文章目录
Leet Code 笔记
53. Maximum Subarray 最大子段和
2019.07.22
leetcode 53
动态规划
原数组
n
u
m
[
]
num[\space]
num[ ]
记录数组
s
u
m
[
i
]
sum[i]
sum[i]保存的是原数组以位置
i
i
i结尾在
n
u
m
[
0...
i
]
num[0...i]
num[0...i]区间内的最大子段和
初始值
s
u
m
[
0
]
sum[0]
sum[0]=
n
u
m
[
0
]
num[0]
num[0]
可以写出如下递推公式:
s
u
m
[
i
]
=
{
s
u
m
[
i
−
1
]
+
n
u
m
[
i
]
if
s
u
m
[
i
−
1
]
>
0
n
u
m
[
i
]
else
sum[i] = \begin{cases} sum[i-1] + num[i] &\text{if} \space sum[i-1]>0\\ num[i] &\text{else} \end{cases}
sum[i]={sum[i−1]+num[i]num[i]if sum[i−1]>0else
因为只需要求得最大的结果,所以可以用一个变量
r
e
s
res
res来代替
s
u
m
[
i
−
1
]
sum[i-1]
sum[i−1]的功能,从前到后扫描一次数组,并用一个变量
m
a
x
v
maxv
maxv记录最大的
r
e
s
res
res返回.
class Solution:
def maxSubArray(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = nums[0]
maxv = nums[0]
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
res = res + nums[i] if res > 0 else nums[i]
if maxv < res:
maxv = res
return maxv
62. Unique Paths 不同的路径
2019.07.22
leetcode 62
组合数学
这个问题其实可以转化成组合数学。因为每次只能向右或向下走一步,最多能走的是向右 m − 1 m-1 m−1步,向下 n − 1 n-1 n−1步。假设 n < m n<m n<m,其实是在 m − 1 m-1 m−1步的间隔位置包括开始和结尾,插入 n − 1 n-1 n−1步,并且可以连续插入在同一个间隔。将向右移视为 1 1 1,向下移视为 0 0 0,问题转化为在 ( m + n − 2 ) (m+n-2) (m+n−2)个位置上选择 ( m − 1 ) (m-1) (m−1)个放置 1 1 1,其余放置 0 0 0,可以直接用组合公式求解。
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m: int, n: int) -> int:
return self.cfun(m+n - 2,n - 1)
def cfun(self,a,b):
min = a-b if a-b < b else b
res = 1
for i in range(min):
res = res * (a - i) // (i + 1)
return res
动态规划
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists 两个链表的交汇点
2019.09.06
leetcode 160
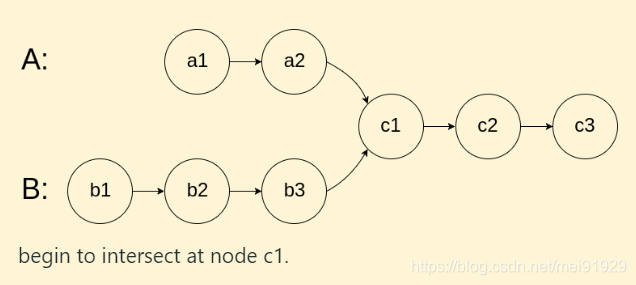
双指针法
- 可以遍历一遍两个链表,然后让长的链表先出发,到达他们长度相同的位置后,同时出发,当两个指针相等时退出循环
- 更巧妙地方法是,让两个指针同时出发,当其中一个走到链表尾端,此时它等于
n
u
l
l
null
null,将它置为另一个链表的开头,继续前进,直到两个指针相等时退出循环。具体证明:
设 A A A链表长度为 l e n A lenA lenA, B B B链表长度为 l e n B lenB lenB,
当其中一个指针走到结尾,将它置为另一个链表的开始,这样他会多走另一个链表的长度,
len A ′ = len A + len B \text{len}A' = \text{len}A + \text{len}B lenA′=lenA+lenB
len B ′ = len B + len A \text{len}B' = \text{len}B + \text{len}A lenB′=lenB+lenA
len A ′ = len B ′ \text{len}A' = \text{len}B' lenA′=lenB′
他们走的总长度相同,所以总会在交汇点处相遇。另外,当 c = 0 c=0 c=0时,他们都为 n u l l null null,此时跳出循环并返回 n u l l null null。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//boundary check
if(headA == null || headB == null) return null;
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
//if a & b have different len, then we will stop the loop after second iteration
while( a != b){
//for the end of first iteration, we just reset the pointer to the head of another linkedlist
a = a == null? headB : a.next;
b = b == null? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
}
167. Two Sum II 两数之和2
双指针法
因为是排序好的数组,头尾各一个指针向中间遍历,如果两数之和等于目标值,跳出循环,如果大于则移动尾指针,使和变小,否则移动头指针,使和变大,直到两个指针相遇。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] ans = new int[2];
int left = 0;
int right = numbers.length-1;
while(left != right){
int sum = numbers[left] + numbers[right];
if(sum == target){
ans[0] = left + 1;
ans[1]= right + 1;
break;
}
else if(sum > target){
right--;
}
else{
left++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
241 加括号的不同结果
分治算法
原问题可以从运算符号位置拆分为左右各一个子问题,运用递归不断求解子问题,组合成原问题。加速的方法使用备忘录,记录之前计算过的子问题。
public class Solution {
private HashMap<String, List<Integer>> hashmap = new HashMap<String, List<Integer>>();
public List<Integer> diffWaysToCompute(String input) {
if(hashmap.containsKey(input))
return hashmap.get(input);
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++){
char ch = input.charAt(i);
if(ch == '*' || ch == '+' || ch == '-')
for(int l: diffWaysToCompute(input.substring(0, i)))
for(int r: diffWaysToCompute(input.substring(i+1)))
switch(ch){
case '*': res.add(l * r);
break;
case '+': res.add(l+r);
break;
case '-': res.add(l-r);
break;
default: break;
}
}
if(res.size()==0)
res.add(Integer.valueOf(input));
hashmap.put(input, res);
return res;
}
}

























 514
514

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








