01 基础语法
VL1 四选一多路器
三元运算符
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module mux4_1(
input [1:0]d1,d2,d3,d0,
input [1:0]sel,
output[1:0]mux_out
);
//*************code***********//
assign mux_out = ~sel[1] ? ~sel[0] ? d3 : d2 : ~sel[0] ? d1 : d0;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL2 异步复位的串联T触发器
T触发器
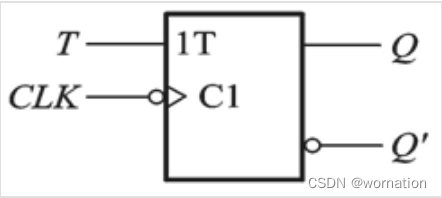
在时钟脉冲控制下,T为1时Q翻转,T为0时保持。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module Tff_2 (
input wire data, clk, rst,
output reg q
);
//*************code***********//
// 第一个TFF的输出
reg q_pre;
/**
q_pre operation
*/
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
q_pre <= 1'b0;
end
else if(data)
q_pre <= ~q_pre;
else
q_pre <= q_pre;
end
/**
q operation
*/
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
q <= 1'b0;
end
else if(q_pre)
q <= ~q;
else
q <= q;
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL3 奇偶校验
奇偶校验(parity check):
奇校验:给定二进制数中的1的个数为偶数时,补1个bit 1,使其为奇数
偶校验:给定二进制数中的1的个数为奇数时,补1个bit 1,使其为偶数
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module odd_sel(
input [31:0] bus,
input sel,
output check
);
//*************code***********//
// sel 1 even check 0 old check
assign check = sel ? ^bus : ~^bus;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL4 移位运算与乘法
使用三段式状态机实现,总共5个状态,IDLE, M1, M3, M7, M8
利用位移运算代替乘法,✖️1 (<< 1), ✖️3 (<< 2 - 1), ✖️7 (<< 3 - 1), ✖️8 (<<3)
注意只有M1状态时,才会获取d的输入
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module multi_sel(
input [7:0]d ,
input clk,
input rst,
output reg input_grant,
output reg [10:0]out
);
//*************code***********//
localparam IDLE = 3'b000, M1 = 3'b001, M3 = 3'b010, M7 = 3'b011
, M8 = 3'b100;
reg [2:0] cur_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
reg [7:0] d_r;
/*
1. current state transfer
*/
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
cur_state <= IDLE;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state;
end
end
/*
2. transfer condition
*/
always @ (*) begin
case(cur_state)
IDLE: next_state <= M1;
M1: next_state <= M3;
M3: next_state <= M7;
M7: next_state <= M8;
M8: next_state <= M1;
default: next_state <= cur_state;
endcase
end
/*
3. state output
*/
always @ (posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
input_grant <= 1'b0;
out <= 11'b0;
end
else begin
case(next_state)
IDLE: begin
out <= 11'b0;
input_grant <= 1'b0;
end
M1: begin
// get d in
d_r <= d;
out <= d;
input_grant <= 1'b1;
end
M3: begin
out <= (d_r << 1) + d_r;
input_grant <= 1'b0;
end
M7: begin
out <= (d_r << 3) - d_r;
input_grant <= 1'b0;
end
M8: begin
out <= (d_r << 3);
input_grant <= 1'b0;
end
endcase
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL5 位拆分与运算
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_cal(
input clk,
input rst,
input [15:0]d,
input [1:0]sel,
output [4:0]out,
output validout
);
//*************code***********//
reg [15:0] d_r;
reg validout;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst) begin
if(!rst) begin
validout <= 0;
d_r <= 16'b0;
end
else if(sel == 2'b0) begin
validout <= 1'b0;
d_r <= d;
end
else begin
d_r <= d_r;
validout <= 1'b1;
end
end
assign out = sel[1] ? (sel[0] ? {
d_r[3:0] + d_r[15:12]} : {
d_r[3:0] + d_r[11:8]}) : (sel[0] ? {
d_r[3:0] + d_r[7:4]} : 4'b0);
//*************code***********//
endmodule
VL6 多功能数据处理器
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_select(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input signed[7:0]a,
input signed[7:0]b,
input [1:0]select,
output reg signed [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
c <= 9'b0;
end
else begin
case(select)
2'b00: c <= {
a[7],a};
2'b01: c <= {
b[7],b};
2'b10: c <= a + b;
2'b11: c <= a - b;
default: c <= c;
endcase
end
end
endmodule
VL7 求两个数的差值
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_minus(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output reg [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
c <= 9'b0;
end
else begin
if(a > b)
c <= a - b;
else
c <= b - a;
end
end
endmodule
VL8 使用generate…for语句简化代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module gen_for_module(
input [7:0] data_in,
output [7:0] data_out
);
genvar i;
generate
for(i = 0; i <= 7; i= i + 1) begin: gen
assign data_out[i] = data_in[7 - i];
end
endgenerate
endmodule
VL9 使用子模块实现三输入数的大小比较
要注意如果先比较a和b的大小得出a_b_min,在比较c和a_b_min的大小这里得出的答案是错误的,因为是并行执行的,导致与c比较的a_b_min永远是前一个时钟周期的a_b_min。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module main_mod(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
input [7:0]c,
output [7:0]d
);
wire [7:0] a_b_min;
sub_mod inst1(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.m(a),
.n(b),
.m_n_min(a_b_min)
);
wire [7:0] b_c_min;
sub_mod inst2(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.m(b),
.n(c),
.m_n_min(b_c_min)
);
sub_mod inst3(
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.m(a_b_min),
.n(b_c_min)







 这篇博客详细记录了Verilog的初步学习过程,包括基础语法如四选一多路器、异步复位T触发器的实现,以及组合逻辑中的数值比较器和优先编码器设计。同时,博主通过状态转移表和图介绍了时序逻辑电路的实现,如ROM和边沿检测等。
这篇博客详细记录了Verilog的初步学习过程,包括基础语法如四选一多路器、异步复位T触发器的实现,以及组合逻辑中的数值比较器和优先编码器设计。同时,博主通过状态转移表和图介绍了时序逻辑电路的实现,如ROM和边沿检测等。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 396
396

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








