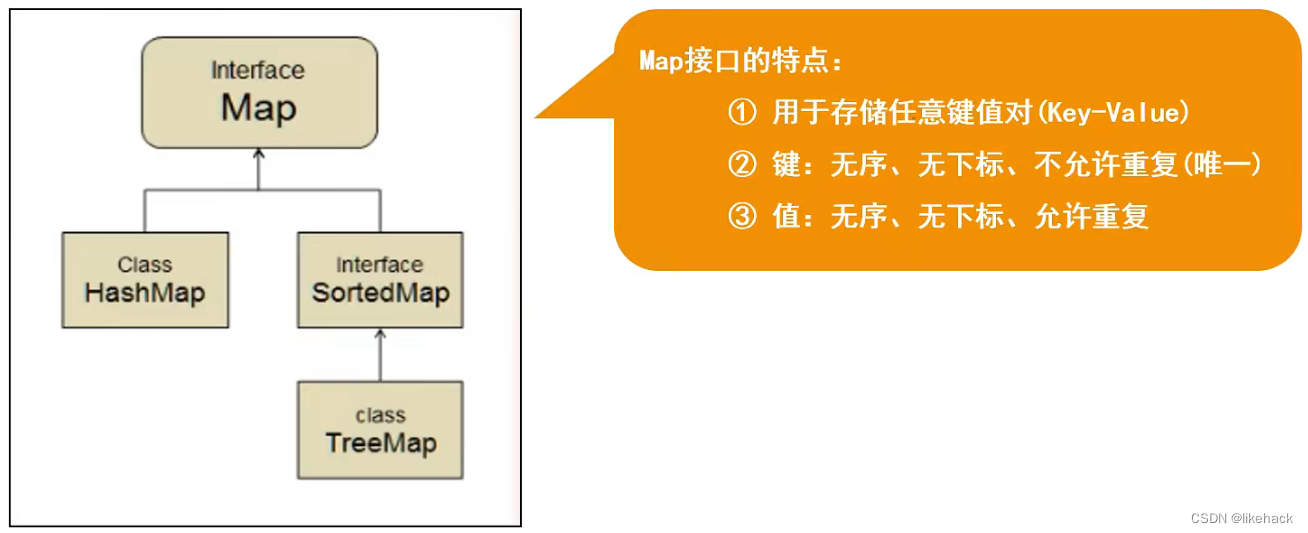
Map集合
Map接口由HashMap类,SortedMap接口组成,其中SortedMap接口由TreeMap类实现。
特点:
- 存储内容为键值对
- 键:无序,无下标,不可重复
- 值:无序,无下标,允许重复
案例
Student类(后续测试实现类存储的对象都是该类)
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//手动重写toString方法
/*public String toString(){
return name+":"+age;
}*/
//alt+insert自动重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return age == student.age &&
Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
int n1=this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
int n2=this.age-o.getAge();
return n2==0?n2:n1;
}
}
public class testMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
addElement(map);
traverseElement(map);
//判断
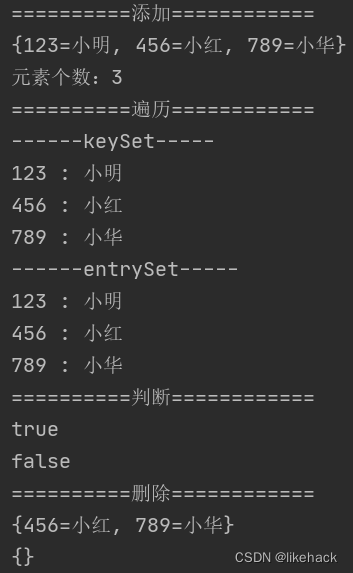
System.out.println("==========判断============");
System.out.println(map.containsKey("123"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue("小米"));
deleteElement(map);
}
private static void traverseElement(Map<String, String> map) {
System.out.println("==========遍历============");
System.out.println("------keySet-----");
Set<String> keySet=map.keySet();
for (String key:keySet) {
System.out.println(key+" : "+map.get(key));
}
//entrySet效率要高于keySet
System.out.println("------entrySet-----");
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entries=map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> key:entries) {
System.out.println(key.getKey()+" : "+key.getValue());
}
}
private static void deleteElement(Map<String, String> map) {
System.out.println("==========删除============");
map.remove("123");
System.out.println(map);
map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
}
private static void addElement(Map<String, String> map) {
System.out.println("==========添加============");
map.put("456","小红");
map.put("123","小明");
map.put("789","小华");
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+map.size());
}
}
代码执行结果
HashMap
特点
- jdk1.2版本引入
- 线程不安全,运行效率快
- 允许使用null作为key或者value
- 构造时,默认构造一个初始容量为16,默认加载因子为0.75的空HashMap
- HashMap没有添加元素时,size=0,添加元素后,size=添加的元素个数。(这样设计的目的时为了节省空间)
- 当HashMap中的元素个数=16*0.75=12时,HashMap会进行扩容,容量变为16*2=32。当元素个数达到32*0.75=24时,继续扩容,32*2=64,以此类推。
