Abstract
Two less addressed issues of deep reinforcement learning are (1) lack of generalization capability to new target goals, and (2) data inefficiency i.e., the model requires several (and often costly) episodes of trial and error to converge, which makes it impractical to be applied to real-world scenarios. In this paper, we address these two issues and apply our model to the task of target-driven visual navigation. To address the first issue, we propose an actor-critic model whose policy is a function of the goal as well as the current state, which allows to better generalize. To address the second issue, we propose AI2- THOR framework, which provides an environment with highquality 3D scenes and physics engine. Our framework enables agents to take actions and interact with objects. Hence, we can collect a huge number of training samples efficiently. We show that our proposed method (1) converges faster than the state-of-the-art deep reinforcement learning methods, (2) generalizes across targets and across scenes, (3) generalizes to a real robot scenario with a small amount of fine-tuning (although the model is trained in simulation), (4) is end-to-end trainable and does not need feature engineering, feature matching between frames or 3D reconstruction of the environment.
深度强化学习中两个较少被提及的问题是:(1)缺乏对新目标目标的泛化能力;,该模型需要多次(而且往往代价高昂)的反复试验和错误来收敛,这使得将其应用于实际场景是不切实际的。在本文中,我们解决了这两个问题,并将我们的模型应用到目标驱动的视觉导航任务中。为了解决第一个问题,我们提出了一个行为批评模型,它的策略是目标和当前状态的函数,这样可以更好地一般化。为了解决第二个问题,我们提出了AI2- THOR框架,它提供了一个具有高质量3D场景和物理引擎的环境。我们的框架允许代理采取行动并与对象交互。因此,我们可以有效地收集大量的训练样本。我们表明,我们建议的方法(1)收敛速度比最先进的强化学习方法快,(2)概括跨越目标和场景,(3) 用少量的微调来推广到一个真正的机器人的场景 (尽管模型在模拟训练),(4)是端到端可训练的和不需要特征工程、帧间特征匹配或环境三维重建。
III. AI2-THOR FRAMEWORK
To train and evaluate our model, we require a framework for performing actions and perceiving their outcomes in a 3D environment. Integrating our model with different types of environments is a main requirement for generalization of our model. Hence, the framework should have a plugn- play architecture such that different types of scenes can be easily incorporated. Additionally, the framework should have a detailed model of the physics of the scene so the movements and object interactions are properly represented.
为了训练和评估我们的模型,我们需要一个在3D环境中执行操作和感知其结果的框架。将模型与不同类型的环境集成是模型泛化的主要要求。因此,这个框架应该有一个即插即用的架构,这样不同类型的场景就可以很容易地合并。此外,框架应该有一个场景物理的详细模型,这样运动和对象交互就能得到适当的表示。
For this purpose, we propose The House Of inteRactions (AI2-THOR) framework, which is designed by integrating a physics engine (Unity 3D) 1 with a deep learning framework (Tensorflow [44]). The general idea is that the rendered images of the physics engine are streamed to the deep learning framework, and the deep learning framework issues a control command based on the visual input and sends it back to the agent in the physics engine. Similar frameworks have been proposed by [36], [37], [41], [39], [38], but the main advantages of our framework are as follows: (1) The physics engine and the deep learning framework directly communicate (in contrast to separating the physics engine from the controller as in [35]). Direct communication is important since the feedback from the environment can be immediately used for online decision making. (2) We tried to mimic the appearance distribution of the real-world images as closely as possible. For example, [36] work on Atari games, which are 2D environments and limited in terms of appearance or [40] is a collection of synthetic scenes that are non-photo-realistic and do not follow the distribution of real-world scenes in terms of lighting, object appearance, textures, and background clutter, etc. This is important for enabling us to generalize to real-world images.
为此,我们提出交互之家(AI2-THOR)框架,它是通过集成物理引擎(Unity 3D) 1和深度学习框架(Tensorflow[44])而设计的。其基本思想是将物理引擎渲染的图像流到深度学习框架中,深度学习框架根据视觉输入发出控制命令,并将其发送回物理引擎中的代理。[36]、[37]、[41]、[39]、[38]也提出了类似的框架,但我们的框架的主要优势是:(1)物理引擎与深度学习框架直接通信(不同于[35]中物理引擎与控制器分离)。直接沟通很重要,因为来自环境的反馈可以立即用于在线决策。(2)我们尽量模拟真实图像的外观分布。例如,[36]在雅达利游戏中工作,这是一个二维环境,在外观上是有限的,或者[40]是一个合成场景的集合,它是非照片真实感的,不遵循现实场景在灯光、物体外观、纹理、背景杂波等方面的分布。这对于使我们能够将其推广到真实的图像中非常重要。
To create indoor scenes for our framework, we provided reference images to artists to create a 3D scene with the texture and lighting similar to the image. So far we have 32 scenes that belong to 4 common scene types in a household environment: kitchen, living room, bedroom, and bathroom. On average, each scene contains 68 object instances.
