawon:
self.targetfig.canvas.draw()
def _on_reset(self, event):
with ExitStack() as stack:
# Temporarily disable drawing on self and self's sliders.
stack.enter_context(cbook._setattr_cm(self, drawon=False))
for slider in self._sliders:
stack.enter_context(cbook._setattr_cm(slider, drawon=False))
# Reset the slider to the initial position.
for slider in self._sliders:
slider.reset()
# Draw the canvas.
if self.drawon:
event.canvas.draw()
self.targetfig.canvas.draw()





 本文介绍了matplotlib的SubplotTool类和subplot_tool函数,用于调整图像子图的布局参数。SubplotTool包含6个滑动条和1个重置按钮,通过滑动条改变子图的边距、间距等,并通过targetfig.subplots_adjust()方法更新。subplot_tool()函数创建SubplotTool实例,若targetfig未指定,则默认为当前图像。案例展示了如何创建并使用SubplotTool和subplot_tool。
本文介绍了matplotlib的SubplotTool类和subplot_tool函数,用于调整图像子图的布局参数。SubplotTool包含6个滑动条和1个重置按钮,通过滑动条改变子图的边距、间距等,并通过targetfig.subplots_adjust()方法更新。subplot_tool()函数创建SubplotTool实例,若targetfig未指定,则默认为当前图像。案例展示了如何创建并使用SubplotTool和subplot_tool。
















 2万+
2万+










