一、模拟springMVC
##定义注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface RequestMapping {
String value();
String name() default "";
}
##DispatcherServlet:
@WebServlet("/*")
public class DispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet {
Map<String,Method> map=new HashMap<String,Method>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取请求URL
String path=request.getRequestURI();
path=path.substring(path.lastIndexOf("/"));
Method method=map.get(path);
Class targetClass=method.getDeclaringClass();
Object targetObject;
try {
targetObject=targetClass.newInstance();
Class[] paramClz=method.getParameterTypes();
if(paramClz==null){
method.invoke(targetObject);
}else{
if(paramClz.length==1){
Class tempClz=paramClz[0];
if(tempClz.getSimpleName().equals("HttpServletRequest")){
method.invoke(targetObject, request);
}else if(tempClz.getSimpleName().equals("HttpServletResponse")){
method.invoke(targetObject, response);
}
}else if(paramClz.length==2){
Class tempClz=paramClz[0];
if(tempClz.getSimpleName().equals("HttpServletRequest")){
method.invoke(targetObject, request,response);
}else if(tempClz.getSimpleName().equals("HttpServletResponse")){
method.invoke(targetObject, response,response);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
//将请求与响应放入map
//super.init();
String pack="com.web";
String rootPath=this.getClass().getResource("/").getPath();
rootPath+="\\com\\web";
File file=new File(rootPath);
File[] files=file.listFiles();
for(File tempFile:files){
try {
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.web."+tempFile.getName().replace(".class", ""));
Method[] ms=clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method:ms){
//判断方法是否加RequestMapping注解
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(RequestMapping.class)){
RequestMapping rm=method.getDeclaredAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
map.put(rm.value(),method);
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(files.length);
}
}
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/login")
public void login(){
System.out.println("login");
}
}
二、springMVC 剖析
1、SpringMVC的运行流程
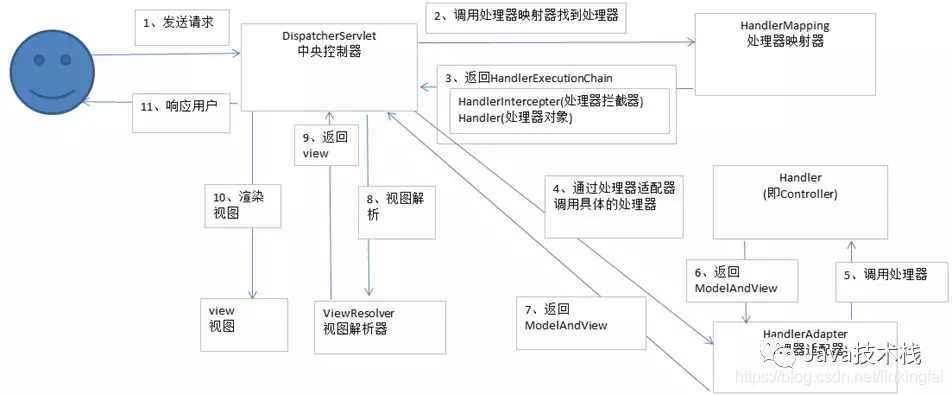
⑴ 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet
⑵ DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
⑶ 处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑷ DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter处理器适配器调用处理器
⑸ 执行处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
⑹ Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView
⑺ HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet
⑻ DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器
⑼ ViewReslover解析后返回具体View
⑽ DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
⑾ DispatcherServlet响应用户。从上面可以看出,DispatcherServlet有接收请求,响应结果,转发等作用。有了DispatcherServlet之后,可以减少组件之间的耦合度。
2、SpringMVC的九大组件
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//用于处理上传请求。处理方法是将普通的request包装成 MultipartHttpServletRequest,后者可以直接调用getFile方法获取File.
