1. 简介
在本实验中,我们将大图像划分为四个大小相等的小图像,并经过预处理后,以 batch 大小为 4 的形式输入 YOLOv5s 模型进行推理和后处理。这种方法有效避免了因非等比例缩放导致的图像失真,减少了缩放带来的像素信息损失,同时无需使用像素填充操作,显著提升了模型对中小目标的识别能力。此外,实验使用的是官方预训练的 YOLOv5 模型(未进行额外训练),复现过程简单,并且提供了样例程序,为目标检测任务提供了一种高效且精准的解决方案。
2. 适用场景
a. 在高分辨率图像场景中,识别目标的像素占比小,即适用于小目标识别任务。
b. 图像的宽高比过大,导致经过letterbox处理后有效像素损失过多,影响识别精度。
c. 使用的框架中,padding操作复杂,而复制抠图更为简便。
d. 其他类似场景。
3. 图像展示
如下图所示,大图片直接预处理后需要填充,而分割图片预处理后不需要填充,并且分割图片的缩放比例更小。
a. 手机后置摄像头拍摄图像,原图为4090*3072


b. 监控摄像头拍摄图像,原图为1920*1080


可以发现,分割后的图像可以保留更多的有效像素(即有效信息)。
4. 逻辑介绍
4.1 拆分
参考:yolov8多batch推理,nms后处理_yolov8 后处理-优快云博客
h, w = img.shape[:2]
w1 = int(w*12/25)
w2 = w - w1
h2 = w2
h1 = h - h2
if w2 > h:
print('small w > big h')
h1 = h2 = h
# w2 = 13/25w, h = w2
# 小图片的宽为原图的13/25,他们之间最好有一定的交汇。
# 但是过多的交汇不利于新增有效信息。
img0 = img[0:h2, 0:w2].copy()
img1 = img[0:h2, w1:w].copy()
img2 = img[h1:h, 0:w2].copy()
img3 = img[h1:h, w1:w].copy()
4.2 4+1一次NMS
对每个小图像的识别框先进行单独的NMS处理,最后再对剩余的框进行一次全局NMS。由于单独的NMS已经过滤掉了大量冗余框,剩余的框数量较少,因此额外的+1次NMS操作对性能影响不大。
因为前面4次的NMS已经处理掉IOU超标的框了,现在剩余的超标框都是同类别间的。
NMS_2会将IOU超标,A嵌入B或者B嵌入A的框按照置信度去除。
参考:yolov8多batch推理,nms后处理_yolov8 后处理-优快云博客
