✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
⛄ 内容介绍
UAV swarms have numerous applications in our modern world. They can facilitate mapping, observing, and overseeing large areas with ease. It is necessary for these agents to autonomously navigate potentially dangerous terrain and airspace in order to log information about areas. In this project we simulate the motion of a swarm of drones, and their interaction with obstacles, and targets.
The goal of this project is to optimize this simulation using a Genetic Algorithm to maximize the number of targets mapped, minimize the number of crashed drones, and minimize the amount of time used in the simulation. To do this we will use 15 design parameters to determine the dynamics and kinematics of each drone, using Forward Euler time discretization to update drone positions.
A Genetic Algorithm will be used to train this swarm of drones by generating random strings of design parameters, and breeding new strings to fifind the optimal string for this simulation. In this paper, I will present relevant background information, and equations to describe the simulation. I will also describe the process by which I go about optimizing the Genetic Algorithm. Finally, I present the outcome of the simulation and Genetic Algorithm, and discuss the relevance of my results.
⛄ 部分代码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function myProgressBar(tock, t, tf, m)
% Provides a status update on a calculation, printed to the command window.
% avoids the issues associated with the GUI-based equilvalent functions.
%
% Inputs:
% tock -- total run time so far, seconds
% t -- cycles, simulation time, etc completed
% tf -- total cycles, etc required for process
