卷积神经网络(CNN, Convolutional Neural Network)是深度学习的核心结构之一,在图像分类、目标检测、语义分割乃至遥感影像分析中都有广泛应用。 很多同学在学习 CNN 的时候,会遇到几个典型问题:卷积参数怎么算?如何在 PyTorch 中搭建?训练循环有什么规范?如何可视化结果?本篇就带大家从零走一遍 PyTorch 构建 CNN 的完整流程。
往期内容:
🧩 CNN 的核心思想
-
局部感受野:卷积核只处理局部区域,而非全局连接,大幅减少参数量。
-
权值共享:同一个卷积核在整张图像上滑动,捕捉相同模式。
-
平移不变性:目标位置发生变化,卷积特征仍然有效。
卷积核大小常为 ,配合步幅(stride)与填充(padding)控制输出特征图的尺寸。常见网络结构是:
Conv → ReLU → Pool → Conv → ReLU → Pool → Flatten → FC
⚙️ PyTorch 中的基本模块
-
nn.Conv2d(in_c, out_c, kernel_size, stride, padding):卷积层 -
nn.ReLU():激活函数 -
nn.MaxPool2d(2):最大池化,下采样一半 -
nn.Linear(in, out):全连接层 -
nn.Sequential:将多个层按顺序组合
这些积木组合起来就能快速搭建 CNN。
💻 一键可跑完整代码
下面的脚本实现了:
-
使用 MNIST 数据(28×28 灰度手写数字)
-
构建一个最小 CNN 模型
-
训练与测试循环(支持 GPU 与混合精度)
-
可视化:训练曲线、混淆矩阵、预测样例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
案例③补充:PyTorch 构建 CNN 全流程
"""
import os, time, numpy as np
import torch, torch.nn as nn, torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt, matplotlib
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
# ===== 中文显示 =====
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# ===== 超参数 =====
BATCH = 128
EPOCHS = 5
LR = 1e-3
SEED = 42
SAVE_DIR = "./cnn_ckpt"
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
# ===== 定义最小 CNN =====
class MiniCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 16, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(32*7*7, 128), nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(128, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.head(self.net(x))
# ===== 构建 DataLoader =====
def build_loaders():
tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])
train_set = datasets.MNIST("./data", train=True, transform=tfm, download=True)
test_set = datasets.MNIST("./data", train=False, transform=tfm, download=True)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=BATCH, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_set, batch_size=BATCH, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
return train_loader, test_loader
# ===== 训练与评估函数 =====
def run_epoch(model, loader, criterion, optimizer=None, device="cpu"):
is_train = optimizer isnotNone
model.train(is_train)
total, correct, loss_sum = 0, 0, 0.0
y_true_all, y_pred_all = [], []
for x, y in loader:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
with torch.set_grad_enabled(is_train):
logits = model(x)
loss = criterion(logits, y)
if is_train:
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss_sum += loss.item() * y.size(0)
pred = logits.argmax(1)
correct += (pred == y).sum().item()
total += y.size(0)
y_true_all.append(y.cpu().numpy())
