数据增强简介
数据增强是机器学习或深度学习中的一种技术,通过应用各种变换(如翻转、旋转、改变亮度/对比度等)从现有数据创建新数据。它通常用于计算机视觉任务,但也适用于自然语言处理和语音识别等领域。
数据增强的重要性
数据增强可以帮助防止过拟合,通过增加训练数据的多样性,帮助模型学习泛化到新的、未见过的数据。它还可以通过让模型接触到更广泛的数据变化来提高模型的准确性和鲁棒性。此外,当可用的训练数据量有限时,数据增强有助于增加数据集的大小,从而提高模型的性能。
数据增强的常见方法
常见的数据增强方法包括但不限于以下几种:
- 图像翻转:水平或垂直翻转图像。
- 图像旋转:将图像旋转一定角度。
- 颜色变换:调整图像的亮度、对比度、饱和度等。
- 随机裁剪:从图像中随机裁剪出一个子区域。
- 缩放:将图像放大或缩小。
- 添加噪声:在图像中添加随机噪声。
YOLOv5和YOLOv8的数据集格式
YOLOv8和YOLOv5的数据集格式相同,主要包含两个目录:
- Images目录:包含图像文件。
- labels目录:包含**.txt文件。每个.txt**文件包含归一化的边界框,格式如下:
[class_label, x_center, y_center, width, height]
数据集格式示例
假设有一个图像文件image1.jpg,对应的标签文件image1.txt内容如下:
0 0.5 0.5 0.2 0.3
1 0.3 0.4 0.1 0.2
这表示图像中有两个目标,第一个目标的类别标签为0,中心点坐标为(0.5, 0.5),宽度和高度分别为0.2和0.3;第二个目标的类别标签为1,中心点坐标为(0.3, 0.4),宽度和高度分别为0.1和0.2。
如何使用Albumentations库?
Albumentations是一个用于图像增强的Python库,提供了一种简单灵活的方式来执行各种图像变换。以下是使用该库的详细步骤:
安装Albumentations库
首先,需要安装Albumentations库。可以通过以下命令进行安装:
pip install -U albumentations
最小增强流程
以下是一个简单的增强流程示例:
import albumentations as A
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 定义增强操作
transform = A.Compose([
A.RandomCrop(width=450, height=450), # 随机裁剪
A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), # 水平翻转,概率为0.5
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.2), # 随机调整亮度和对比度,概率为0.2
], bbox_params=A.BboxParams(format='yolo'))
# 加载图像和边界框
image = cv2.imread('image1.jpg')
bboxes = [[0.5, 0.5, 0.2, 0.3, 0], [0.3, 0.4, 0.1, 0.2, 1]]
# 应用增强操作
transformed = transform(image=image, bboxes=bboxes)
transformed_image = transformed['image']
transformed_bboxes = transformed['bboxes']
# 显示增强后的图像
cv2.imshow('Transformed Image', transformed_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
代码说明
- 导入库:首先需要导入albumentations库。
- 定义增强操作:在A.Compose对象中定义要应用的增强操作。可以添加多种增强操作,每种操作都可以设置相应的概率。
- 转换YOLO格式:需要将YOLO输入边界框标签转换为Albumentations格式。Albumentations格式为
[x_center, y_center, width, height, class_name]。 - 应用增强操作:将YOLO输入图像和边界框列表传递给transform对象,返回的增强结果存储在transformed字典中。
保存增强结果
如果需要保存增强后的图像和标签,可以使用以下方法:
# 保存增强后的图像
cv2.imwrite('transformed_image.jpg', transformed_image)
# 保存增强后的标签
with open('transformed_labels.txt', 'w') as f:
for bbox in transformed_bboxes:
class_label = int(bbox[4])
x_center, y_center, width, height = bbox[:4]
f.write(f'{class_label} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}\n')
结果展示
输入
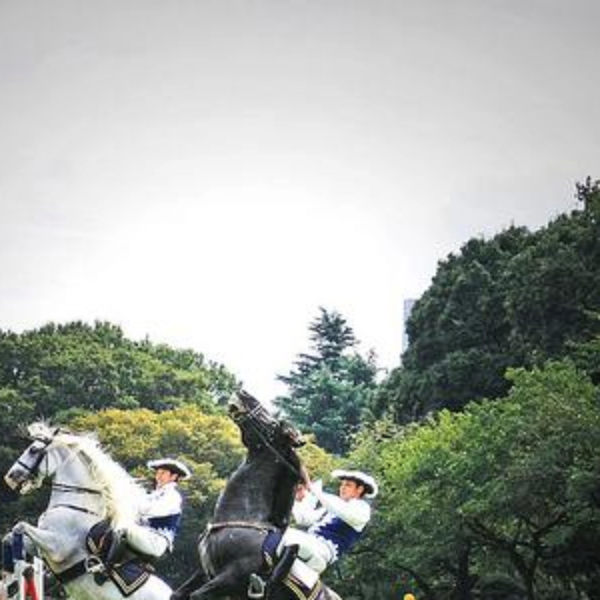
- 输入图像:

- 输入标签:
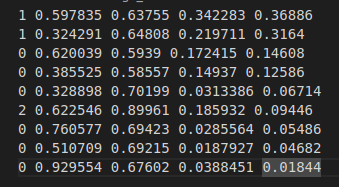
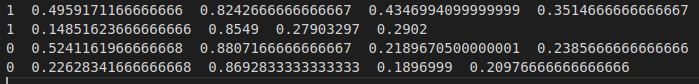
输出
- 增强后的图像:

- 增强后的文本文件:
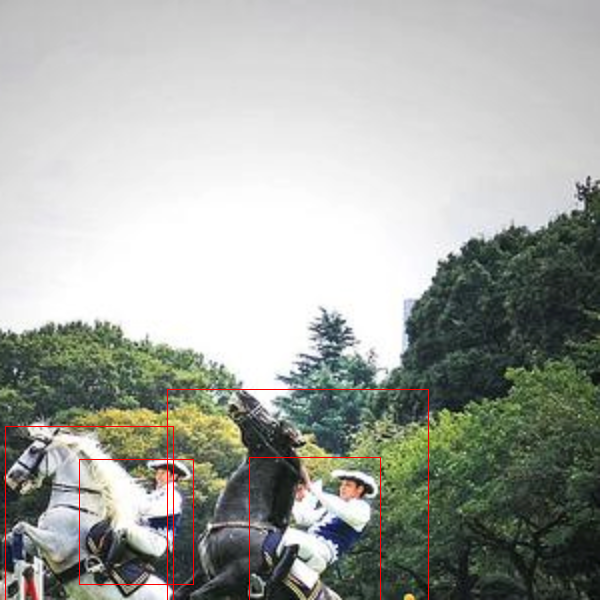
- 通过在增强后的图像上绘制标签来可视化增强输出:

完整代码
import albumentations as A
import cv2
import os
import yaml
import pybboxes as pbx
with open("contants.yaml", 'r') as stream:
CONSTANTS = yaml.safe_load(stream)
def is_image_by_extension(file_name):
"""
Check if the given file has a recognized image extension.
Args:
file_name (str): Name of the file.
Returns:
bool: True if the file has a recognized image extension, False otherwise.
"""
# List of common image extensions
image_extensions = ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'png', 'gif', 'bmp', 'tiff', 'webp']
# Get the file extension
file_extension = file_name.lower().split('.')[-1]
# Check if the file has a recognized image extension
return file_extension in image_extensions
def get_inp_data(img_file):
"""
Get input data for image processing.
Args:
img_file (str): Name of the input image file.
Returns:
tuple: A tuple containing the image, ground truth bounding boxes, and augmented file name.
"""
file_name = os.path.splitext(img_file)[0]
aug_file_name = f"{file_name}_{CONSTANTS['transformed_file_name']}"
image = cv2.imread(os.path.join(CONSTANTS["inp_img_pth"], img_file))
lab_pth = os.path.join(CONSTANTS["inp_lab_pth"], f"{file_name}.txt")
gt_bboxes = get_bboxes_list(lab_pth, CONSTANTS['CLASSES'])
return image, gt_bboxes, aug_file_name
def get_album_bb_list(yolo_bbox, class_names):
"""
Extracts bounding box information for a single object from YOLO format.