def NMS_2(boxes, iou_thresh=0.5, h_iou=0.5):
# 按类别划分。
unique_groups = np.unique(boxes[:, 5])
grouped = {group: boxes[boxes[:, 5] == group] for group in unique_groups}
keep_boxes = []
for cls, nmsed_boxes in grouped.items():
# Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS)
index = np.argsort(nmsed_boxes[:, 4])[::-1] # Sort by score
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
keep_boxes.append(nmsed_boxes[i])
# Calculate IoU between the current box and the remaining ones
x1 = np.maximum(nmsed_boxes[i, 0], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 0])
y1 = np.maximum(nmsed_boxes[i, 1], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 1])
x2 = np.minimum(nmsed_boxes[i, 2], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 2])
y2 = np.minimum(nmsed_boxes[i, 3], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 3])
w = np.maximum(0, x2 - x1)
h = np.maximum(0, y2 - y1)
inter_area = w * h
area_a = (nmsed_boxes[i, 2] - nmsed_boxes[i, 0]) * (nmsed_boxes[i, 3] - nmsed_boxes[i, 1])
area_b = (nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 2] - nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 0]) * (nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 3] - nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 1])
# Calculate IoU
iou0 = inter_area / (area_a + area_b - inter_area)
iou1 = inter_area / area_a
iou2 = inter_area / area_b
# Conditions to keep the boxes
condition1 = iou0 <= iou_thresh
condition2 = iou1 <= iou_thresh
condition3 = iou2 <= iou_thresh
idx = np.where(condition1 & condition2 & condition3)[0]
index = index[idx + 1] # Update index
return np.array(keep_boxes)
上述NMS处理方法在识别到中、大目标,且目标靠近原图像W/2处时会有割裂现象,同时不会有IOU超标、内嵌的情况。因此可以在上述方法中增加合并操作,将H方向上IOU异常的框合并。
def merge_and_nms(boxes, iou_thresh=0.5, h_iou=0.5):
# 按类别划分。
unique_groups = np.unique(boxes[:, 5])
grouped = {group: boxes[boxes[:, 5] == group] for group in unique_groups}
keep_boxes = []
for cls, nmsed_boxes in grouped.items():
# NMS_2
index = np.argsort(nmsed_boxes[:, 4])[::-1] # Sort by score
temp_list = []
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
temp_list.append(nmsed_boxes[i])