% m -- optional message input, empty by default
% Outputs:
% no variables, prints information to the command window in the format:
% "#######-----------" + "m" + "Time remaining: " + "HH:MM:SS"
if nargin < 4
m = '';
end
rem = max(tock*(tf/t - 1), 0);
clock = sec2Clock(rem);
totchar = 20;
fprintf(repeatStr("#", floor(t/tf*totchar)) + repeatStr("-", totchar - floor(t/tf*totchar)) ...
+ " " + m + " Time remaining: " + clock + "\n\n");
end
function out = sec2Clock(s)
% returns a string of characters that represents a number of seconds in
% format HH:MM:SS. Can include arbitrarily many hour digits to account for
% large times. Rounded down to nearest number of seconds.
remh = floor(s / 3600); s = s - 3600*remh; remm = floor(s / 60); s = s - 60*remm; rems = floor(s);
out = padStr(num2str(remh), "0", 2) + ":" + padStr(num2str(remm), "0", 2) ...
+ ":" + padStr(num2str(rems), "0", 2);
end
function out = padStr(st, pad, minlength)
% returns string st plus some number of pad characters such that the total
% string length is as least minlength. Puts the padding on the left side.
out = st;
while (strlength(out) < minlength) out = pad + out; end
end
function out = repeatStr(st, n)
% returns a given string st repeated n times
out = ""; for i = 1:n out = out + st; end
end
⛄ 运行结果
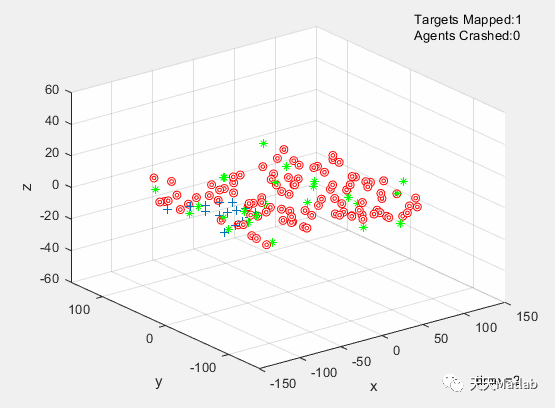
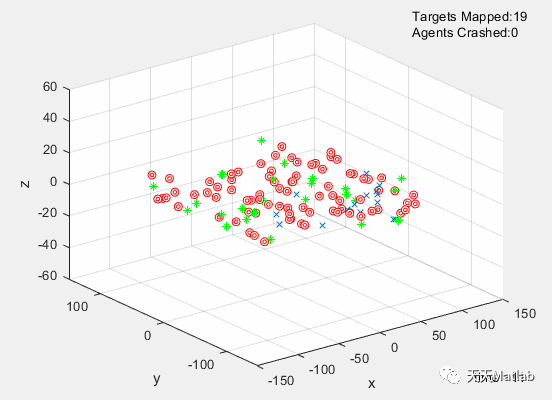
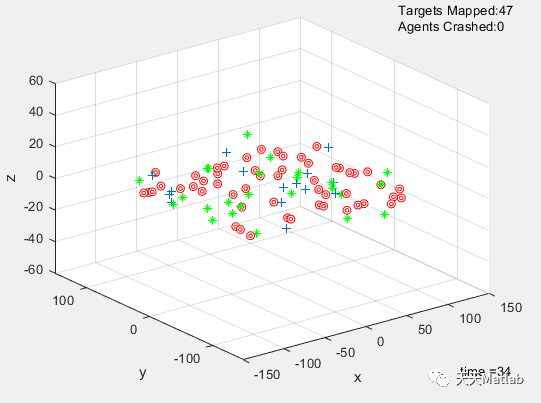
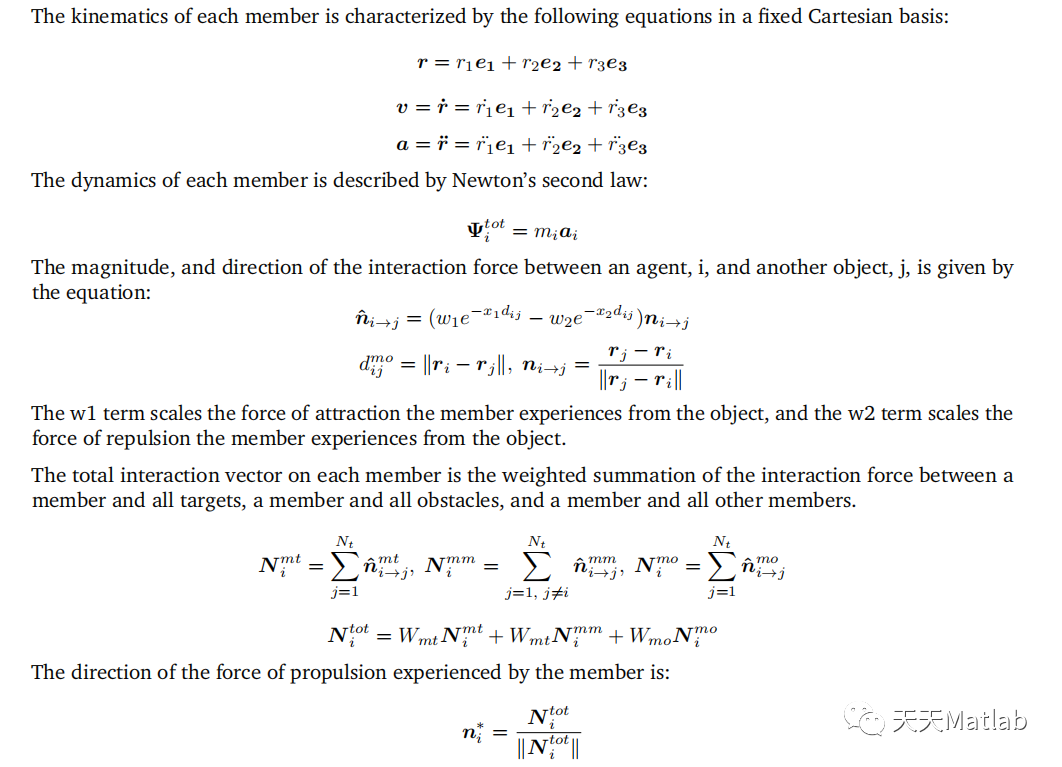
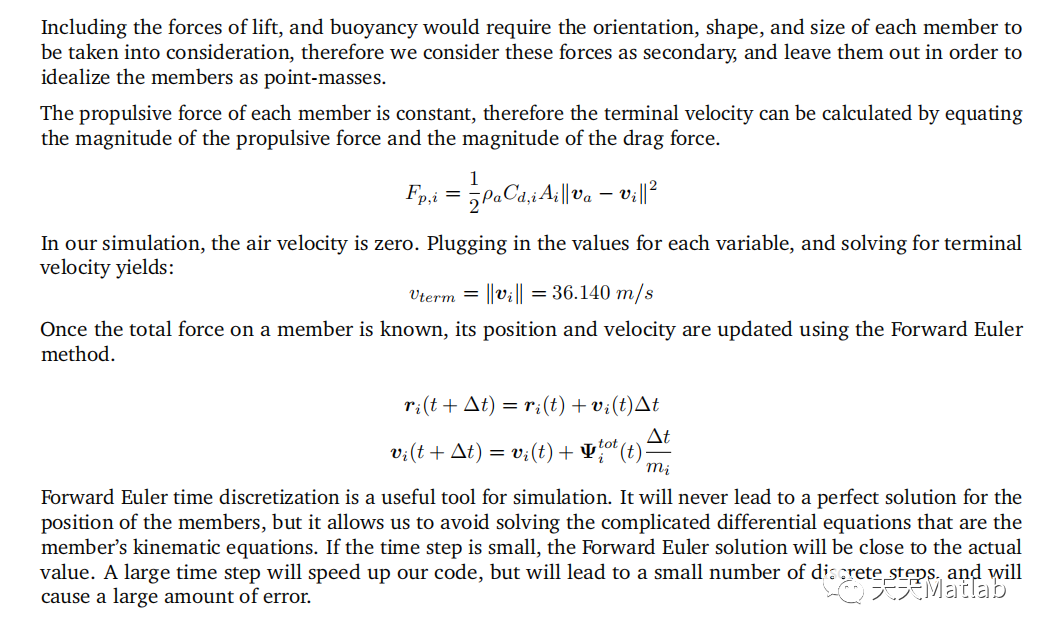
The simulation was successfully optimized using a Genetic Algorithm. The dynamics, and kinematic equations of 15 UAVs were used to simulate the movements of these drones. Each drone was affected by a repulsive,and an attractive force from each other member, target, and obstacle. These