initMultipartResolver(context);
//SpringMVC主要有两个地方用到了Locale:一是ViewResolver视图解析的时候;二是用到国际化资源或者主题的时候。
initLocaleResolver(context);
//用于解析主题。SpringMVC中一个主题对应 一个properties文件,里面存放着跟当前主题相关的所有资源、//如图片、css样式等。SpringMVC的主题也支持国际化,
initThemeResolver(context);
//用来查找Handler的。
initHandlerMappings(context);
//从名字上看,它就是一个适配器。Servlet需要的处理方法的结构却是固定的,都是以request和response为参数的方法。//如何让固定的Servlet处理方法调用灵活的Handler来进行处理呢?这就是HandlerAdapter要做的事情
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//其它组件都是用来干活的。在干活的过程中难免会出现问题,出问题后怎么办呢?//这就需要有一个专门的角色对异常情况进行处理,在SpringMVC中就是HandlerExceptionResolver。
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//有的Handler处理完后并没有设置View也没有设置ViewName,这时就需要从request获取ViewName了,//如何从request中获取ViewName就是RequestToViewNameTranslator要做的事情了。
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//ViewResolver用来将String类型的视图名和Locale解析为View类型的视图。//View是用来渲染页面的,也就是将程序返回的参数填入模板里,生成html(也可能是其它类型)文件。
initViewResolvers(context);
//用来管理FlashMap的,FlashMap主要用在redirect重定向中传递参数。
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
3、梳理SpringMVC的设计思路
3.1、读取配置
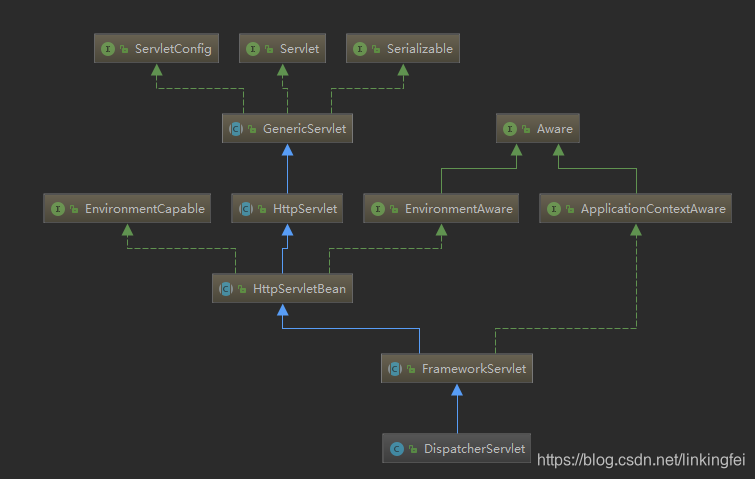
从图中可以看出,SpringMVC本质上是一个Servlet,这个 Servlet 继承自 HttpServlet。FrameworkServlet负责初始化SpringMVC的容器,并将Spring容器设置为父容器。
为了读取web.xml中的配置,我们用到ServletConfig这个类,它代表当前Servlet在web.xml中的配置信息。通过web.xml中加载我们自己写的MyDispatcherServlet和读取配置文件。
3.2、初始化阶段
在前面我们提到DispatcherServlet的initStrategies方法会初始化9大组件,但是这里将实现一些SpringMVC的最基本的组件而不是全部,按顺序包括:
- 加载配置文件
- 扫描用户配置包下面所有的类
- 拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化。并且放到ioc容器中(Map的键值对 beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写
- 初始化HandlerMapping,这里其实就是把url和method对应起来放在一个k-v的Map中,在运行阶段取出
3.3、运行阶段
每一次请求将会调用doGet或doPost方法,所以统一运行阶段都放在doDispatch方法里处理,它会根据url请求去HandlerMapping中匹配到对应的Method,然后利用反射机制调用Controller中的url对应的方法,并得到结果返回。按顺序包括以下功能:
- 异常的拦截
- 获取请求传入的参数并处理参数
- 通过初始化好的handlerMapping中拿出url对应的方法名,反射调用。
三、常用注解
-
Controller
注解一个类表示控制器,Spring MVC会自动扫描标注了这个注解的类。 -
RequestMapping
请求路径映射,可以标注类,也可以是方法,可以指定请求类型,
默认不指定为全部接收。 -
RequestParam(get请求参数或表单请求参数)
放在参数前,表示只能接收参数a=b格式的数据,即 Content-Type为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型的内容。 -
RequestBody
放在参数前,表示参数从request body中获取,而不是从地址栏获取,所以这肯定是接收一个POST请求的非a=b格式的数据,即 Content-Type不为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型的内容。 -
ResponseBody
放在方法上或者返回类型前,表示此方法返回的数据放在response body里面,而不是跳转页面。一般用于ajax请求,返回json数据。 -
RestController
这个是Controller和ResponseBody的组合注解,表示@Controller标识的类里面的所有返回参数都放在response body里面。 -
PathVariable
路径绑定变量,用于绑定restful路径上的变量。 -
RequestHeader
放在方法参数前,用来获取request header中的参数值。 -
CookieValue;
放在方法参数前,用来获取request header cookie中的参数值。 -
GetMapping PostMapping PutMapping… *Mapping的是Spring4.3加入的新注解,表示特定的请求类型路径映射,而不需要写RequestMethod来指定请求类型。





















 3531
3531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