- 存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
- 数组长度大于等于64时,数组中某个位置的链表长度大于8,链表变为红黑树(平衡查找树)
- jdk1.8之前链表时头插入,jdk1.8之后链表是尾插入
案例
public class testHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student,String> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
//刚创建的hashMap没有添加元素时,size=0,目的时节省空间
Student s1=new Student("小明",18);
Student s2=new Student("小华",19);
Student s3=new Student("小红",20);
Student s4=new Student("小华",20);
addElement(hashMap, s1, s2, s3, s4);
traverseElement(hashMap);
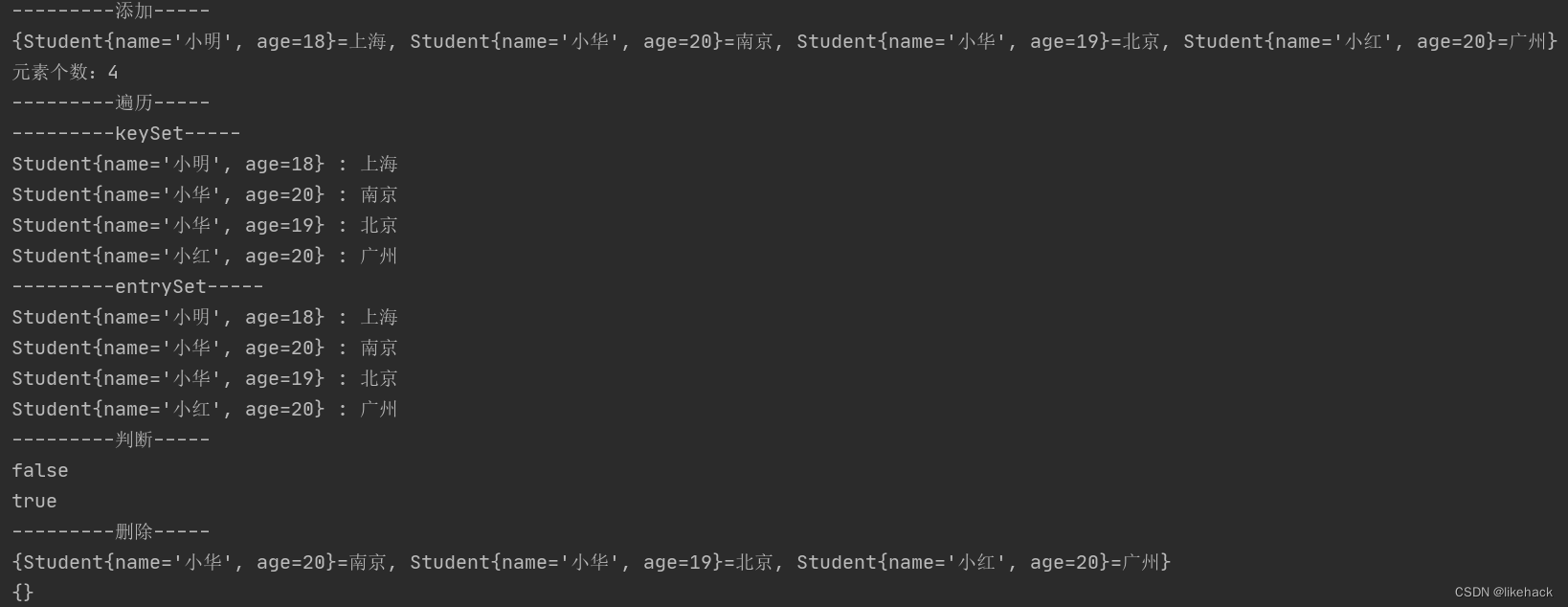
System.out.println("---------判断-----");
System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue("深圳"));
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey(s1));
deleteElement(hashMap, s1);
}
private static void deleteElement(HashMap<Student, String> hashMap, Student s1) {
System.out.println("---------删除-----");
hashMap.remove(s1);
System.out.println(hashMap);
hashMap.clear();
System.out.println(hashMap);
}
private static void traverseElement(HashMap<Student, String> hashMap) {
System.out.println("---------遍历-----");
System.out.println("---------keySet-----");
for (Student key:hashMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key.toString()+" : "+hashMap.get(key));
}
System.out.println("---------entrySet-----");
for (Map.Entry<Student,String> entry:hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" : "+entry.getValue());
}
}
private static void addElement(HashMap<Student, String> hashMap, Student s1, Student s2, Student s3, Student s4) {
System.out.println("---------添加-----");
hashMap.put(s1,"上海");
hashMap.put(s2,"北京");
hashMap.put(s3,"深圳");
//重复添加同一个键,该键对应的值会被重写为最后一次添加的值
hashMap.put(s3,"广州");
hashMap.put(s4,"深圳");
//如果想要删除重复键,需要重写equals方法
hashMap.put(new Student("小华",20),"南京");
System.out.println(hashMap);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+hashMap.size());
}
}
代码执行结果
TreeMap
特点
- 基于排序顺序实现元素不重复
- 实现了SortedMap接口,可以对key自动排序
- 元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排序规则
- 通过CompareTo来确定重复元素
案例
public class testTreeMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可以使用定制比较器,方法和TreeSet相同
TreeMap<Student,String> treeMap=new TreeMap<>();
