1 内容介绍
阈值法是一种简单且有效的图像分割技术.但是随着阈值数目的增加,求解阈值的计算量增大并且实时性降低,这给多阈值图像分割带来了很大的困难.为了克服这一困难,把多阈值分割看作一个优化问题.将最大类间方差法当作要优化的函数,用回溯搜索优化算法求解要优化的函数,从而实现多阈值图像分割.将提出的多阈值算法应用于基准测试图像上,并与传统阈值分割法比较.实验结果表明:回溯搜索优化算法很好的解决了最大类间方差算法求解多阈值分割实时性差的问题,并验证了该算法应用在图像分割上是可行的.






2 仿真代码
%{
Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm (BSA)
Platform: Matlab 2013a
Cite this algorithm as;
[1] P. Civicioglu, "Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm for
numerical optimization problems", Applied Mathematics and Computation, 219, 8121?144, 2013.
Copyright Notice
Copyright (c) 2012, Pinar Civicioglu
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in
the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
%}
function bsa(fnc,mydata,popsize,dim,DIM_RATE,low,up,epoch)
%INITIALIZATION
if numel(low)==1, low=low*ones(1,dim); up=up*ones(1,dim); end % this line must be adapted to your problem
pop=GeneratePopulation(popsize,dim,low,up); % see Eq.1 in [1]
fitnesspop=feval(fnc,pop,mydata);
historical_pop=GeneratePopulation(popsize,dim,low,up); % see Eq.2 in [1]
% historical_pop is swarm-memory of BSA as mentioned in [1].
% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
for epk=1:epoch
%SELECTION-I
if rand<rand, historical_pop=pop; end % see Eq.3 in [1]
historical_pop=historical_pop(randperm(popsize),:); % see Eq.4 in [1]
F=get_scale_factor; % see Eq.5 in [1], you can other F generation strategies
map=zeros(popsize,dim); % see Algorithm-2 in [1]
if rand<rand,
for i=1:popsize, u=randperm(dim); map(i,u(1:ceil(DIM_RATE*rand*dim)))=1; end
else
for i=1:popsize, map(i,randi(dim))=1; end
end
% RECOMBINATION (MUTATION+CROSSOVER)
offsprings=pop+(map.*F).*(historical_pop-pop); % see Eq.5 in [1]
offsprings=BoundaryControl(offsprings,low,up); % see Algorithm-3 in [1]
% SELECTON-II
fitnessoffsprings=feval(fnc,offsprings,mydata);
ind=fitnessoffsprings<fitnesspop;
fitnesspop(ind)=fitnessoffsprings(ind);
pop(ind,:)=offsprings(ind,:);
[globalminimum,ind]=min(fitnesspop);
globalminimizer=pop(ind,:);
% EXPORT SOLUTIONS
assignin('base','globalminimizer',globalminimizer);
assignin('base','globalminimum',globalminimum);
fprintf('BSA|%5.0f -----> %9.16f\n',epk,globalminimum);
end
return
function pop=GeneratePopulation(popsize,dim,low,up)
pop=ones(popsize,dim);
for i=1:popsize
for j=1:dim
pop(i,j)=rand*(up(j)-low(j))+low(j);
end
end
return
function pop=BoundaryControl(pop,low,up)
[popsize,dim]=size(pop);
for i=1:popsize
for j=1:dim
k=rand<rand; % you can change boundary-control strategy
if pop(i,j)<low(j), if k, pop(i,j)=low(j); else pop(i,j)=rand*(up(j)-low(j))+low(j); end, end
if pop(i,j)>up(j), if k, pop(i,j)=up(j); else pop(i,j)=rand*(up(j)-low(j))+low(j); end, end
end
end
return
function F=get_scale_factor % you can change generation strategy of scale-factor,F
F=3*randn; % STANDARD brownian-walk
% F=4*randg; % brownian-walk
% F=lognrnd(rand,5*rand); % brownian-walk
% F=1/normrnd(0,5); % pseudo-stable walk (levy-like)
% F=1./gamrnd(1,0.5); % pseudo-stable walk (levy-like, simulates inverse gamma distribution; levy-distiribution)
return
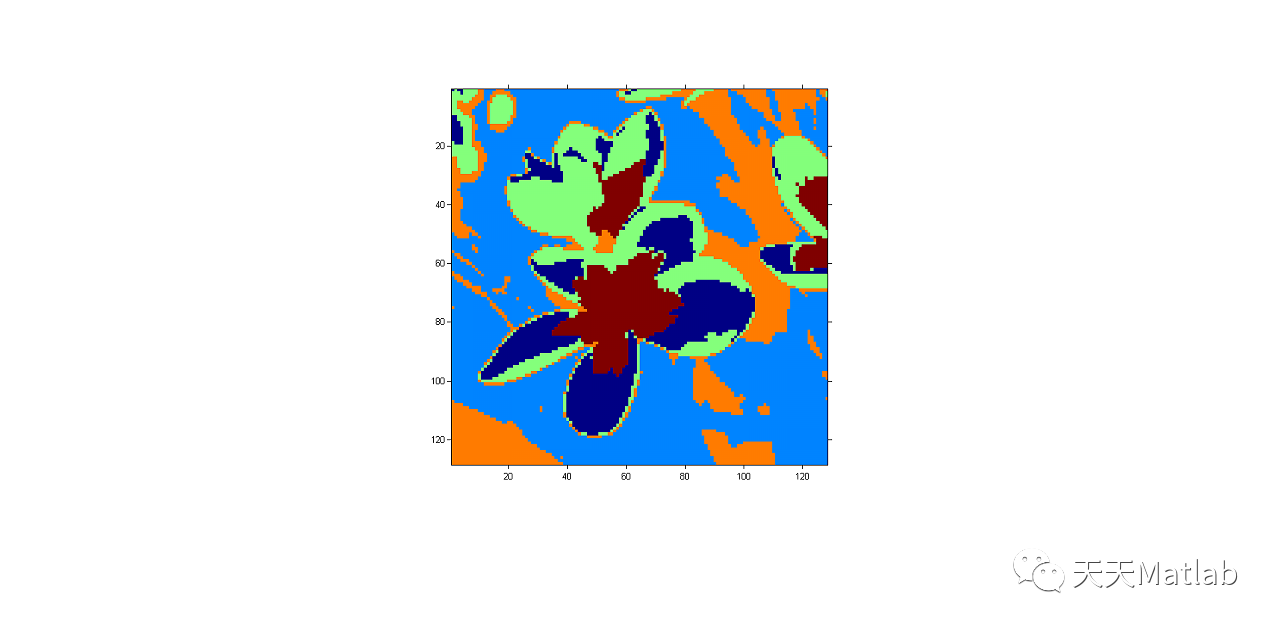
3 运行结果

4 参考文献
[1]LI Sheng-jie. 基于回溯搜索优化算法的图像分割[J]. 新一代信息技术, 2019, 2(11):7.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。






















 208
208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










