单卡从这里进入推理:
elif not distributed: # 进入
model = MMDataParallel(model, device_ids=[0])
outputs = single_gpu_test(model, data_loader, args.show, args.show_dir)特征提取和准备工作
提取特征:
def simple_test(self, img, **data):
feature_maps = self.extract_feat(img) # img: torch.Size([1, 6, 3, 256, 704]) else: # 进入
feature_maps = self.img_backbone(img)四种尺度的特征图(从torch.Size([6, 256, 64, 176]) 到 torch.Size([6, 2048, 8, 22]))

经过FPN:
if self.img_neck is not None:
feature_maps = list(self.img_neck(feature_maps))四种尺度的特征图,特征通道都是256(从torch.Size([6, 256, 64, 176]) 到 torch.Size([6, 256, 8, 22]))

对后面可变形注意力做准备工作:
if self.use_deformable_func: # 进入
feature_maps = feature_maps_format(feature_maps)把特征图的长和宽合并为一维:
bs, num_cams = feature_maps[0].shape[:2]
spatial_shape = []
col_feats = []
for i, feat in enumerate(feature_maps):
spatial_shape.append(feat.shape[-2:])
col_feats.append(
torch.reshape(feat, (bs, num_cams, feat.shape[2], -1))
)

四个特征图合并,并交换顺序:(89760=【64*176+32*88+16*44+8*22】*6个视图)
col_feats = torch.cat(col_feats, dim=-1).permute(0, 1, 3, 2).flatten(1, 2) # torch.Size([1, 89760, 256])复制6份:
spatial_shape = [spatial_shape] * num_cams
每层特征开始的位置:
scale_start_index = spatial_shape[..., 0] * spatial_shape[..., 1]
scale_start_index = scale_start_index.flatten().cumsum(dim=0)
scale_start_index = torch.cat(
[torch.tensor([0]).to(scale_start_index), scale_start_index[:-1]]
)
分成6个视角:
scale_start_index = scale_start_index.reshape(num_cams, -1)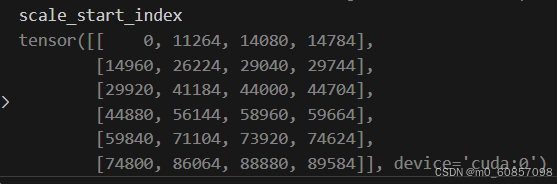
此时显存:
![]()
进入Sparse4DHead:
model_outs = self.head(feature_maps, data)进入InstanceBank:
(
instance_feature,
anchor,
temp_instance_feature,
temp_anchor,
time_interval,
) = self.instance_bank.get(
batch_size, metas, dn_metas=self.sampler.dn_metas
)metas是一些基础信息

self.instance_feature是初始化为0的nn.Parameter()
def get(self, batch_size, metas=None, dn_metas=None):
instance_feature = torch.tile(
self.instance_feature[None], (batch_size, 1, 1) # self.instance_feature: torch.Size([900, 256])
)anchor是900个的初始化的锚框:
anchor = torch.tile(self.anchor[None], (batch_size, 1, 1)) # torch.Size([1, 900, 11]) else: # 进入
self.reset()
time_interval = instance_feature.new_tensor(
[self.default_time_interval] * batch_size
)anchor特征映射编码
anchor_embed = self.anchor_encoder(anchor)这里的box_3d就是前面的 anchor:torch.Size([1, 900, 11])
def forward(self, box_3d: torch.Tensor):
pos_feat = self.pos_fc(box_3d[..., [X, Y, Z]]) # torch.Size([1, 900, 128])
size_feat = self.size_fc(box_3d[..., [W, L, H]]) # torch.Size([1, 900, 32])
yaw_feat = self.yaw_fc(box_3d[..., [SIN_YAW, COS_YAW]]) # torch.Size([1, 900, 32])四层LN:

concat: 最后输出的特征向量是torch.Size([1, 900, 256])
elif self.mode == "cat": # 进入
output = torch.cat([pos_feat, size_feat, yaw_feat], dim=-1) # torch.Size([1, 900, 192])
if self.vel_dims > 0: # 有速度,进入
vel_feat = self.vel_fc(box_3d[..., VX : VX + self.vel_dims]) # torch.Size([1, 900, 64])
if self.mode == "add":
output = output + vel_feat
elif self.mode == "cat":
output = torch.cat([output, vel_feat], dim=-1) # torch.Size([1, 900, 256]) 具体步骤:(一共39小步)
可以分成组:第一组(00:'deformable';01:'ffn';02:'norm';03:'refine';04:'temp_gnn';05:'gnn';06:'norm')第二组(同上)第三组(同上)第四组(同上)第五组(同上)第六组(35:'deformable';36:'ffn';37:'norm';38:'refine' 少了最后三个步骤)
①'deformable' (DeformableFeatureAggregation)
elif op == "deformable":
instance_feature = self.layers[i](
instance_feature,
anchor,
anchor_embed,
feature_maps,
metas,
)生成关键点:(SparseBox3DKeyPointsGenerator)
key_points = self.kps_generator(anchor, instance_feature)7个固定的点:
size = anchor[..., None, [W, L, H]].exp() # torch.Size([1, 900, 1, 3])
key_points = self.fix_scale * size # torch.Size([1, 900, 7, 3]) 7个点?6个通过学习到的点:
if self.num_learnable_pts > 0 and instance_feature is not None: # 进入
learnable_scale = ( # torch.Size([1, 900, 6, 3]) 6个点?
self.learnable_fc(instance_feature)
.reshape(bs, num_anchor, self.num_learnable_pts, 3)
.sigmoid()
- 0.5
)
key_points = torch.cat(
[key_points, learnable_scale * size], dim=-2 # 合并成13维 torch.Size([1, 900, 13, 3])
)加上旋转:(一共13个点)
rotation_mat = anchor.new_zeros([bs, num_anchor, 3, 3]) # torch.Size([1, 900, 3, 3])
rotation_mat[:, :, 0, 0] = anchor[:, :, COS_YAW]
rotation_mat[:, :, 0, 1] = -anchor[:, :, SIN_YAW]
rotation_mat[:, :, 1, 0] = anchor[:, :, SIN_YAW]
rotation_mat[:, :, 1, 1] = anchor[:, :, COS_YAW]
rotation_mat[:, :, 2, 2] = 1
key_points = torch.matmul(
rotation_mat[:, :, None], key_points[..., None]
).squeeze(-1) # torch.Size([1, 900, 13, 3]) 旋转
key_points = key_points + anchor[..., None, [X, Y, Z]] # torch.Size([1, 900, 13, 3])获得关键点对应的权重
weights = self._get_weights(instance_feature, anchor_embed, metas)
相机投影矩阵编码:
def _get_weights(self, instance_feature, anchor_embed, metas=None):
bs, num_anchor = instance_feature.shape[:2]
feature = instance_feature + anchor_embed
if self.camera_encoder is not None: # 进入
camera_embed = self.camera_encoder(
metas["projection_mat"][:, :, :3].reshape(
bs, self.num_cams, -1
)
)
feature = feature[:, :, None] + camera_embed[:, None]相机编码,6个相机,每个相机都是4*3(12)的参数:

实例的特征加上相机编码特征,组成的features算出权重,256特征到416(4个特征图尺度*13个点*8个注意力分组)个权重:
weights = (
self.weights_fc(feature)
.reshape(bs, num_anchor, -1, self.num_groups)
.softmax(dim=-2)
.reshape(
bs,
num_anchor,
self.num_cams,
self.num_levels,
self.num_pts,
self.num_groups,
)
) # torch.Size([1, 900, 6, 4, 13, 8])算出关键点在图像上的投影像素坐标:
if self.use_deformable_func:
points_2d = (
self.project_points(
key_points,
metas["projection_mat"],
metas.get("image_wh"),
)
.permute(0, 2, 3, 1, 4)
.reshape(bs, num_anchor, self.num_pts, self.num_cams, 2)
)里面的细节,主要过程是坐标投影,把900个锚框的13个关键点投影到6个视图上,得到投影点的像素坐标:
@staticmethod
def project_points(key_points, projection_mat, image_wh=None):
bs, num_anchor, num_pts = key_points.shape[:3] # torch.Size([1, 900, 13, 3])
pts_extend = torch.cat(
[key_points, torch.ones_like(key_points[..., :1])], dim=-1
) # torch.Size([1, 900, 13, 4]) 在右边新增全1的一列(应该是生成齐次坐标)
points_2d = torch.matmul( # torch.Size([1, 6, 900, 13, 4]) points_2d应该是投影到6个视图的13个点的坐标
projection_mat[:, :, None, None], pts_extend[:, None, ..., None]
).squeeze(-1) # projection_mat:torch.Size([1, 6, 4, 4])
points_2d = points_2d[..., :2] / torch.clamp(
points_2d[..., 2:3], min=1e-5
) # 除以深度
if image_wh is not None:
points_2d = points_2d / image_wh[:, :, None, None] # 坐标的归一化 torch.Size([1, 6, 900, 13, 2])
return points_2d真正的可变形注意力部分
features = DAF(*feature_maps, points_2d, weights).reshape(
bs, num_anchor, self.embed_dims
)里面就是算子,最后输出这900个框的256维特征:
class DeformableAggregationFunction(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(
ctx,
mc_ms_feat,
spatial_shape,
scale_start_index,
sampling_location,
weights,
):
# output: [bs, num_pts, num_embeds]
mc_ms_feat = mc_ms_feat.contiguous().float()
spatial_shape = spatial_shape.contiguous().int()
scale_start_index = scale_start_index.contiguous().int()
sampling_location = sampling_location.contiguous().float()
weights = weights.contiguous().float()
output = deformable_aggregation_ext.deformable_aggregation_forward(
mc_ms_feat,
spatial_shape,
scale_start_index,
sampling_location,
weights,
) # torch.Size([1, 900, 256])
ctx.save_for_backward(
mc_ms_feat,
spatial_shape,
scale_start_index,
sampling_location,
weights,
)
return outputoutput = self.proj_drop(self.output_proj(features)) # torch.Size([1, 900, 256])还要和原来的instance_feature 拼接一下,256+256=512维的特征向量
elif self.residual_mode == "cat":
output = torch.cat([output, instance_feature], dim=-1) # torch.Size([1, 900, 512])②ffn (AsymmetricFFN)

具体过程:(好像就是一个残差连接)
def forward(self, x, identity=None):
if self.pre_norm is not None:
x = self.pre_norm(x) # torch.Size([1, 900, 512])
out = self.layers(x) # torch.Size([1, 900, 256]) 又回到256维
if not self.add_identity: # 不进入
return self.dropout_layer(out)
if identity is None: # 进入
identity = x
identity = self.identity_fc(identity) # torch.Size([1, 900, 256])
return identity + self.dropout_layer(out) # 残差连接?③norm
![]()
④refine (SparseBox3DRefinementModule)


通过特征生成对anchor的修正量(前8维):
feature = instance_feature + anchor_embed # 现在这个实例特征是经过了投影到图像之后的图像实例特征 torch.Size([1, 900, 256])
output = self.layers(feature) # torch.Size([1, 900, 11]) 256下降到11维
output[..., self.refine_state] = (
output[..., self.refine_state] + anchor[..., self.refine_state]
) # self.refine_state有从0到7 一共8个 修正量加上anchor本身的值等于输出的值通过除以帧间时间间隔得到三个方向上速度的修正量(后三维):
if self.output_dim > 8: # 进入
if not isinstance(time_interval, torch.Tensor): # 不进入
time_interval = instance_feature.new_tensor(time_interval)
translation = torch.transpose(output[..., VX:], 0, -1)
velocity = torch.transpose(translation / time_interval, 0, -1) # 三个方向上的速度torch.Size([1, 900, 3]) time_interval是帧间隔时间?
output[..., VX:] = velocity + anchor[..., VX:] # 加上修正10个目标类别的预测:
if return_cls: # 进入
assert self.with_cls_branch, "Without classification layers !!!"
cls = self.cls_layers(instance_feature) # torch.Size([1, 900, 10])质量的预测:
if return_cls and self.with_quality_estimation: # 进入
quality = self.quality_layers(feature) # torch.Size([1, 900, 2])对应论文:


保存预测框、类别和质量:
prediction.append(anchor)
classification.append(cls)
quality.append(qt)更新实例库:(InstanceBank)
if len(prediction) == self.num_single_frame_decoder: # 1
instance_feature, anchor = self.instance_bank.update(
instance_feature, anchor, cls
) # 更新实例库# 如果是第一帧self.cached_feature就是None
def update(self, instance_feature, anchor, confidence):
if self.cached_feature is None: # 如果是第一帧self.cached_feature就是None
return instance_feature, anchor如果不到最后一步,anchor必须再次编码:
if i != len(self.operation_order) - 1:
anchor_embed = self.anchor_encoder(anchor) # anchor继续编码⑤temp_gnn

elif op == "temp_gnn":
instance_feature = self.graph_model(
i,
instance_feature,
temp_instance_feature,
temp_instance_feature,
query_pos=anchor_embed,
key_pos=temp_anchor_embed,
attn_mask=attn_mask
if temp_instance_feature is None
else None,
)对应论文:

如引言中所述,我们对Sparse4Dv2中的锚编码器、自我注意和时间交叉注意进行了简单的改进。该体系结构如图5所示。设计原则是以串联的方式组合来自不同模式的特征,而不是使用加法方法。与条件DETR[33]相比,有一些差异。首先,我们对查询之间的注意进行了改进,而不是查询和图像特征之间的交叉注意;交叉注意仍然利用来自Sparse4D的可变形聚合。此外,我们没有在多头注意力级别连接位置嵌入和查询特征,而是在多头注意力级别外部进行修改,为神经网络提供更大的灵活性。
图 5:锚编码器和注意力的架构。我们独立地对锚的多个组件进行高维特征编码,然后将它们连接起来。与原始 Sparse4D 相比,这种方法会导致更低的计算量和参数开销。E 和 F 分别表示锚嵌入和实例特征。
⑥gnn
gnn和之前的temp_gnn其实结构都一样

最终,经过6组上述步骤之后,更新预测结果:
output.update(
{
"classification": classification,
"prediction": prediction,
"quality": quality,
}classification和quality都只有两个不是None:


prediction是6层都有输出:

缓存当前的实例特征
# cache current instances for temporal modeling
self.instance_bank.cache(
instance_feature, anchor, cls, metas, feature_maps
)缓存的时候就不保存梯度了:
instance_feature = instance_feature.detach()
anchor = anchor.detach()
confidence = confidence.detach()生成置信度:
confidence = confidence.max(dim=-1).values.sigmoid()
if self.confidence is not None:
confidence[:, : self.num_temp_instances] = torch.maximum(
self.confidence * self.confidence_decay,
confidence[:, : self.num_temp_instances],
)
self.temp_confidence = confidence选出置信度最高的600个实例特征和锚框:
(
self.confidence,
(self.cached_feature, self.cached_anchor),
) = topk(confidence, self.num_temp_instances, instance_feature, anchor)具体过程:
def topk(confidence, k, *inputs):
bs, N = confidence.shape[:2]
confidence, indices = torch.topk(confidence, k, dim=1) # 选出600个置信度最高的
indices = (
indices + torch.arange(bs, device=indices.device)[:, None] * N
).reshape(-1)
outputs = []
for input in inputs:
outputs.append(input.flatten(end_dim=1)[indices].reshape(bs, k, -1))# 按照索引,把实例特征和锚框整理好
return confidence, outputs推理的最后会得到实例的ID
if not self.training:
instance_id = self.instance_bank.get_instance_id(
cls, anchor, self.decoder.score_threshold
)
output["instance_id"] = instance_id初始化实例ID:
def get_instance_id(self, confidence, anchor=None, threshold=None):
confidence = confidence.max(dim=-1).values.sigmoid()
instance_id = confidence.new_full(confidence.shape, -1).long() # 初始化实例ID筛选出新的实例,给它们赋上新的ID:
mask = instance_id < 0
if threshold is not None:
mask = mask & (confidence >= threshold)
num_new_instance = mask.sum()
new_ids = torch.arange(num_new_instance).to(instance_id) + self.prev_id
instance_id[torch.where(mask)] = new_ids准备传给下一帧的实例:
if self.num_temp_instances > 0:
self.update_instance_id(instance_id, confidence)具体过程:
def update_instance_id(self, instance_id=None, confidence=None):
if self.temp_confidence is None:
if confidence.dim() == 3: # bs, num_anchor, num_cls
temp_conf = confidence.max(dim=-1).values
else: # bs, num_anchor
temp_conf = confidence
else:
temp_conf = self.temp_confidence
instance_id = topk(temp_conf, self.num_temp_instances, instance_id)[1][
0
] # torch.Size([1, 600, 1]) 从900个里面再筛选出600个置信度最高的ID
instance_id = instance_id.squeeze(dim=-1)
self.instance_id = F.pad(
instance_id,
(0, self.num_anchor - self.num_temp_instances),
value=-1,
) # 剩下的300个用-1补齐到900个实例后处理
Sparse4DHead结束之后就开始后处理了:
results = self.head.post_process(model_outs)从10个类别中筛选出置信度最高的那一类,再筛选出300个最高的实例:
cls_scores = cls_scores[output_idx].sigmoid() # torch.Size([1, 900, 10])
if squeeze_cls: # 进入
cls_scores, cls_ids = cls_scores.max(dim=-1) # torch.Size([1, 900]) 从10个类别中选出置信度最高的那一个类别
cls_scores = cls_scores.unsqueeze(dim=-1) # torch.Size([1, 900, 1])
box_preds = box_preds[output_idx] # torch.Size([1, 900, 11])
bs, num_pred, num_cls = cls_scores.shape
cls_scores, indices = cls_scores.flatten(start_dim=1).topk(
self.num_output, dim=1, sorted=self.sorted
) # torch.Size([1, 300]) 只输出300个框用centerness再对置信度加权:
if qulity is not None: # 进入
centerness = qulity[output_idx][..., CNS] # torch.Size([1, 900])
centerness = torch.gather(centerness, 1, indices // num_cls) # torch.Size([1, 300])
cls_scores_origin = cls_scores.clone()
cls_scores *= centerness.sigmoid() # torch.Size([1, 300]) 乘上centerness
cls_scores, idx = torch.sort(cls_scores, dim=1, descending=True) # 再排序
if not squeeze_cls: # 不进入
cls_ids = torch.gather(cls_ids, 1, idx)
if self.score_threshold is not None: # 不进入
mask = torch.gather(mask, 1, idx)
indices = torch.gather(indices, 1, idx)把框框拿出来:
for i in range(bs):
category_ids = cls_ids[i] # torch.Size([900])
if squeeze_cls:
category_ids = category_ids[indices[i]] # torch.Size([300])
scores = cls_scores[i] # torch.Size([300])
box = box_preds[i, indices[i] // num_cls] # torch.Size([300, 11])解码框框,得到10维的3D框:
def decode_box(self, box):
yaw = torch.atan2(box[:, SIN_YAW], box[:, COS_YAW]) # torch.Size([300])
box = torch.cat(
[
box[:, [X, Y, Z]],
box[:, [W, L, H]].exp(),
yaw[:, None],
box[:, VX:],
],
dim=-1,
) # torch.Size([300, 10])
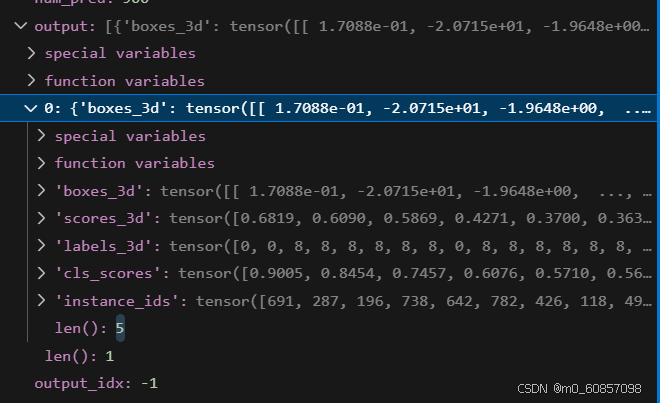
return box最后输出有5个东西,3D框、3D置信度、类别、分类置信度、实例ID(都是300个):
























 1195
1195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








