@TOC
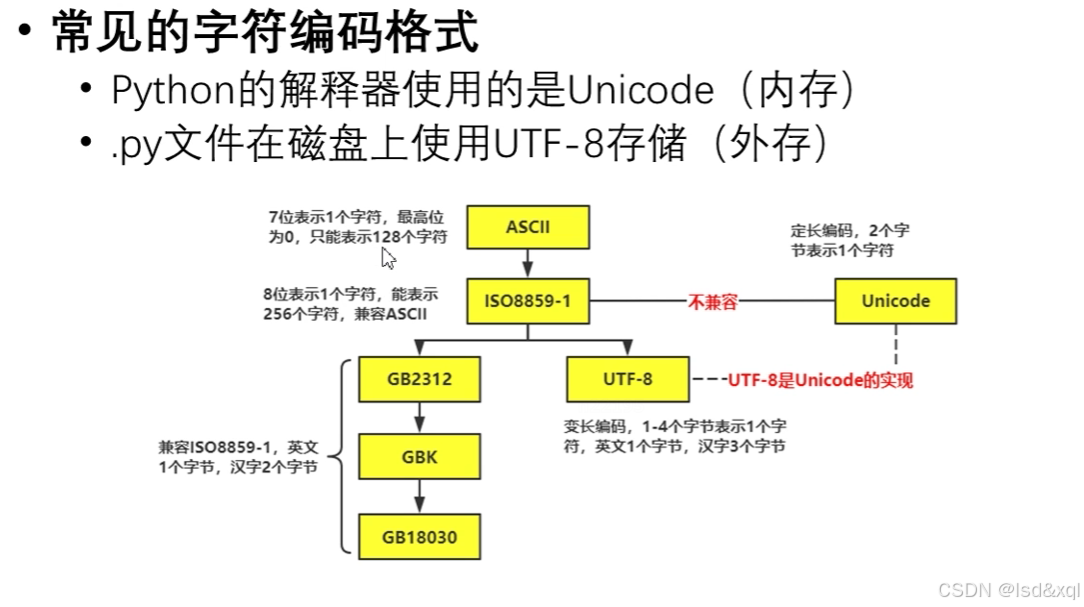
编码格式介绍
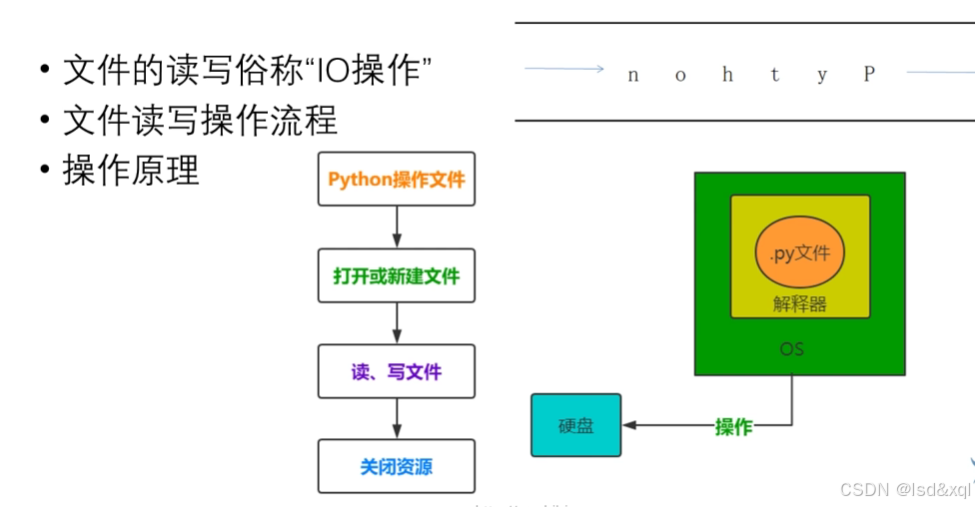
文件的读写原理
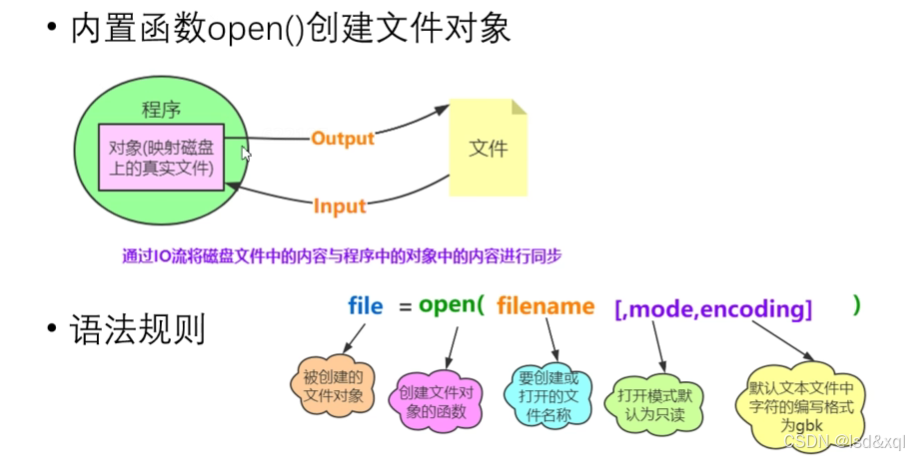

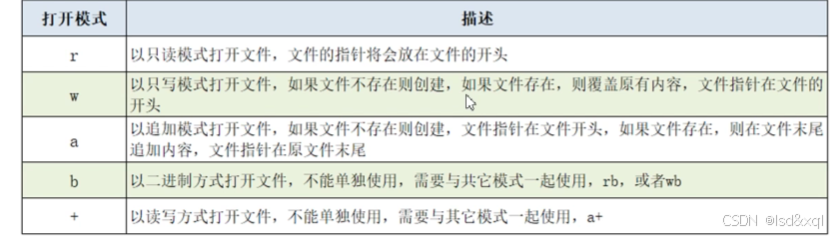
常见的文件打开模式

file = open('b.txt','w')
file.write('Python')
file.close()
file = open('b.txt','a')
file.write('Python')
file.close()
src_file = open('logo.png','rb')
target_file = open('copylogo.png','wb')
print(target_file.write(src_file.read()))
src_file.close()
target_file.close()
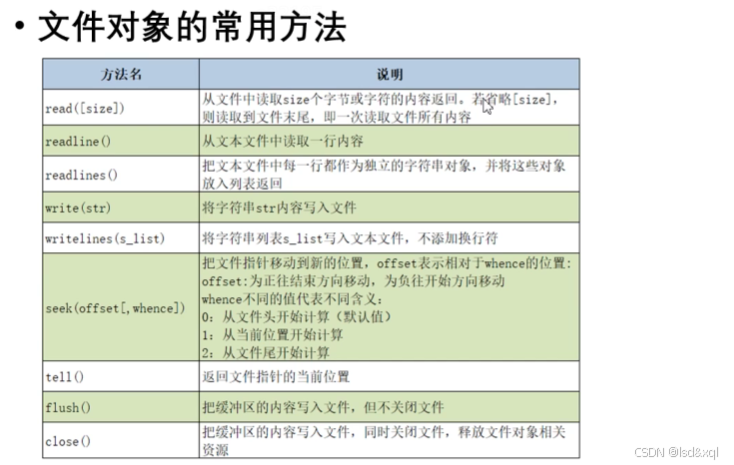
文件对象的常用方法
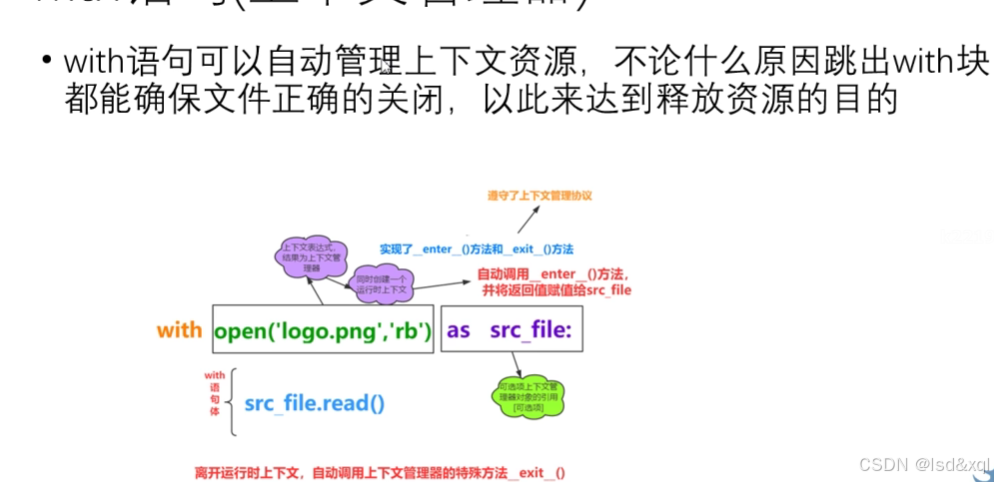
with语句,上下文资源管理器
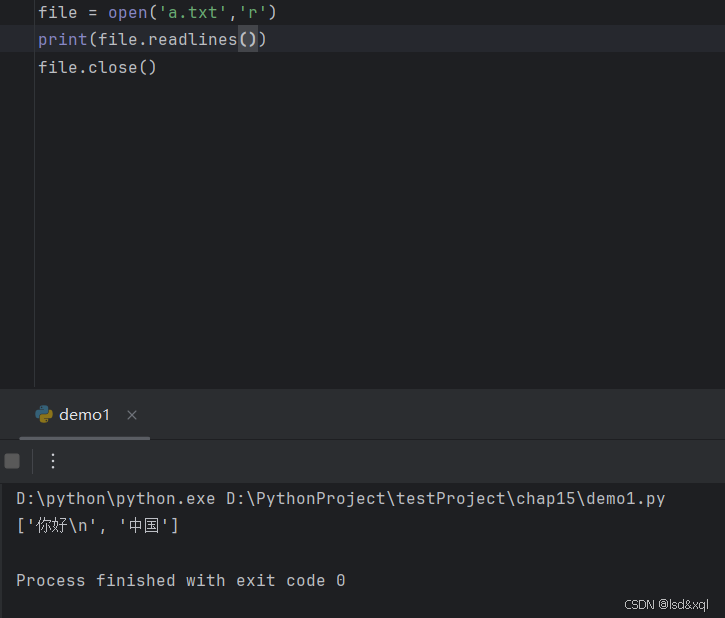
with open('a.txt','r') as file:
print(file.read())
本质上是一个上下文管理器,它实现了特殊的enter方法和exit方法进入和退出方法
'''这个类对象遵守了上下文管理器'''
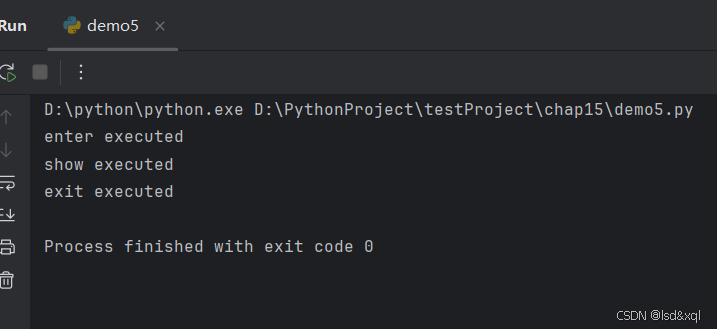