//刚创建的treeMap没有添加元素时,size=0,目的是节省空间
Student s1=new Student("小明",18);
Student s2=new Student("小华",19);
Student s3=new Student("小红",20);
Student s4=new Student("小华",20);
addElement(treeMap, s1, s2, s3, s4);
traverseElement(treeMap);
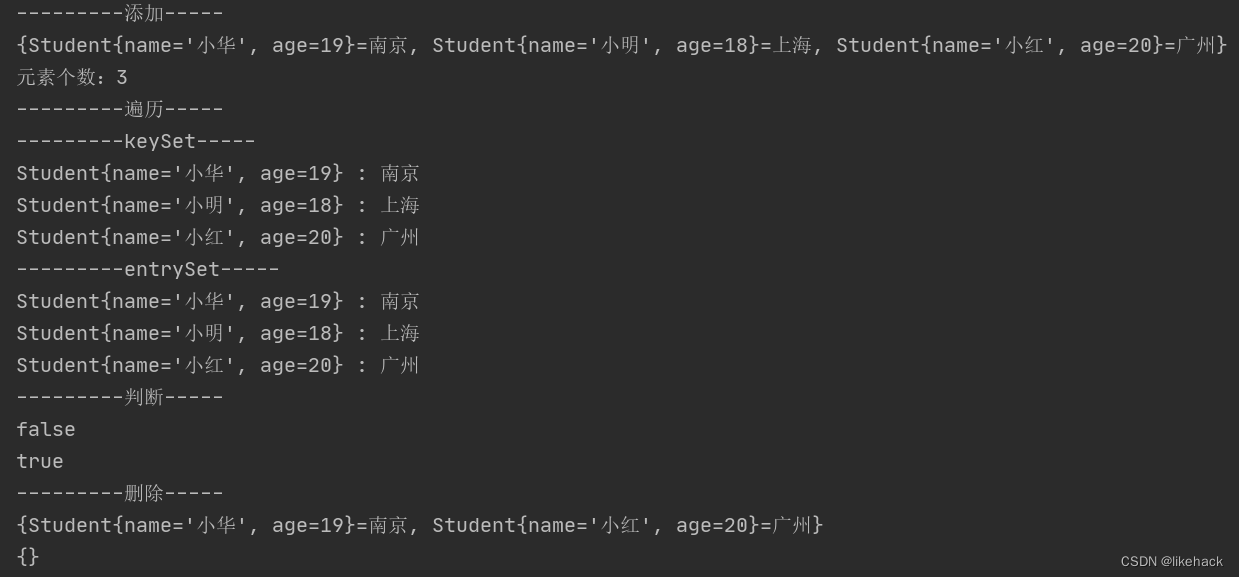
System.out.println("---------判断-----");
System.out.println(treeMap.containsValue("深圳"));
System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(s1));
deleteElement(treeMap, s1);
}
private static void deleteElement(TreeMap<Student, String> treeMap, Student s1) {
System.out.println("---------删除-----");
treeMap.remove(s1);
System.out.println(treeMap);
treeMap.clear();
System.out.println(treeMap);
}
private static void traverseElement(TreeMap<Student, String> treeMap) {
System.out.println("---------遍历-----");
System.out.println("---------keySet-----");
for (Student key:treeMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key.toString()+" : "+treeMap.get(key));
}
System.out.println("---------entrySet-----");
for (Map.Entry<Student,String> entry:treeMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" : "+entry.getValue());
}
}
private static void addElement(TreeMap<Student, String> treeMap, Student s1, Student s2, Student s3, Student s4) {
System.out.println("---------添加-----");
/*Student s1=new Student("小明",18);
Student s2=new Student("小华",19);
Student s3=new Student("小红",20);
Student s4=new Student("小华",20);*/
treeMap.put(s1,"上海");
treeMap.put(s2,"北京");
treeMap.put(s3,"深圳");
//重复添加同一个键,该键对应的值会被重写为最后一次添加的值
treeMap.put(s3,"广州"); //重复键,修改值
//如果想要删除重复键,需要重写equals方法
treeMap.put(s4,"深圳"); //重复键不会添加
treeMap.put(new Student("小华",20),"南京");
System.out.println(treeMap);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+treeMap.size());
}
}
代码执行结果
其他相关文章
- Java知识梳理:Java知识梳理
- Java知识梳理–内部类:Java知识梳理–内部类
- Java常用类–Object类:Java常用类–Object类
- Java常用类–包装类:Java常用类–包装类
- Java常用类–String类:java常用类–String类
- Java常用类–时间相关类:Java常用类–时间相关类
- Java常用类–BigDecimal类和System类:Java常用类–BigDecimal类和System类
- Java集合–Collection集合:Java集合–Collection集合
- Java集合–泛型集合:Java集合–泛型集合
























 330
330

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










