上一篇博客中我们通过滑动窗口切分和文本向量化技术,结合余弦相似度检索实现了Query中所有实体在知识图谱中的定位和匹配。这篇博客将介绍实体语义地图的生长。
语义地图概念
语义地图即由一些实体(ENTITY)及其连接的描述(DESCRITION),练习(EXERCISE)构成的,知识图谱的关键子图。如果Query直接检索构成的语义地图范围不够大,就需要进行语义地图的生长。
假设“计算机网络中TCP/IP协议和传输层的关系”这个userQuery中根据滑动窗口切分并在实体列表里根据余弦相似度检索识别出了向量化的TCP/IP协议,传输层,计算机网络 三个实体,首先将向量表示返还为文本表示,然后在知识图谱中进行检索。
基于Query的基础语义地图
CYPHER查询首先通过Describe方法,Exercise方法(均对应数据库操作)
拓展三个实体的DESCRIPTION节点,QUESTION节点到D集合和Q集合中。
def expand(self, entity_name):
query = (
"MATCH (a:Entity {name: $entity_name})-[r]->(b:Entity) "
"RETURN b AS child,r.type AS relation_type"
)
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(query, entity_name=entity_name)
linked_nodes = []
for record in result:
if record["child"].id is not None and record["child"].id != '':
linked_nodes.append(
{
"id": record["child"].id,
"name": record["child"]["name"],
"type": record["relation_type"],
}
)
return linked_nodes添加实体
通过GROW或EXPAND添加实体以扩展语义地图
如果查询到的DESCRIPTION和QUESTION数量均较少,说明该Query对应实体的描述较少。
通过Entity_grow或Expand向语义地图中添加实体。
def entity_grow(self, entity):
entities = get_similar_entities_single_entity(entity_name=entity, entity_names=self.entity_names, model=bert,
tokenizer=bert_tokenizer,
entity_embeddings=self.entity_embeddings, temperture=0.5)
return entitiesExpands的方式有两种:
一种是拓展有RELATION关系连接的下一层实体。(Expand)
一种是根据余弦相似度在实体列表中对这三个实体进行检索和匹配,在依据最高相似度排序的其他实体列表中依次遍历。(Entity_Grow)
拓展DQ
根据ENTITY拓展DESCRIPTION和QUESTION
Expand后,拓展其DESCRIPTION和QUESTION并加入D集和Q集。
直到满足DESCRITION和QUESTTION的数量限制停止。
Expand方法示例:
def expand(self, entity_name):
query = (
"MATCH (a:Entity {name: $entity_name})-[r]->(b:Entity) "
"RETURN b AS child,r.type AS relation_type"
)
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(query, entity_name=entity_name)
linked_nodes = []
for record in result:
if record["child"].id is not None and record["child"].id != '':
linked_nodes.append(
{
"id": record["child"].id,
"name": record["child"]["name"],
"type": record["relation_type"],
}
)
return linked_nodes示例代码:单实体通过余弦相似度进行向量化检索,拓展实体列表中前TopK个相似实体
def get_similar_entities_single_entity(entity_name, entity_names, model, tokenizer, entity_embeddings, temperture=0.5):
embedding = get_embedding(entity_name, model, tokenizer)
best_matches = []
cos_sim = cosine_similarity(embedding, entity_embeddings)
indices = np.argsort(cos_sim[0])[::-1]
for idx in indices:
if cos_sim[0][idx] >= temperture:
best_matches.append((entity_names[idx], cos_sim[0][idx]))
best_matches.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
unique_best_matches = {}
for name, score in best_matches:
if name not in unique_best_matches:
unique_best_matches[name] = score
final_matches = [(name, score) for name, score in unique_best_matches.items()]
final_matches.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return final_matches
语义地图的生长和最终构建
最终,根据整体语义地图,使用struct方法查询所有节点集其关系,构成语义地图
def expand(self, entity_name):
query = (
"MATCH (a:Entity {name: $entity_name})-[r]->(b:Entity) "
"RETURN b AS child,r.type AS relation_type"
)
with self.driver.session() as session:
result = session.run(query, entity_name=entity_name)
linked_nodes = []
for record in result:
if record["child"].id is not None and record["child"].id != '':
linked_nodes.append(
{
"id": record["child"].id,
"name": record["child"]["name"],
"type": record["relation_type"],
}
)
return linked_nodes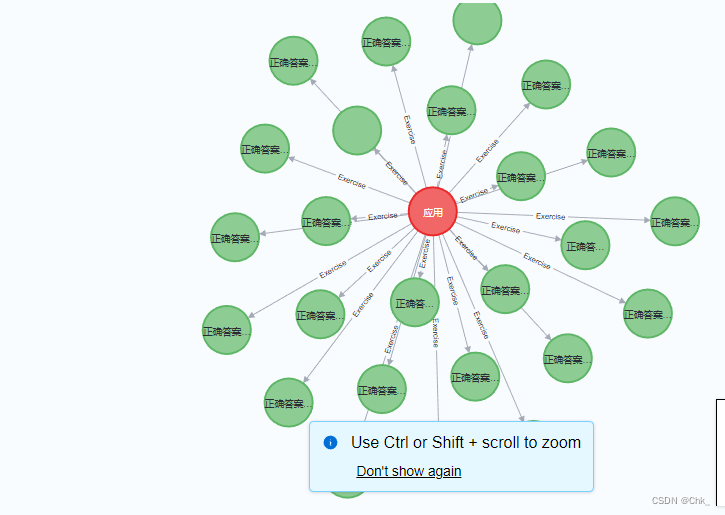



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








