C++中的继承类构造函数注意事项
构造原则如下:
1. 如果子类没有定义构造方法,则调用父类的无参数的构造方法。
2. 如果子类定义了构造方法,不论是无参数还是带参数,在创建子类的对象的时候,首先执行父类无参数的构造方法,然后执行自己的构造方法。
3. 在创建子类对象时候,如果子类的构造函数没有显示调用父类的构造函数,则会调用父类的默认无参构造函数。
4. 在创建子类对象时候,如果子类的构造函数没有显示调用父类的构造函数且父类自己提供了无参构造函数,则会调用父类自己的无参构造函数。
5. 在创建子类对象时候,如果子类的构造函数没有显示调用父类的构造函数且父类只定义了自己的有参构造函数,则会出错(如果父类只有有参数的构造方法,则子类必须显示调用此带参构造方法)。
6. 如果子类调用父类带参数的构造方法,需要用初始化父类成员对象的方式
关键代码举例
class People
{
public:
virtual void print();
People(string nm);
void getID(int num);
protected:
int ID;
string name;
};
class Student : public People
{
public:
void print();
Student(string sch);
private:
string school;
//string name;
};
People::People(string nm)
{
name = nm;
}
//子类必须显示的调用父类的带参数构造函数
Student::Student(string sch) : People("yzj")
{
school = sch;
}
完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class People
{
public:
virtual void print();
People(string nm);
void getID(int num);
protected:
int ID;
string name;
};
class Student : public People
{
public:
void print();
Student(string sch);
private:
string school;
//string name;
};
People::People(string nm)
{
name = nm;
}
Student::Student(string sch) : People("yzj")//子类必须显示的调用父类的带参数构造函数
{
school = sch;
}
void People::print()
{
cout << "The name is " << name << endl;
cout << "The ID is " << ID << endl;
}
void People::getID(int num)
{
ID = num;
}
void Student::print()
{
cout << "The name is " << name << endl;
cout << "The school is " << school << endl;
}
int main()
{
People people("lzq");
people.getID(123);
Student student("MaEr");
people.print();
student.print();
return 0;
}
输出
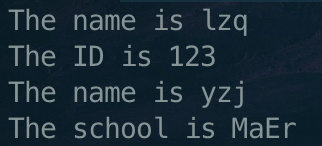
总结
- 在类的继承的过程中,如果子类没有定义构造函数,程序就会自动调用父类的构造函数。
- 如果子类定义了构造函数且父类是无参的构造函数,那么创建类的时候会自动先调用父类的构造函数,再调用子类的构造函数。
- 如果子类定义了构造函数且没有显示调用父类中唯一的带参构造函数,程序会报错。
- 调用父类构造函数的时候得用初始化父类成员对象的方式。





















 5040
5040

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