为了给我们的框架创建室内场景,我们为艺术家提供了参考图像,以创建一个纹理和灯光与图像相似的3D场景。到目前为止,我们有32个场景,属于家庭环境中的4种常见场景类型:厨房、客厅、卧室和浴室。平均每个场景包含68个对象实例。
The advantage of using a physics engine for modeling the world is that it is highly scalable (training a robot in real houses is not easily scalable). Furthermore, training the models can be performed cheaper and safer (e.g., the actions of the robot might damage objects). One main drawback of using synthetic scenes is that the details of the real world are under-modeled. However, recent advances in the graphics community make it possible to have a rich representation of the real-world appearance and physics, narrowing the discrepancy between real world and simulation. Fig. 2 provides a qualitative comparison between a scene in our framework and example scenes in other frameworks and datasets. As shown, our scenes better mimic the appearance properties of real world scenes. In this work, we focus on navigation, but the framework can be used for more fine-grained physical interactions, such as applying a force, grasping, or object manipulations such as opening and closing a microwave. Fig. 3 shows a few examples of high-level interactions. We will provide Python APIs with our framework for an AI agent to interact with the 3D scenes.
使用物理引擎为世界建模的优点是它具有高度可伸缩性(在真实的房子中训练机器人是不容易伸缩的)。此外,训练模型可以更便宜、更安全(例如,机器人的动作可能会损坏物体)。使用合成场景的一个主要缺点是对真实世界的细节建模不足。然而,图形社区的最新进展使得对真实世界的外观和物理具有丰富的表示成为可能,缩小了真实世界和模拟之间的差异。图2给出了我们框架中的场景与其他框架和数据集中的示例场景的定性比较。如图所示,我们的场景更好地模拟了真实世界场景的外观属性。在这项工作中,我们主要关注导航,但是这个框架可以用于更细粒度的物理交互,比如应用一个力、抓取,或者对象操作,比如打开和关闭一个微波炉。图3显示了一些高层交互的例子。我们将为Python api提供我们的框架,让AI代理与3D场景进行交互。
IV. TARGET-DRIVEN NAVIGATION MODEL
In this section, we first define our formulation for targetdriven visual navigation. Then we describe our deep siamese actor-critic network for this task.
在本节中,我们首先定义用于目标驱动的可视化导航的公式。然后我们为这项任务描述我们的孪生演员-批评家网络(?)。
Siamese network 孪生神经网络
Siamese network就是“连体的神经网络”,神经网络的“连体”是通过共享权值来实现的,如下图所示。
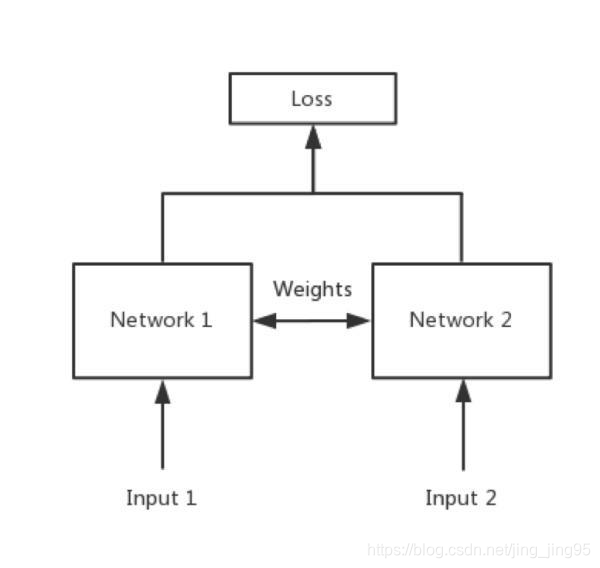
共享权值是左右两个神经网络的权重一模一样,在代码实现的时候,甚至可以是同一个网络,不用实现另外一个,因为权值都一样。对于siamese network,两边可以是lstm或者cnn,都可以。
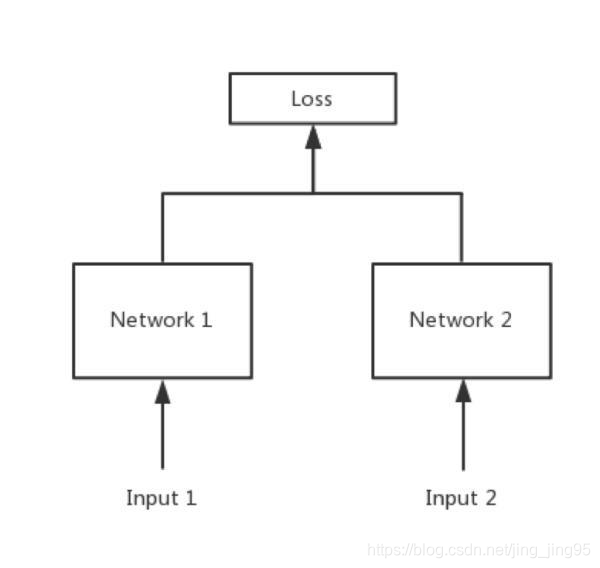
如果左右两边不共享权值,而是两个不同的神经网络,叫pseudo-siamese network,伪孪生神经网络,如下图所示。对于pseudo-siamese network,两边可以是不同的神经网络(如一个是lstm,一个是cnn),也可以是相同类型的神经网络。
孪生神经网络的用途是什么?