class MyContentMgr:
def __enter__(self):
print('enter executed')
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
print('exit executed')
def show(self):
print('show executed')
with MyContentMgr() as m:
m.show()
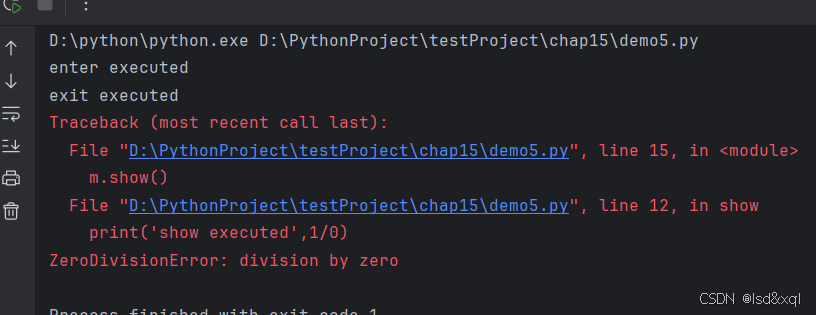
当有异常情况时exit还是会执行
'''这个类对象遵守了上下文管理器'''
class MyContentMgr:
def __enter__(self):
print('enter executed')
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
print('exit executed')
def show(self):
print('show executed',1/0)
with MyContentMgr() as m:
m.show()
文件赋值写法:
with open('logo.png','rb') as src_file:
with open('copy2log.png','wb') as dst_file:
dst_file.write(src_file.read())
OS模块

操作目录:
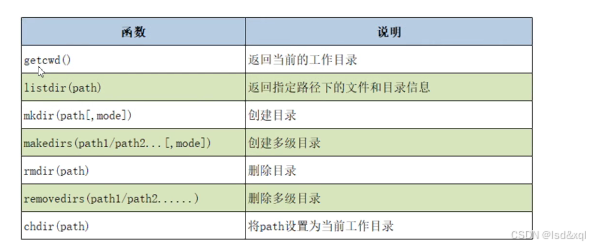
import os
print(os.getcwd())
lst = os.listdir('../chap15')
