一.二叉树的遍历概念
二叉树的遍历是指从根结点触发,按照某种次序依次访问二叉树中所有结点,使得每个结点被访问一次且仅被访问一次。
(1). 前(先)序遍历
前序遍历:若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则先访问根结点,然后前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子书。
特点:①. 根----->左------->右
②. 根据前序遍历的结果可知第一个访问的必定是root结点。
(2). 中序遍历
中序遍历:若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则从根结点开始(注意并不是先访问根结点),中序遍历根结点的左子树,然后访问根结点,最后中序遍历右子树。
特点:①. 左----->根------->右
②. 根据中序遍历的结果,再结合前序遍历的root结点去划分root结点的左右子树。
(3). 后序遍历
后序遍历:若二叉树为空,则空操作返回,否则从左到右先叶子结点后结点的方式遍历访问左右子树,最后访问根结点。
特点:①. 左------>右------>根
②. 根据后序遍历的结果可知最后访问的必定是root结点。
(4). 层序遍历
层序遍历:若二叉树为空,则空返回,否则从树的第一层,即根结点开始访问,从上而下逐层遍历,在同一层中,按从左到右的顺序对结点逐个访问。
特点:①. 从左到右,从上到下
②. 可知第一个访问的必定是root结点
二.例子分析先/中/后序遍历
假如有如下的二叉树:
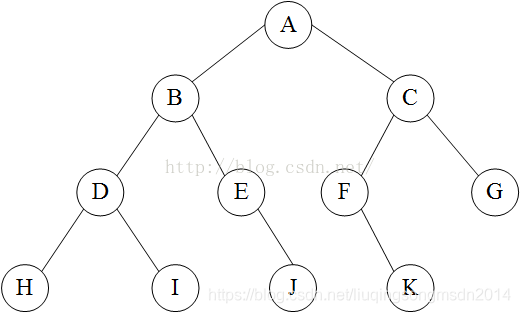
根据上面的定义,得出如下的遍历结果
前序遍历:ABDHIEJCFKG
中序遍历:HDIBEJAFKCG
后序遍历:HIDJEBKFGCA
层序遍历:ABCDEFGHIJK
三.代码实例(instance analysis)
1.思路分析
数据类型
typedef struct btree
{
DATATYPE data;
struct btree *lchild;
struct btree *rchild;
}BTREE;
例如:创建一个有N(6)个节点的完全二叉树
特性:
对于给定的序号K
左存在 2 * k <= N ,序号:2k
右存在 2 * k + 1 <= N,序号:2k + 1
创建过程:
create_binaytree(1)
|
root : 1
root->lchild = create_binaytree(2)
|
root : 2
root->lchild = create_binaytree(4)
|
root : 4
..
..
return root;
root->rchild = create_binaytree(5)
|
root : 5
..
..
return root;
return root;
root->rchild = create_binaytree(3)
|
root : 3
root->lchild = create_binaytree(6)
|
root:6
..
..
return root;
..
return root;
return root;
2. instance analysis
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 6
typedef struct btree
{
int data;
struct btree *lchild;
struct btree *rchild;
}BTREE;
BTREE *space_node(int data)
{
BTREE *tree;
tree = (BTREE *)malloc(sizeof(BTREE));
tree->data = data;
tree->lchild = tree->rchild = NULL;
return tree;
}
BTREE *create_binarytree(int num)
{
BTREE *root;
root = space_node(num);
if(2 * root->data <= N)
{
root->lchild = create_binarytree(2 * root->data);
}
if(2 * root->data + 1 <= N)
{
root->rchild = create_binarytree(2 * root->data + 1);
}
return root;
}
void PreOrder(BTREE *tree)
{
if(tree == NULL)
return;
printf("%d ",tree->data);
PreOrder(tree->lchild);
PreOrder(tree->rchild);
return;
}
void InOrder(BTREE *tree)
{
if(tree == NULL)
return;
InOrder(tree->lchild);
printf("%d ",tree->data);
InOrder(tree->rchild);
return;
}
void PostOrder(BTREE *tree)
{
if(tree == NULL)
return;
PostOrder(tree->lchild);
PostOrder(tree->rchild);
printf("%d ",tree->data);
return;
}
int NoOrder(BTREE *root)
{
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
BTREE *root;
root = create_binarytree(1);
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
//NoOrder(root);
return 0;
}
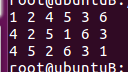
打印:








 本文详细介绍了二叉树的四种遍历方式:前序、中序、后序和层序遍历,并通过例子分析了它们的特点。同时,提供了C语言的代码实例,演示了如何创建二叉树并进行遍历操作。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的四种遍历方式:前序、中序、后序和层序遍历,并通过例子分析了它们的特点。同时,提供了C语言的代码实例,演示了如何创建二叉树并进行遍历操作。


















 36万+
36万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










