真是奇了怪了。。我的博客分类里怎么都没有数据结构呢。。这么重要的东西。。。
今天就来添个二叉树,但是重点讲基础,实现这种东西就先不复习了。
本博属转载,原创博客链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/songwenjie/p/8955856.html
二叉树遍历方法:

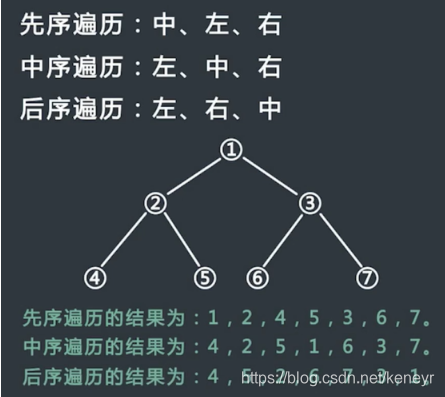
前序遍历:
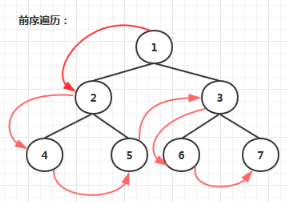
递归方式实现前序遍历
具体过程:
- 先访问根节点
- 再序遍历左子树
- 最后序遍历右子树
public static void PreOrderRecur(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
Console.Write(treeNode.Data);
PreOrderRecur(treeNode.LChild);
PreOrderRecur(treeNode.RChild);
}非递归方式实现前序遍历
具体过程:
- 首先申请一个新的栈,记为stack;
- 将头结点head压入stack中;
- 每次从stack中弹出栈顶节点,记为cur,然后打印cur值,如果cur右孩子不为空,则将右孩子压入栈中;如果cur的左孩子不为空,将其压入stack中;
- 重复步骤3,直到stack为空.
public static void PreOrder(TreeNode<char> head)
{
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode<char>> stack = new Stack<TreeNode<char>>();
stack.Push(head);
while (!(stack.Count == 0))
{
TreeNode<char> cur = stack.Pop();
Console.Write(cur.Data);
if (cur.RChild != null)
{
stack.Push(cur.RChild);
}
if (cur.LChild != null)
{
stack.Push(cur.LChild);
}
}
}
中序遍历:
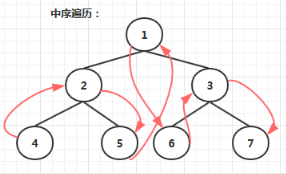
递归方式实现中序遍历
具体过程:
- 先中序遍历左子树
- 再访问根节点
- 最后中序遍历右子树
public static void InOrderRecur(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
InOrderRecur(treeNode.LChild);
Console.Write(treeNode.Data);
InOrderRecur(treeNode.RChild);
}非递归方式实现中序遍历
具体过程:
- 申请一个新栈,记为stack,申请一个变量cur,初始时令cur为头节点;
- 先把cur节点压入栈中,对以cur节点为头的整棵子树来说,依次把整棵树的左子树压入栈中,即不断令cur=cur.left,然后重复步骤2;
- 不断重复步骤2,直到发现cur为空,此时从stack中弹出一个节点记为node,打印node的值,并让cur = node.right,然后继续重复步骤2;
- 当stack为空并且cur为空时结束。
public static void InOrder(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode<char>> stack = new Stack<TreeNode<char>>();
TreeNode<char> cur = treeNode;
while (!(stack.Count == 0) || cur != null)
{
while (cur != null)
{
stack.Push(cur);
cur = cur.LChild;
}
TreeNode<char> node = stack.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(node.Data);
cur = node.RChild;
}
}后序遍历:
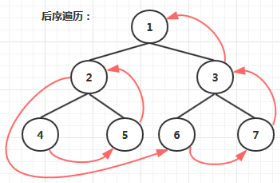
递归方式实现后序遍历
- 先后序遍历左子树
- 再后序遍历右子树
- 最后访问根节点
public static void PosOrderRecur(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
PosOrderRecur(treeNode.LChild);
PosOrderRecur(treeNode.RChild);
Console.Write(treeNode.Data);
}非递归方式实现后序遍历一
具体过程:
使用两个栈实现
- 申请两个栈stack1,stack2,然后将头结点压入stack1中;
- 从stack1中弹出的节点记为cur,然后先把cur的左孩子压入stack1中,再把cur的右孩子压入stack1中;
- 在整个过程中,每一个从stack1中弹出的节点都放在第二个栈stack2中;
- 不断重复步骤2和步骤3,直到stack1为空,过程停止;
- 从stack2中依次弹出节点并打印,打印的顺序就是后序遍历的顺序;