Args:
yolo_bbox (str): YOLO format string representing bounding box information.
class_names (list): List of class names corresponding to class numbers.
Returns:
list: A list containing [x_center, y_center, width, height, class_name].
"""
str_bbox_list = yolo_bbox.split()
class_number = int(str_bbox_list[0])
class_name = class_names[class_number]
bbox_values = list(map(float, str_bbox_list[1:]))
album_bb = bbox_values + [class_name]
return album_bb
def get_album_bb_lists(yolo_str_labels, classes):
"""
Extracts bounding box information for multiple objects from YOLO format.
Args:
yolo_str_labels (str): YOLO format string containing bounding box information for multiple objects.
classes (list): List of class names corresponding to class numbers.
Returns:
list: A list of lists, each containing [x_center, y_center, width, height, class_name].
"""
album_bb_lists = []
yolo_list_labels = yolo_str_labels.split('\n')
for yolo_str_label in yolo_list_labels:
if yolo_str_label:
album_bb_list = get_album_bb_list(yolo_str_label, classes)
album_bb_lists.append(album_bb_list)
return album_bb_lists
def get_bboxes_list(inp_lab_pth, classes):
"""
Reads YOLO format labels from a file and returns bounding box information.
Args:
inp_lab_pth (str): Path to the YOLO format labels file.
classes (list): List of class names corresponding to class numbers.
Returns:
list: A list of lists, each containing [x_center, y_center, width, height, class_name].
"""
yolo_str_labels = open(inp_lab_pth, "r").read()
if not yolo_str_labels:
print("No object")
return []
lines = [line.strip() for line in yolo_str_labels.split("\n") if line.strip()]
album_bb_lists = get_album_bb_lists("\n".join(lines), classes) if len(lines) > 1 else [get_album_bb_list("\n".join(lines), classes)]
return album_bb_lists
def single_obj_bb_yolo_conversion(transformed_bboxes, class_names):
"""
Convert bounding boxes for a single object to YOLO format.
Parameters:
- transformed_bboxes (list): Bounding box coordinates and class name.
- class_names (list): List of class names.
Returns:
- list: Bounding box coordinates in YOLO format.
"""
if transformed_bboxes:
class_num = class_names.index(transformed_bboxes[-1])
bboxes = list(transformed_bboxes)[:-1]
bboxes.insert(0, class_num)
else:
bboxes = []
return bboxes
def multi_obj_bb_yolo_conversion(aug_labs, class_names):
"""
Convert bounding boxes for multiple objects to YOLO format.
Parameters:
- aug_labs (list): List of bounding box coordinates and class names.
- class_names (list): List of class names.
Returns:
- list: List of bounding box coordinates in YOLO format for each object.
"""
yolo_labels = [single_obj_bb_yolo_conversion(aug_lab, class_names) for aug_lab in aug_labs]
return yolo_labels
def save_aug_lab(transformed_bboxes, lab_pth, lab_name):
"""
Save augmented bounding boxes to a label file.
Args:
transformed_bboxes (list): List of augmented bounding boxes.
lab_pth (str): Path to the output label directory.
lab_name (str): Name of the label file.
"""
lab_out_pth = os.path.join(lab_pth, lab_name)
with open(lab_out_pth, 'w') as output:
for bbox in transformed_bboxes:
updated_bbox = str(bbox).replace(',', ' ').replace('[', '').replace(']', '')
output.write(updated_bbox + '\n')
def save_aug_image(transformed_image, out_img_pth, img_name):
"""
Save augmented image to an output directory.
Args:
transformed_image (numpy.ndarray): Augmented image.
out_img_pth (str): Path to the output image directory.
img_name (str): Name of the image file.
"""
out_img_path = os.path.join(out_img_pth, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(out_img_path, transformed_image)
def draw_yolo(image, labels, file_name):
"""
Draw bounding boxes on an image based on YOLO format.
Args:
image (numpy.ndarray): Input image.
labels (list): List of bounding boxes in YOLO format.