equations utilized 15 design parameters that were optimized by a Genetic Algorithm. Random strings of design parameters were created at the beginning, passed into the simulator, and the resulting success of the strings was evaluated. The strings were then ranked, and the top strings were mated with each other, resulting in child strings. The next generation was fifilled out with more randomly generated strings, and the process was repeated for 100 generations. The GA resulted in a fifinal cost of 25.3333. Additional optimizations for T*, and prevention of inbreeding could signifificantly decrease the cost, and should be implemented in future work on this, and other projects.
⛄ 参考文献
⛳️ 代码获取关注我
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
🍅 仿真咨询
1.卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
2.图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
3.旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划
4.无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配
5.传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位
6.信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号
7.生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化
8.微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
9.元胞自动机交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长





 该文介绍了一个使用Matlab进行的无人机群模拟项目,目标是通过遗传算法优化无人机的路径规划,最大化目标测绘数量,最小化坠毁无人机数量及时间消耗。作者利用15个设计参数来定义无人机的动力学和运动学,并通过前向欧拉时间离散化更新无人机位置。遗传算法生成随机参数字符串并繁殖,以找到最佳模拟参数。经过100代优化,最终成本达到25.3333,未来工作将考虑进一步优化和防止近亲繁殖的问题。
该文介绍了一个使用Matlab进行的无人机群模拟项目,目标是通过遗传算法优化无人机的路径规划,最大化目标测绘数量,最小化坠毁无人机数量及时间消耗。作者利用15个设计参数来定义无人机的动力学和运动学,并通过前向欧拉时间离散化更新无人机位置。遗传算法生成随机参数字符串并繁殖,以找到最佳模拟参数。经过100代优化,最终成本达到25.3333,未来工作将考虑进一步优化和防止近亲繁殖的问题。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