print(lst)
os.mkdir('newdir')
os.makedirs('A/B/C')
os.rmdir('newdir')
os.removedirs('A/B/C')
os.chdir('')
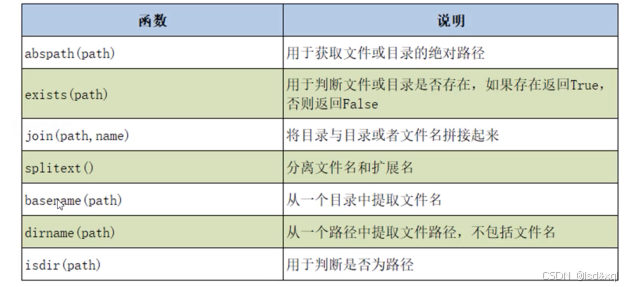
os.path操作目录相关函数:
列出指定目录下所有的py文件
import os
path = os.getcwd()
lst = os.listdir(path)
for filename in lst:
if filename.endswith('.py'):
print(filename)
递归的打印所有的:
import os
path = os.getcwd()
print(path)
lst_files = os.walk(path)
print(lst_files)
for dirpath,dirnames,filenames in lst_files:
# print(dirpath)
# print(dirnames)
# print(filenames)
# print('-----------------')
for dir in dirnames:
print(os.path.join(dirpath, dir))
for filename in filenames:
print(os.path.join(dirpath, filename))
print('-----------------')






















 1451
1451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








