Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.
方法一:递归。
1、找最高的那个,下标为i
2、i的左右分别找最高
3、往左右迭代
方法二:
这道题的思路是采用l和r两个指针,维护装水两边的位置。
当l处高度低时,说明l右侧装的水肯定和l处一样高,此时逐步右移l,同是加上l处与右移后位置高度差(因为这里都能装水啊),直到再遇到同样高或者更高的位置。然后进行下一轮判断。
同样,当r处高度低时,说明r左侧的水肯定和r处一样高,此时逐步左移r,同是加上r处与左移后位置高度差,直到再遇到同样高或者更高的位置
最后直到l和r相遇,结束。
时间复杂度:O(n)
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.
方法一:递归。
1、找最高的那个,下标为i
2、i的左右分别找最高
3、往左右迭代
class Solution {
public:
int findleft(vector<int>& height, int flag, int sum)
{
int ff;
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < flag; i++)
{
if (height[i] > max)
{
max = height[i];
ff = i;
}
}
if (max == 0)
return sum;
for (int i = ff + 1; i < flag; i++)
sum += height[ff] - height[i];
sum = findleft(height, ff, sum);
return sum;
}
int findright(vector<int>& height,int flag,int sum)
{
int ff;
int max = 0;
for(int i = flag + 1; i < height.size(); i++)
{
if (height[i] > max)
{
max = height[i];
ff = i;
}
}
if (max == 0)
return sum;
for(int i = flag + 1; i < ff; i++)
sum += height[ff] - height[i];
sum = findright(height, ff, sum);
return sum;
}
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
int max = 0;
int flag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < height.size(); i++)
{
if (height[i] > max)
{
max = height[i];
flag = i;
}
}
int sum = 0;
sum = findleft(height, flag, sum);
sum = findright(height, flag, sum);
return sum;
}
};方法二:
这道题的思路是采用l和r两个指针,维护装水两边的位置。
当l处高度低时,说明l右侧装的水肯定和l处一样高,此时逐步右移l,同是加上l处与右移后位置高度差(因为这里都能装水啊),直到再遇到同样高或者更高的位置。然后进行下一轮判断。
同样,当r处高度低时,说明r左侧的水肯定和r处一样高,此时逐步左移r,同是加上r处与左移后位置高度差,直到再遇到同样高或者更高的位置
最后直到l和r相遇,结束。
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
int n = height.size();
int l = 0, r = n - 1, res = 0, minh;
while (l < r)
{
minh = min(height[l],height[r]);
if (height[l] == minh)
{
while(++l < r && height[l] < minh)
{
res += minh - height[l];
}
}
else
{
while (l < --r && height[r] < minh)
{
res += minh - height[r];
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
407. Trapping Rain Water II
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each
unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.
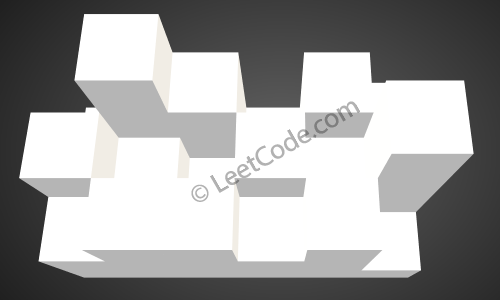
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before
the rain.
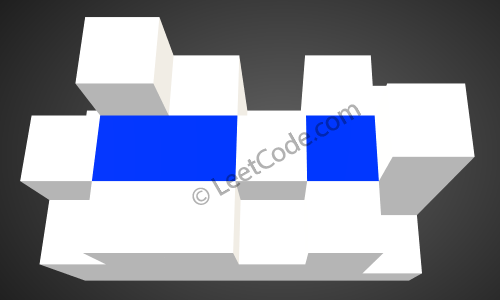
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap)
{
multimap<int, pair<int,int>> A; // 高度 和 位置
int row = heightMap.size();
if (row == 0) return 0;
int col = heightMap[0].size();
if (col == 0) return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> flag(row, vector<bool>(col, false));
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == row - 1 || j == col - 1) //先把边界存入。因为要从边界开始遍历
{
A.insert(make_pair(heightMap[i][j], make_pair(i, j)));
flag[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
int haiba = INT_MIN;
int a[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int b[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int ret = 0;
while (!A.empty())
{
auto it = A.begin(); //当前最矮
int h = it->first, x = it->second.first, y = it->second.second;
A.erase(it);
haiba = max(haiba, h); //海拔 是在上升的
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int _x = x + a[i], _y = y + b[i];
if (!isvaild(_x, _y, row, col) || flag[_x][_y])
continue;
flag[_x][_y] = true;
if (heightMap[_x][_y] < haiba) //比 能流出去的最低海拔矮 就能存水
ret += haiba - heightMap[_x][_y];
A.insert(make_pair(heightMap[_x][_y], make_pair(_x, _y)));
}
}
return ret;
}
bool isvaild(int x, int y, int row, int col)
{
return x >= 0 && x < row && y >= 0 && y < col;
}
};








 本文介绍两种算法来计算地形图中能够存储的雨水量。第一种使用递归方式寻找最高点并计算左右两侧的储水量;第二种采用双指针法,通过比较左右两侧高度来高效计算储水量。
本文介绍两种算法来计算地形图中能够存储的雨水量。第一种使用递归方式寻找最高点并计算左右两侧的储水量;第二种采用双指针法,通过比较左右两侧高度来高效计算储水量。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