"""
H, W = image.shape[:2]
for label in labels:
yolo_normalized = label[1:]
box_voc = pbx.convert_bbox(tuple(yolo_normalized), from_type="yolo", to_type="voc", image_size=(W, H))
cv2.rectangle(image, (box_voc[0], box_voc[1]),
(box_voc[2], box_voc[3]), (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv2.imwrite(f"bb_image/{file_name}.png", image)
# cv2.imshow(f"{file_name}.png", image)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
def has_negative_element(lst):
"""
Check if the given list contains any negative element.
Args:
lst (list): List of elements.
Returns:
bool: True if there is any negative element, False otherwise.
"""
return any(x < 0 for x in lst)
def get_augmented_results(image, bboxes):
"""
Apply data augmentation to an input image and bounding boxes.
Parameters:
- image (numpy.ndarray): Input image.
- bboxes (list): List of bounding boxes in YOLO format [x_center, y_center, width, height, class_name].
Returns:
- tuple: A tuple containing the augmented image and the transformed bounding boxes.
"""
# Define the augmentations
transform = A.Compose([
A.RandomCrop(width=300, height=300),
A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.2, contrast_limit=0),
A.CLAHE(clip_limit=(0, 1), tile_grid_size=(8, 8), always_apply=True),
A.Resize(300, 300)
], bbox_params=A.BboxParams(format='yolo'))
# Apply the augmentations
transformed = transform(image=image, bboxes=bboxes)
transformed_image, transformed_bboxes = transformed['image'], transformed['bboxes']
return transformed_image, transformed_bboxes
def has_negative_element(matrix):
"""
Check if there is a negative element in the 2D list of augmented bounding boxes.
Args:
matrix (list[list]): The 2D list.
Returns:
bool: True if a negative element is found, False otherwise.
"""
return any(element < 0 for row in matrix for element in row)
def save_augmentation(trans_image, trans_bboxes, trans_file_name):
"""
Saves the augmented label and image if no negative elements are found in the transformed bounding boxes.
Parameters:
trans_image (numpy.ndarray): The augmented image.
trans_bboxes (list): The transformed bounding boxes.
trans_file_name (str): The name for the augmented output.
Returns:
None
"""
tot_objs = len(trans_bboxes)
if tot_objs:
# Convert bounding boxes to YOLO format
trans_bboxes = multi_obj_bb_yolo_conversion(trans_bboxes, CONSTANTS['CLASSES']) if tot_objs > 1 else [single_obj_bb_yolo_conversion(trans_bboxes[0], CONSTANTS['CLASSES'])]
if not has_negative_element(trans_bboxes):
# Save augmented label and image
save_aug_lab(trans_bboxes, CONSTANTS["out_lab_pth"], trans_file_name + ".txt")
save_aug_image(trans_image, CONSTANTS["out_img_pth"], trans_file_name + ".png")
# Draw bounding boxes on the augmented image
draw_yolo(trans_image, trans_bboxes, trans_file_name)
else:
print("Found Negative element in Transformed Bounding Box...")
else:
print("Label file is empty")
from utils import *
def run_yolo_augmentor():
"""
Run the YOLO augmentor on a set of images.
This function processes each image in the input directory, applies augmentations,
and saves the augmented images and labels to the output directories.
"""
imgs = [img for img in os.listdir(CONSTANTS["inp_img_pth"]) if is_image_by_extension(img)]
for img_num, img_file in enumerate(imgs):
print(f"{img_num+1}-image is processing...\n")
image, gt_bboxes, aug_file_name = get_inp_data(img_file)
aug_img, aug_label = get_augmented_results(image, gt_bboxes)
if len(aug_img) and len(aug_label):
save_augmentation(aug_img, aug_label, aug_file_name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_yolo_augmentor()
总结
本文主要讨论了如何为YOLOv5和YOLOv8的目标检测任务获取增强后的数据集。我们也可以使用相同的Python库为其他格式的数据集获取增强后的数据集。该方法不仅适用于目标检测,还可以用于分类和分割任务。






















 653
653

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