public static void PosOrderOne(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode<char>> stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode<char>>();
Stack<TreeNode<char>> stack2 = new Stack<TreeNode<char>>();
stack1.Push(treeNode);
TreeNode<char> cur = treeNode;
while (!(stack1.Count == 0))
{
cur = stack1.Pop();
if (cur.LChild != null)
{
stack1.Push(cur.LChild);
}
if (cur.RChild != null)
{
stack1.Push(cur.RChild);
}
stack2.Push(cur);
}
while (!(stack2.Count == 0))
{
TreeNode<char> node = stack2.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(node.Data); ;
}
}
非递归方式实现后序遍历二
具体过程:
使用一个栈实现
申请一个栈stack,将头节点压入stack,同时设置两个变量 h 和 c,在整个流程中,h代表最近一次弹出并打印的节点,c代表当前stack的栈顶节点,初始时令h为头节点,,c为null;
每次令c等于当前stack的栈顶节点,但是不从stack中弹出节点,此时分一下三种情况:
(1)如果c的左孩子不为空,并且h不等于c的左孩子,也不等于c的右孩子,则吧c的左孩子压入stack中
(2)如果情况1不成立,并且c的右孩子不为空,并且h不等于c的右孩子,则把c的右孩子压入stack中;
(3)如果情况1和2不成立,则从stack中弹出c并打印,然后令h等于c;
- 一直重复步骤2,直到stack为空.
public static void PosOrderTwo(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if (treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode<char>> stack = new Stack<TreeNode<char>>();
stack.Push(treeNode);
TreeNode<char> h = treeNode;
TreeNode<char> c = null;
while (!(stack.Count == 0))
{
c = stack.Peek();
//c结点有左孩子 并且 左孩子没被遍历(输出)过 并且 右孩子没被遍历过
if (c.LChild != null && h != c.LChild && h != c.RChild)
stack.Push(c.LChild);
//c结点有右孩子 并且 右孩子没被遍历(输出)过
else if (c.RChild != null && h != c.RChild)
stack.Push(c.RChild);
//c结点没有孩子结点 或者孩子结点已经被遍历(输出)过
else
{
TreeNode<char> node = stack.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(node.Data);
h = c;
}
}
}
层序遍历:
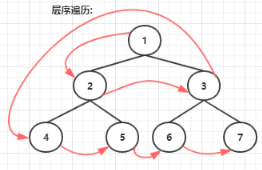
具体过程:
- 首先申请一个新的队列,记为queue;
- 将头结点head压入queue中;
- 每次从queue中出队,记为node,然后打印node值,如果node左孩子不为空,则将左孩子入队;如果node的右孩子不为空,则将右孩子入队;
- 重复步骤3,直到queue为空。
public static void LevelOrder(TreeNode<char> treeNode)
{
if(treeNode == null)
{
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode<char>> queue = new Queue<TreeNode<char>>();
queue.Enqueue(treeNode);
while (queue.Any())
{
TreeNode<char> node = queue.Dequeue();
Console.Write(node.Data);
if (node.Left != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(node.Left);
}
if (node.Right != null)
{
queue.Enqueue(node.Right);
}
}
}





 本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序及层序遍历的递归与非递归实现方法。通过具体的代码示例,帮助读者深入理解不同遍历方式的原理及其应用场景。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序及层序遍历的递归与非递归实现方法。通过具体的代码示例,帮助读者深入理解不同遍历方式的原理及其应用场景。

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








