List<T>
转载刘老师课程PPT



List<int> intList = new List<int> { 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 };
var seg = intList.GetRange(1, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < seg.Count; i++)
{
seg[i]++;
}
List<int>.Enumerator e = intList.GetEnumerator();
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
while (e.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Current);
}
Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------");
foreach (var item in intList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------");
int sum = 0;
intList.ForEach(a => sum += a);
//intList.ForEach(action);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
Console.WriteLine("------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", intList));
Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", seg));
using System.Text.Json;
namespace ListSearch
{
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return JsonSerializer.Serialize(this);
}
public override bool Equals(object? obj)
{
if (obj == null) return false;
Book other = obj as Book;
if (other == null)
{
return false;
}
else if (other.Id == this.Id && other.Name == this.Name && other.Price == this.Price)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
using ListSearch;
List<double> list1 = new List<double> { 100.0, 200.0, 300.0, 400.0, 100.0, 200.0, 300.0, 400.0 };
Book book1 = new Book { Id = 1, Name = "Book-1", Price = 10 }, book6 = book1;
Book book2 = new Book { Id = 2, Name = "Book-2", Price = 20 };
Book book3 = new Book { Id = 3, Name = "Book-3", Price = 30 };
Book book4 = new Book { Id = 4, Name = "Book-4", Price = 40 };
Book book5 = new Book { Id = 1, Name = "Book-1", Price = 10 };
List<Book> list2 = new List<Book> { book1, book2, book3, book4 };
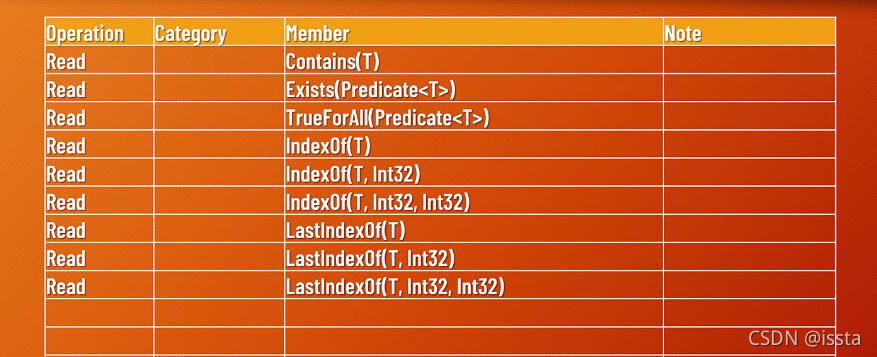
//bool res = list2.Contains(book5);
//bool res = list2.Exists(e => e.Price <= 30);
//bool res = list2.TrueForAll(e => e.Price <= 40);
//bool res = list1.TrueForAll(e => e % 100 == 0);
//Console.WriteLine(res);
//int idx = list1.IndexOf(300.0);
//int idx = list2.IndexOf(book5);
//int idx = list1.IndexOf(300, 2);
//Console.WriteLine(idx);
/*
int i = -1;
while (true)
{
i = list1.IndexOf(300, i + 1);
if (i == -1)
{
break;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
*/
//int idx = list1.IndexOf(300, 3, 3);
int idx = list1.LastIndexOf(300);
Console.WriteLine(idx);
public class Book:IComparable<Book>
public class Book:IComparable<Book>
{
..........
public int CompareTo(Book? other)
{
if (other == null) return 1;
return (this.Id - other.Id);
}
..........
}
List<double> list1 = new List<double> { 80.0, 70.0, 60.0, 50.0 ,40.0, 30.0, 20.0, 10.0 };
Book book1 = new Book { Id = 1, Name = "Book-1", Price = 10 };
Book book2 = new Book { Id = 2, Name = "Book-2", Price = 20 };
Book book3 = new Book { Id = 3, Name = "Book-3", Price = 30 };
Book book4 = new Book { Id = 4, Name = "Book-4", Price = 40 };
Book book5 = new Book { Id = 1, Name = "Book-1", Price = 10 };
List<Book> list2 = new List<Book> { book1, book2, book3, book4 };
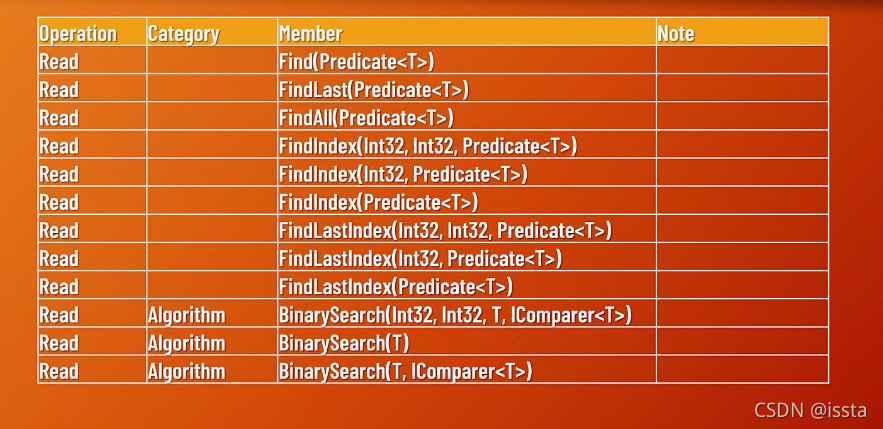
//var idx = list1.Find(e => e % 3 == 0);
//var idx = list2.Find(e => e.Price % 3 == 0);
//var idx = list2.FindLast(e => e.Price % 4 == 0);
//var idx = list1.FindLast(e => e % 3 == 0);
//Console.WriteLine(idx);
//var list = list1.FindAll(e => e % 3 == 0);
//var list = list2.FindAll(book => book.Price % 4 == 0);
//Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", list));
//var idx = list1.FindIndex(e => e % 3 == 0);
//var idx = list1.FindIndex(1, e => e % 3 == 0);
//var idx = list2.FindIndex(2, 2, e => e.Price % 4 == 0);
//var idx = list2.FindLastIndex(2, 2, e => e.Price % 4 == 0);
//Console.WriteLine(idx);
//Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", list1));
//list1.Sort();
//Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", list1));
//var res = list1.BinarySearch(30);
//Console.WriteLine(res);
//Console.WriteLine(list1[res]);
Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", list2));
list2.Sort();
Console.WriteLine(String.Join(",", list2));
var res = list2.BinarySearch(book5);
Console.WriteLine( res);





 本文探讨了List<T>的数据结构及其在编程中的使用,包括其属性和方法。内容源自刘老师的课程PPT,主要关注C#中的实现。
本文探讨了List<T>的数据结构及其在编程中的使用,包括其属性和方法。内容源自刘老师的课程PPT,主要关注C#中的实现。

















 1237
1237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










