概述:本文主要介绍了DataFrame、DataSet常见API的使用
1、DataFrame的使用
object DataFrameApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
//将json转为DataFrame
val peopleDF = spark.read.format("json").load("file:///F:/people.json")
//hdfs://hadoop:8020/input/wc/people.json
peopleDF.printSchema()
//默认输出前20条记录
peopleDF.show()
//查询某列数据
peopleDF.select("name", "age").show()
//查询列数据并进行计算
peopleDF.select(peopleDF.col("name"), (peopleDF.col("age") + 9).as("newAge"))
//条件查询
peopleDF.filter(peopleDF.col("age") > 19).show()
peopleDF.where(peopleDF.col("age") > 19).show()
//分组与聚合操作 select age,count(1) from table group by age
peopleDF.groupBy("age").count().show()
spark.stop()
}
}
2、RDD与DataFrame的互操作
(1)反射方式
object DataFrameRDDApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("DataFrameRDDApp").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
//RDD转DataFrame
val rdd = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///F:/people.txt")
//toDF需要导入隐式转换
import spark.implicits._
val peopleDF = rdd.map(_.split(",")).map(line => people(line(0).toInt, line(1).toString, line(2).toInt)).toDF()
peopleDF.printSchema()
peopleDF.show()
peopleDF.filter(peopleDF.col("age")<25).show()
//创建临时视图 使用sql操作数据库
peopleDF.createOrReplaceTempView("peopleTmpView")
spark.sql("select p.id ID,p.name USERNAME,p.age AGE from peopleTmpView p WHERE name LIKE '%an%'").show()
spark.stop()
}
case class people(id: Int, name: String, age: Int)
}
(2)编程方式
使用情形:
-
When case classes cannot be defined ahead of time (for example, the structure of records is encoded in a string, or a text dataset will be parsed and fields will be projected differently for different users).
创建DataFrame步骤:
- Create an RDD of Rows from the original RDD;
- Create the schema represented by a StructType matching the structure of Rows in the RDD created in Step 1.
- Apply the schema to the RDD of Rows via createDataFrame method provided by SparkSession.
代码:
object DataFrameRDDApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("DataFrameRDDApp").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
//RDD转DataFrame
val rdd = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///F:/people.txt")
val peopleRDD = rdd.map(_.split(",")).map(line => Row(line(0).toInt, line(1).toString, line(2).toInt))
val structType = StructType(Array(StructField("id", IntegerType, true), StructField("name", StringType, true), StructField("age", IntegerType, true)))
val peopleDF = spark.createDataFrame(peopleRDD, structType)
peopleDF.printSchema()
peopleDF.show()
peopleDF.filter(peopleDF.col("age") < 25).show()
//创建临时视图 使用sql操作数据库
peopleDF.createOrReplaceTempView("peopleTmpView")
spark.sql("select p.id ID,p.name username,p.age AGE from peopleTmpView p WHERE name LIKE '%li%'").show()
spark.stop()
}
}
模糊查询结果:

选型说明:如果字段名称、类型可知,优先选择反射方式
(3)DataFrame其他API
object DataFrameCase {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("DataFrameCase ").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
//RDD转DataFrame
val rdd = spark.sparkContext.textFile("file:///F:/student.data")
import spark.implicits._
val studentDF = rdd.map(_.split("\\|")).map(line => student(line(0).toInt, line(1).toString, line(2).toString, line(3).toString)).toDF()
studentDF.first()
studentDF.printSchema()
studentDF.show(30,false)
studentDF.filter("name='' OR name='null'")
//查找以M开头的学生
studentDF.filter("SUBSTR(name,0,1)='E'").show()
studentDF.sort(studentDF("name")).show()
studentDF.sort("name","email").show()
studentDF.sort(studentDF("name").desc).show()
studentDF.select(studentDF("name").as("studentName")).show()
//默认内连接 需要使用三个=
val newStudentDF = rdd.map(_.split("\\|")).map(line => student(line(0).toInt, line(1).toString, line(2).toString, line(3).toString)).toDF()
studentDF.join(newStudentDF,studentDF("id")=!=newStudentDF("id"),"right").show(500,false)
studentDF.take(10).foreach(println)
studentDF.first()
studentDF.head(5)
spark.stop()
}
case class student(id:Int,name:String,phone:String,email:String)
}
根据姓名排序结果:
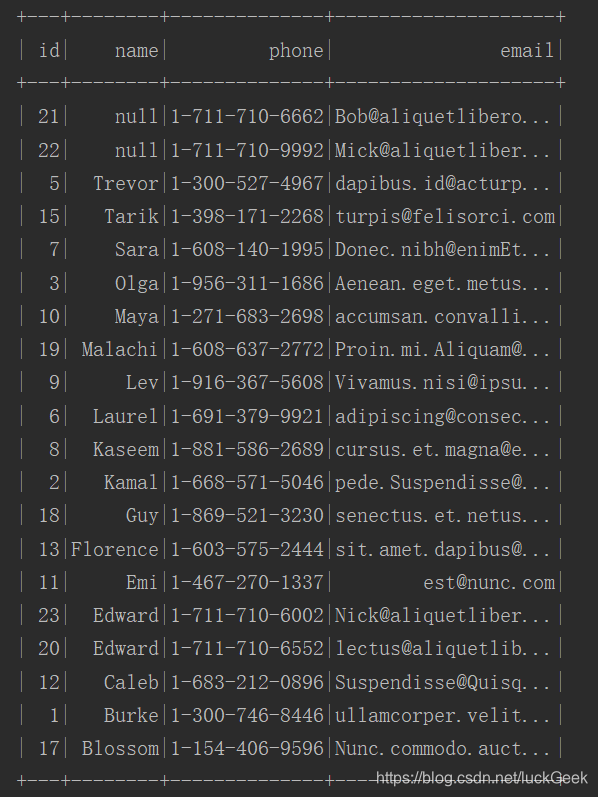
3、DataSet的使用
(1)DataFrame转DataSet
object DataSetApp {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("DataSetApp").master("local[2]").getOrCreate()
val path = "file:///F:/student.csv"
//解析csv文件 外部数据源功能
val df = spark.read.option("header", "true").option("inferSchema", true).csv(path)
df.show()
//隐式转换 df转ds
import spark.implicits._
val ds = df.as[student]
ds.map(line=>line.email).show()
spark.stop()
}
case class student(id: Int, studentName: String, phone: String, email: String)
}
DataSet的查询邮箱结果:
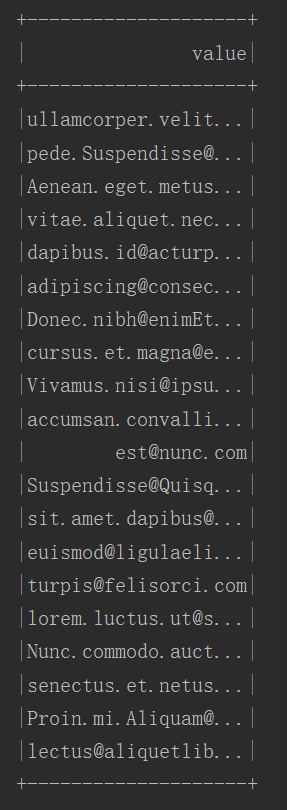
(2)DataSet静态类型(Static-typing)和运行时类型安全(runtime type-safety)
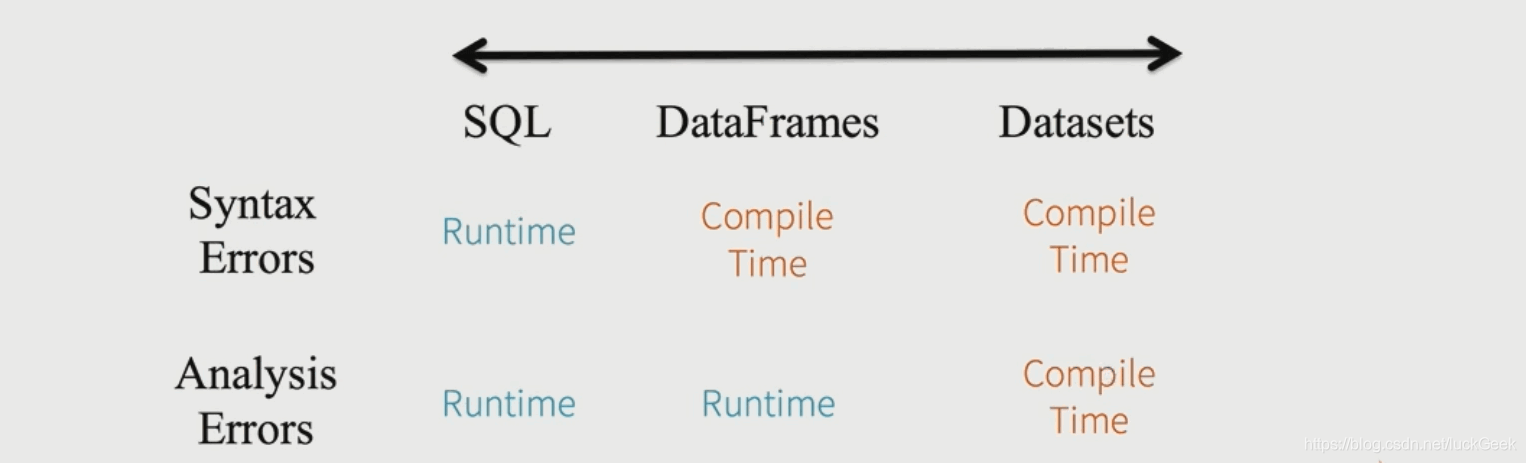
说明:
- spark.sql("seletc * from emp e join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno").show()编译可以通过,执行sql时报错
- studentDF.seletc(studentDF("name").as("studentName")).show()中编译将不能通过
- ds.map(line=>line.emails).show()中编译将不能通过,Dataset不管是哪种状态都是安全的,即静态类型和运行时类型安全,因为Dataset两种状态都能把错误抛出来。




 本文详述了Spark中的DataFrame和DataSet的使用,包括DataFrame的创建、从RDD转换、反射与编程方式的操作,以及DataSet的转换和其静态类型与运行时类型安全的特性。在字段名称和类型已知的情况下,推荐使用反射方式创建DataFrame。文中还通过实例展示了如何根据姓名排序和查询邮箱等操作。
本文详述了Spark中的DataFrame和DataSet的使用,包括DataFrame的创建、从RDD转换、反射与编程方式的操作,以及DataSet的转换和其静态类型与运行时类型安全的特性。在字段名称和类型已知的情况下,推荐使用反射方式创建DataFrame。文中还通过实例展示了如何根据姓名排序和查询邮箱等操作。
















 1067
1067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