简单来说,衡量两个输入的相似程度。孪生神经网络有两个输入(Input1 and Input2),将两个输入feed进入两个神经网络(Network1 and Network2),这两个神经网络分别将输入映射到新的空间,形成输入在新的空间中的表示。通过Loss的计算,评价两个输入的相似度。
随着SVM等算法的兴起,neural network被人们遗忘,还好有一些执着的人们,坚守在了神经网络研究的阵地。2010年Hinton在ICML上发表了文章《Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines》,用来做人脸验证,效果很好。其原理很简单,将两个人脸feed进卷积神经网络,输出same or different。
孪生神经网络用于处理两个输入"比较类似"的情况。伪孪生神经网络适用于处理两个输入"有一定差别"的情况。比如,我们要计算两个句子或者词汇的语义相似度,使用siamese network比较适合;如果验证标题与正文的描述是否一致(标题和正文长度差别很大),或者文字是否描述了一幅图片(一个是图片,一个是文字),就应该使用pseudo-siamese network。也就是说,要根据具体的应用,判断应该使用哪一种结构,哪一种Loss。
Siamese network loss function一般用哪一种呢?
Softmax当然是一种好的选择,但不一定是最优选择,即使是在分类问题中。传统的siamese network使用Contrastive Loss。损失函数还有更多的选择,siamese network的初衷是计算两个输入的相似度,。左右两个神经网络分别将输入转换成一个"向量",在新的空间中,通过判断cosine距离就能得到相似度了。Cosine是一个选择,exp function也是一种选择,欧式距离什么的都可以,训练的目标是让两个相似的输入距离尽可能的小,两个不同类别的输入距离尽可能的大。其他的距离度量没有太多经验,这里简单说一下cosine和exp在NLP中的区别。
根据实验分析,cosine更适用于词汇级别的语义相似度度量,而exp更适用于句子级别、段落级别的文本相似性度量。其中的原因可能是cosine仅仅计算两个向量的夹角,exp还能够保存两个向量的长度信息,而句子蕴含更多的信息(当然,没有做实验验证这个事情)。
我们在论文里使用了exp距离做多分类,解决Fakenewschallenge上标题与正文立场是否一致的衡量问题。[1]
A. Problem Statement
Our goal is to find the minimum length sequence of actions that move an agent from its current location to a target that is specified by an RGB image. We develop a deep reinforcement learning model that takes as input an RGB image of the current observation and another RGB image of the target. The output of the model is an action in 3D s





 本文提出了一种深度强化学习模型,用于解决目标驱动的室内视觉导航问题,克服了数据效率低和泛化能力不足的难题。通过引入AI2-THOR框架,模型能在大量高效的3D场景数据中训练。实验表明,模型能快速收敛,且能跨目标和场景泛化,甚至推广到真实机器人场景。同时,模型无需特征工程,具备端到端训练能力。
本文提出了一种深度强化学习模型,用于解决目标驱动的室内视觉导航问题,克服了数据效率低和泛化能力不足的难题。通过引入AI2-THOR框架,模型能在大量高效的3D场景数据中训练。实验表明,模型能快速收敛,且能跨目标和场景泛化,甚至推广到真实机器人场景。同时,模型无需特征工程,具备端到端训练能力。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1853
1853

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