# Calculate IoU between the current box and the remaining ones
x1 = np.maximum(nmsed_boxes[i, 0], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 0])
y1 = np.maximum(nmsed_boxes[i, 1], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 1])
x2 = np.minimum(nmsed_boxes[i, 2], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 2])
y2 = np.minimum(nmsed_boxes[i, 3], nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 3])
w = np.maximum(0, x2 - x1)
h = np.maximum(0, y2 - y1)
inter_area = w * h
area_a = (nmsed_boxes[i, 2] - nmsed_boxes[i, 0]) * (nmsed_boxes[i, 3] - nmsed_boxes[i, 1])
area_b = (nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 2] - nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 0]) * (nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 3] - nmsed_boxes[index[1:], 1])
# Calculate IoU
iou0 = inter_area / (area_a + area_b - inter_area)
iou1 = inter_area / area_a
iou2 = inter_area / area_b
# Conditions to keep the boxes
condition1 = iou0 <= iou_thresh
condition2 = iou1 <= iou_thresh
condition3 = iou2 <= iou_thresh
idx = np.where(condition1 & condition2 & condition3)[0]
index = index[idx + 1] # Update index
# merge and remove
nmsed_boxes = np.array(temp_list)
new_index = np.argsort(nmsed_boxes[:, 4])[::-1]
Len = nmsed_boxes.shape[0]
for i in range(Len):
box1 = nmsed_boxes[new_index[i]]
j = i + 1
while j < Len:
box2 = nmsed_boxes[new_index[j]]
x1 = max(box1[0], box2[0], 0)
y1 = max(box1[1], box2[1], 0)
x2 = min(box1[2], box2[2], )
y2 = min(box1[3], box2[3], )
w = max(0, x2 - x1)
h = max(0, y2 - y1)
inter = w * h
Iou = inter / ((box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1]) + (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1]) - inter)
Iou1 = max(h / (box1[3] - box1[1]), h / (box2[3] - box2[1]))
# 如果有交集,并且 H 方向的交并比大于iou_threash, 合并框
if Iou > 0 and Iou1 > h_iou:
nmsed_boxes[i][0] = min(box1[0], box2[0])
nmsed_boxes[i][1] = min(box1[1], box2[1])
nmsed_boxes[i][2] = max(box1[2], box2[2])
nmsed_boxes[i][3] = max(box1[3], box2[3])
area1 = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
area2 = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
# 根据面积占比获取新的置信度
nmsed_boxes[i][4] = (area1 * box1[4] + area2 * box2[4]) / (area1 + area2)