y_pred_all.append(pred.cpu().numpy())
avg_loss = loss_sum / total
acc = correct / total
y_true_all = np.concatenate(y_true_all)
y_pred_all = np.concatenate(y_pred_all)
return avg_loss, acc, y_true_all, y_pred_all
# ===== 主流程 =====
def main():
torch.manual_seed(SEED)
device = "cuda"if torch.cuda.is_available() else"cpu"
print("使用设备:", device)
train_loader, test_loader = build_loaders()
model = MiniCNN().to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=LR)
hist_tr, hist_te = [], []
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS+1):
trL, trA, _, _ = run_epoch(model, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device)
teL, teA, y_t, y_p = run_epoch(model, test_loader, criterion, None, device)
hist_tr.append((trL, trA)); hist_te.append((teL, teA))
if teA > best_acc:
best_acc = teA
torch.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, "best.pth"))
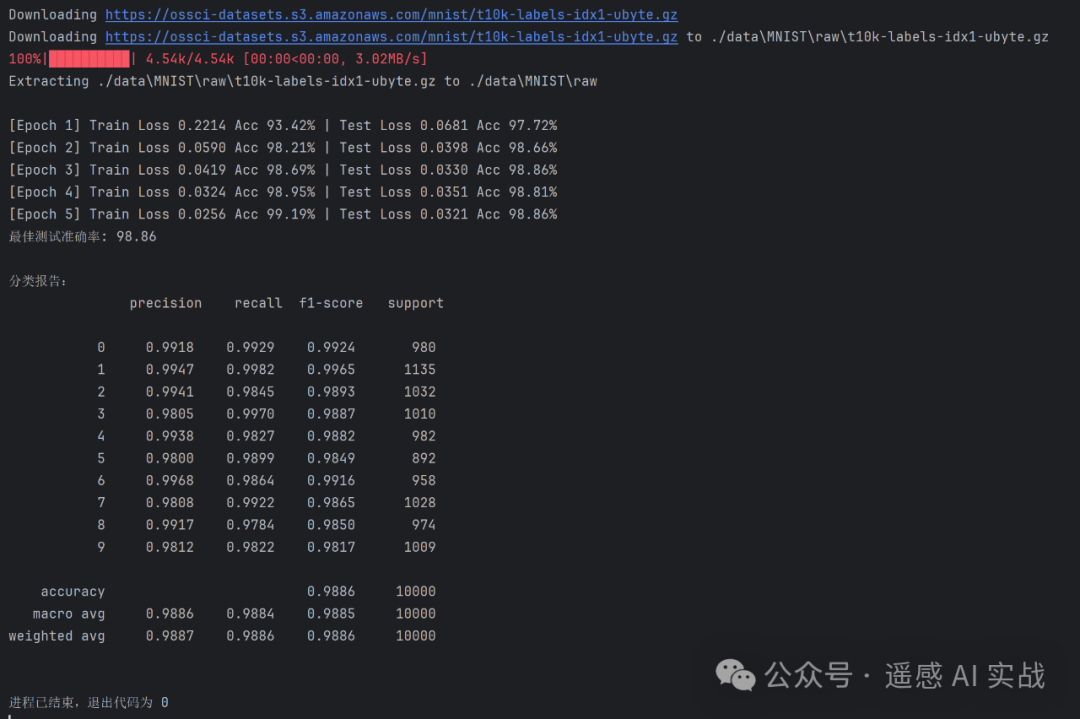
print(f"[Epoch {epoch}] Train Loss {trL:.4f} Acc {trA*100:.2f}% | "
f"Test Loss {teL:.4f} Acc {teA*100:.2f}%")
print("最佳测试准确率:", best_acc*100)
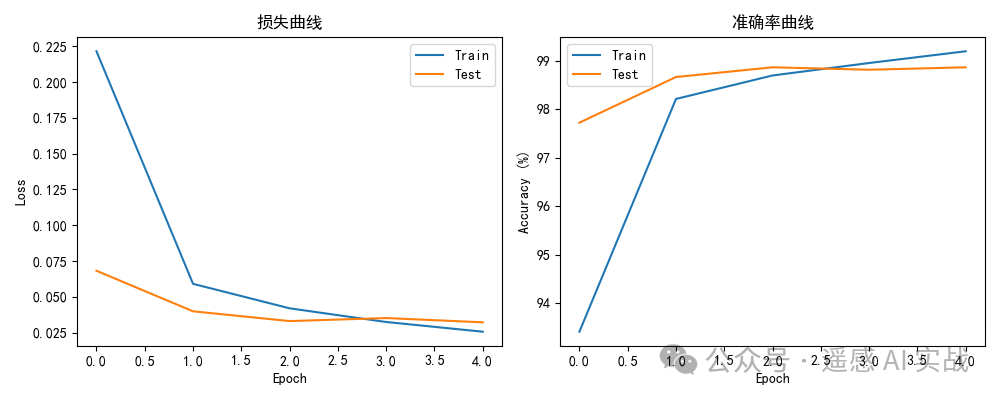
# ===== 训练曲线 =====
trL, trA = zip(*hist_tr); teL, teA = zip(*hist_te)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.subplot(1,2,1); plt.plot(trL,label="Train"); plt.plot(teL,label="Test")
plt.title("损失曲线"); plt.xlabel("Epoch"); plt.ylabel("Loss"); plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1,2,2); plt.plot([a*100for a in trA],label="Train")
plt.plot([a*100for a in teA],label="Test")
plt.title("准确率曲线"); plt.xlabel("Epoch"); plt.ylabel("Accuracy (%)"); plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()
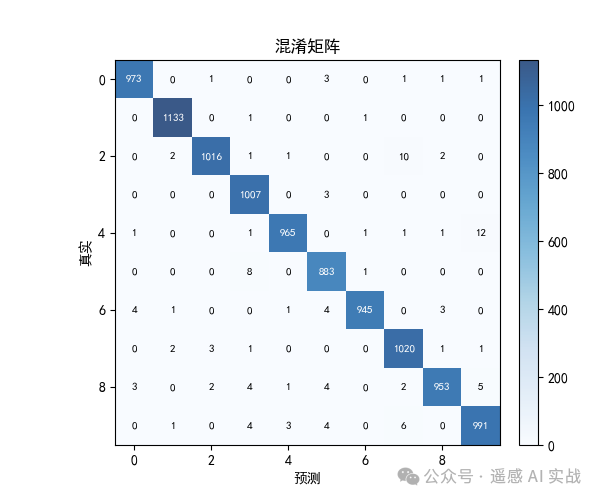
# ===== 混淆矩阵 =====
cm = confusion_matrix(y_t, y_p)
plt.figure(figsize=(6,5))
plt.imshow(cm, cmap=plt.cm.Blues, alpha=0.8)
plt.title("混淆矩阵"); plt.xlabel("预测"); plt.ylabel("真实")
for i in range(cm.shape[0]):
for j in range(cm.shape[1]):
plt.text(j,i,str(cm[i,j]),
ha="center", va="center",
color="white"if cm[i,j]>cm.max()/2else"black", fontsize=8)
plt.colorbar(fraction=0.046, pad=0.04); plt.show()
print("\n分类报告:\n", classification_report(y_t, y_p, digits=4))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
📦 本文小结
-
CNN 的核心是 卷积+权值共享+局部感受野,相比全连接更适合图像。
-
在 PyTorch 中,常用的积木是
Conv2d、ReLU、MaxPool2d、Linear。 -
训练流程遵循:
train()→ 前向传播 → loss → backward → optimizer.step();测试时eval()+no_grad()。 -
混淆矩阵与训练曲线能帮助快速诊断模型表现。
结果展示:
🔗 下一步
后续我们会将 CNN 迁移到遥感影像切片上,用于实际的分类任务,展示卷积网络在地物识别中的威力。
欢迎大家关注下方公众号获取更多内容!!























 182
182

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