# 置信度小的框设置为非法框
nmsed_boxes[j][0] = nmsed_boxes[j][1] = nmsed_boxes[j][2] = nmsed_boxes[j][3] = -100
j += 1
nmsed_boxes = nmsed_boxes[nmsed_boxes[:, 0] > 0]
keep_boxes.extend(nmsed_boxes)
return np.array(keep_boxes)
5. 结果对比与展示
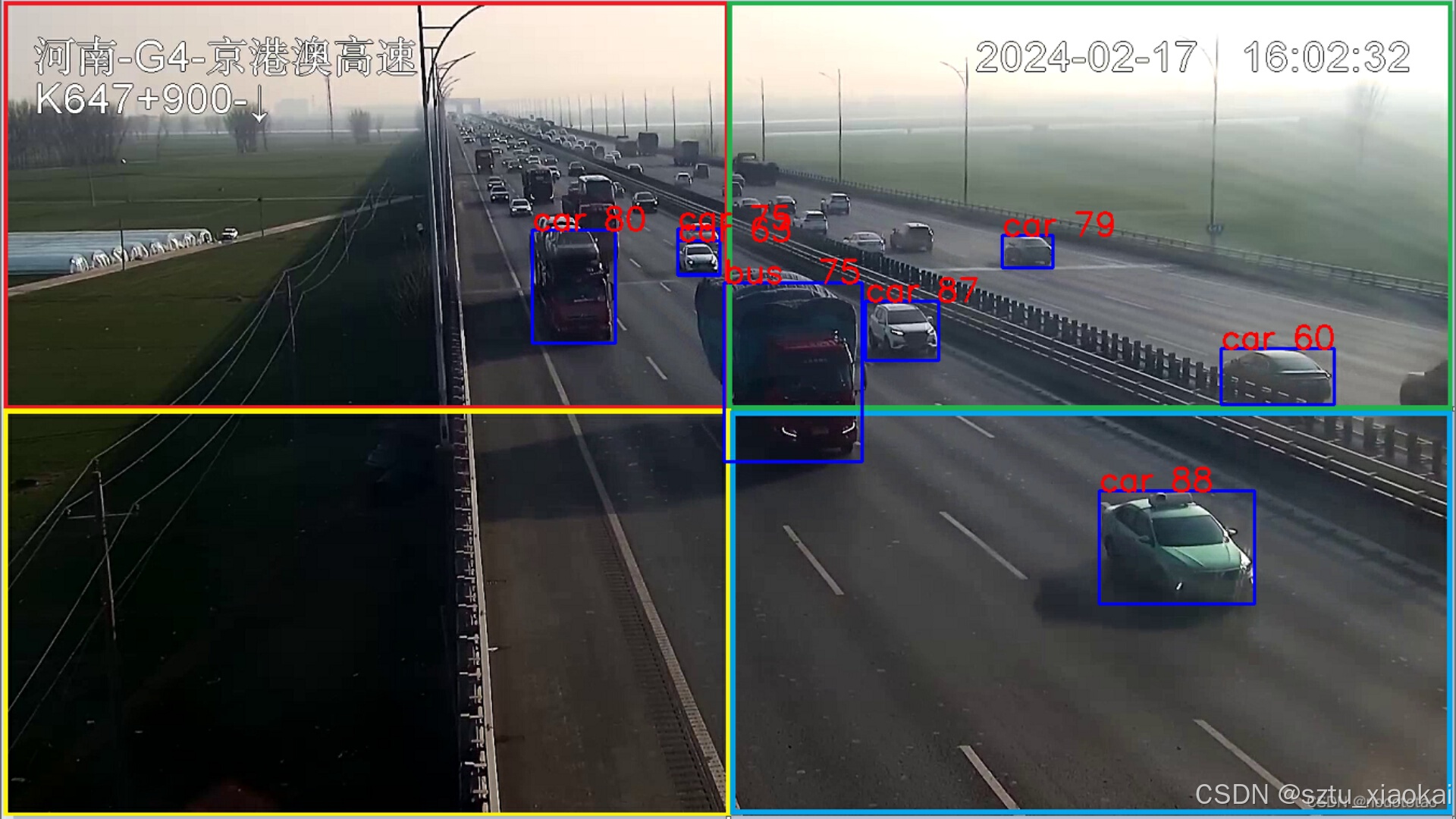
5.1 对于小目标的识别对比,如下两图所示,可以观察到该操作有效地提高了模型对小目标的识别能力。
直接将原图片进行letterbox推理(原图760P)
原图片来自(yolov8多batch推理,nms后处理_yolov8 后处理-优快云博客)

4batch识别,4+1次nms处理(NMS_2)
5.2 不同方法的识别对比
a. 将原图像letterbox处理后,直接推理。
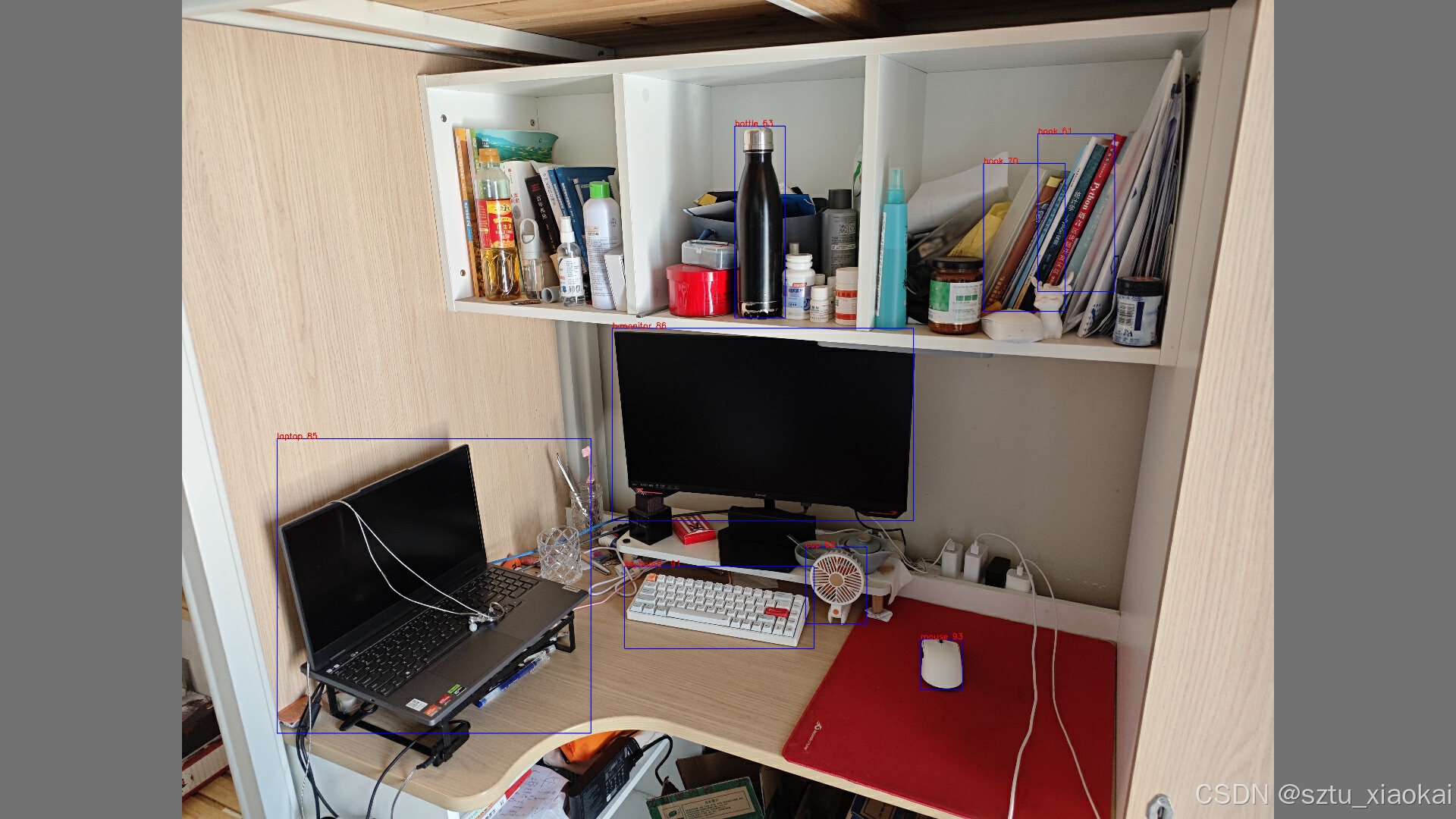


b. 将原图按照4.1所示方法分割成4个图片,预处理后推理,使用4+1次NMS_2处理。
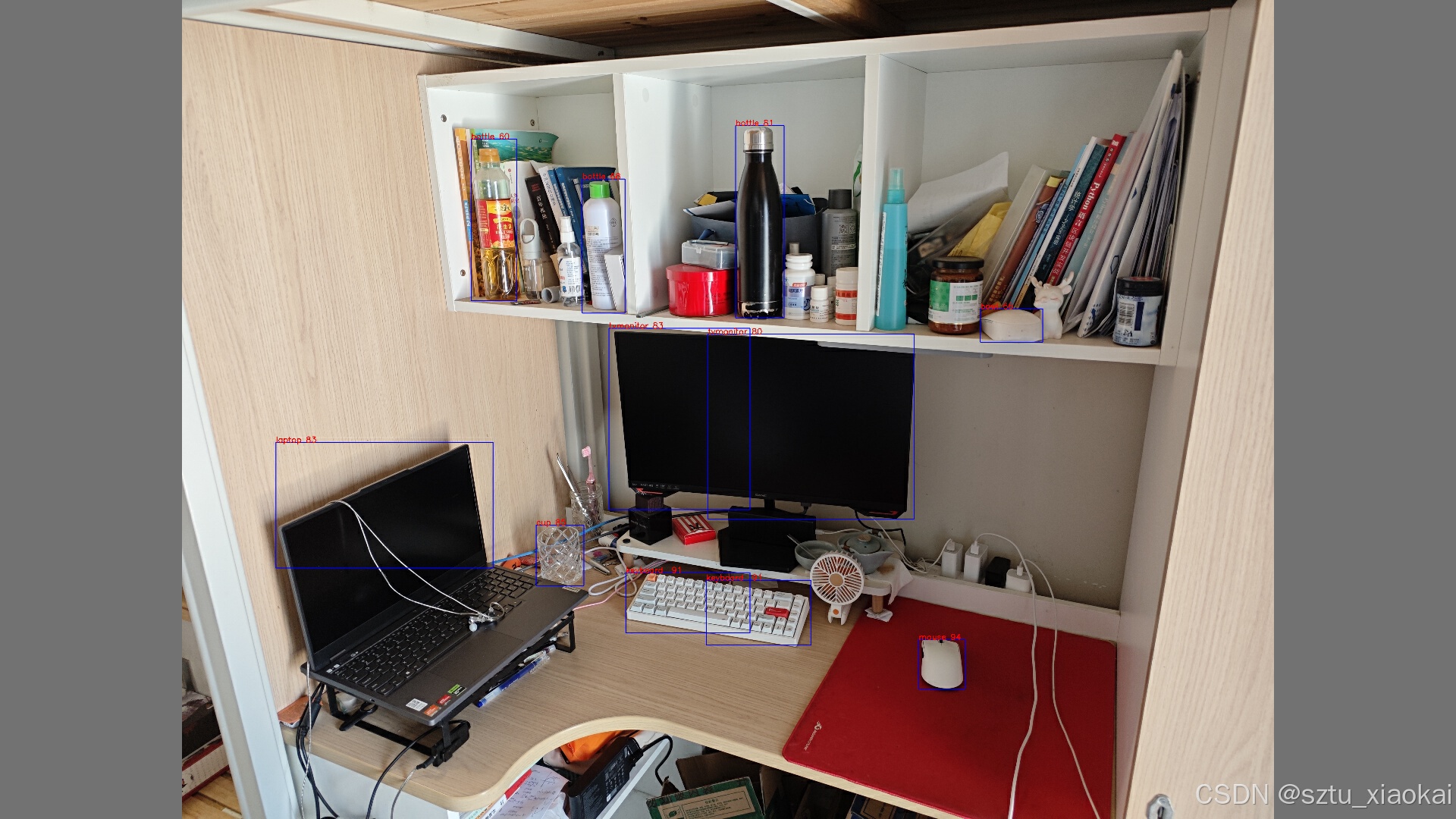


c. 将原图按照4.1所示方法分割成4个图片,预处理后推理,使用4+1merge_and_nms处理。
因为筛选后框变得很少,所以不会影响到程序的性能。
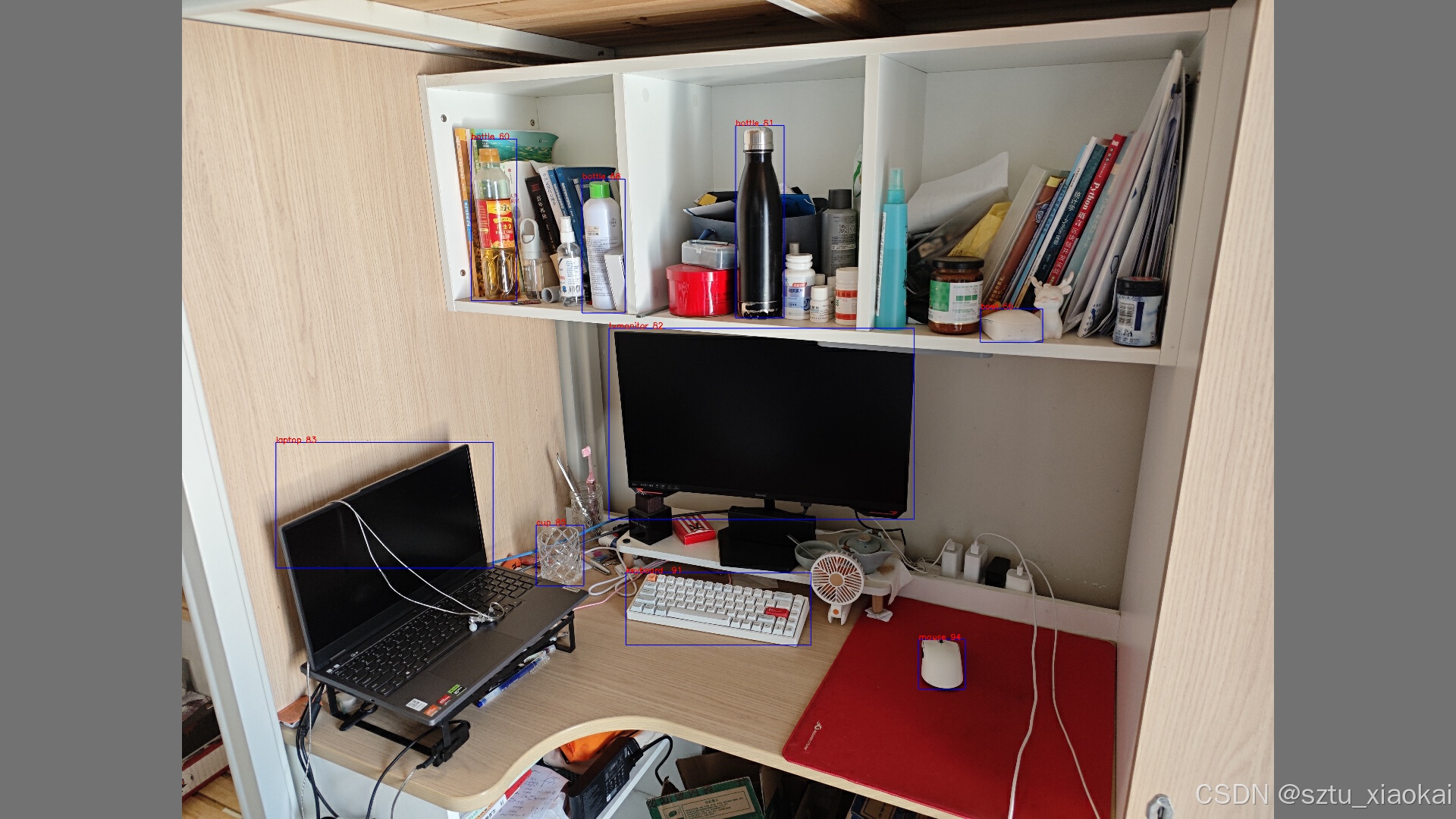



通过对比处理前后的图片,发现经过该处理后,模型对小目标的识别率和置信度明显提高,同时对大目标的识别置信度也有所提升。
因为本次实验使用的是YOLO官方提供的预训练V5s模型,如果针对实际的场景和分割方法进行针对性的训练,识别的精度可以进一步提高。
sztukai/4batch_yolov5s: 拆分图片进行多batch识别 (github.com)![]() https://github.com/sztukai/4batch_yolov5s
https://github.com/sztukai/4batch_yolov5s
这里提供了样例程序,如果这篇文章对你有帮助,记得点赞。👍👍👍























 5791
5791

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








